오버로딩:
간다하게 말하면 중복정의한다는 뜻
- 위키백과: 같은 함수 이름을 가지고 있으나 매개변수, 리턴타입 등의 특징은 다른 여러개의 서브프로그램 생성을 가능하게 한다
연산자 오버로딩의 종류
- 숫자 자료형 관련 연산
- 컨테이너 자료형(len, in, next, iter, [] 등) 관련 연산
수 관련 연산자와 특수 Method
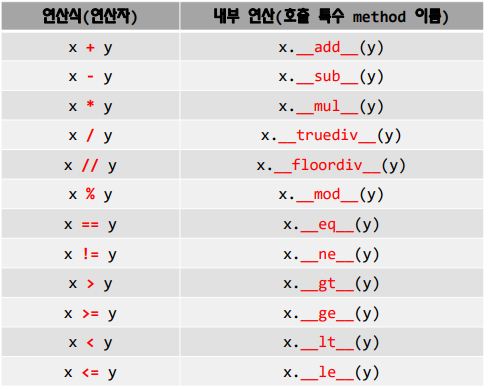
+ 연산자 오버로딩 예제
자료형에 따라 서로 다른 기능을 수행하도록 특수 함수(Method)를 사용하여 정의
- 특수 함수란?
ex) init(), str()
class SampleClass:
def __init__(self, value):
self.value = value
def __add__(self, another):
result = self.value + another.value
return SampleClass(result)
def __str__(self):
return f'값은: {self.value}'
if __name__ == '__main__':
obj1 = SampleClass(10)
obj2 = SampleClass(20)
obj3 = obj1 + obj2
print(obj3)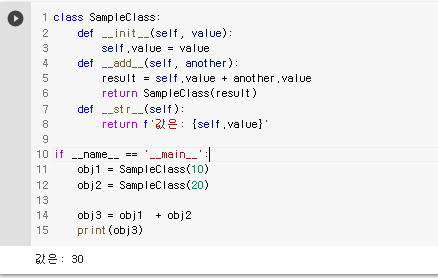
=> + 연산자가 add 라는 특수 메쏘드로 구현이 되는 것을 확인 할 수 있다.
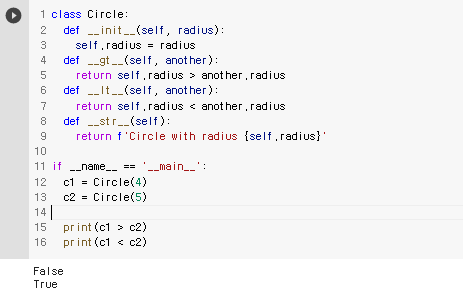
비교 연산자 오버로딩
class Circle:
def __init__(self, radius):
self.radius = radius
def __gt__(self, another):
return self.radius > another.radius
def __lt__(self, another):
return self.radius < another.radius
def __str__(self):
return f'Circle with radius {self.radius}'
if __name__ == '__main__':
c1 = Circle(4)
c2 = Circle(5)
print(c1 > c2)
print(c1 < c2)