📌 프로세스와 스레드
프로세스(process)란 실행 중인 하나의 프로그램이다. 하나의 프로그램이 다중 프로세스를 만들기도 한다.
💡 멀티 태스킹(multi tasking)
멀티 태스킹이란 두 가지 이상의 작업을 동시에 처리하는 것을 뜻한다. 멀티 프로세스는 독립적으로 프로그램들을 실행하고 여러 가지 작업을 처리한다. 멀티 스레드는 한 개의 프로그램을 실행하고 내부적으로 여러 가지 작업을 처리한다.
💡 메인(main) 스레드
모든 자바 프로그램은 메인 스레드가 main() 메소드를 실행하며 시작한다. main() 메소드의 첫 코드부터 아래로 순차적으로 실행한다.
- 실행 종료 조건 : 마지막 코드 실행, return 문을 만났을 때
main 스레드는 작업 스레드들을 만들어 병렬로 코드들을 실행한다.(멀티 스레드를 생성해 멀티 태스킹 수행)
프로스세의 종료
- 싱글 스레드 : 메인 스레드가 종료하면 프로세스도 종료
- 멀티 스레드 : 실행 중인 스레드가 하나라도 있다면, 프로세스 미종료
스레드 실행 명령어 : .start()
📌 스레드 상태 제어(1)
상태 제어란 실행 중인 스레드의 상태를 변경하는 것이다. 아래는 상태 변화를 가져오는 메소드의 종류로 취소선을 가진 메소드는 사용하지 않는다.
| 상태 | 메소드 |
|---|---|
| 일시정지 | sleep(), join(), wait(), |
| 실행대기 | interrupt(), notify(), notifyAll(), |
| 실행 | yield() |
| 종료 |
💡 sleep()
sleep()은 주어진 시간 동안 일시 정지하는 기능으로 try-catch문으로 감싸서 사용한다. 얼마 동안 일시 정지 상태로 있을 것인지 밀리초(1/1000) 단위로 지정한다.
public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SampleThread st = new SampleThread(1);
System.out.println("start");
st.start();
System.out.println("end");
}
}
//Thread 상속
class SampleThread extends Thread {
int seq;
public SampleThread(int seq) {
this.seq = seq;
}
public void run() {
System.out.println(seq + " start");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000); //밀리초
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(seq + " end");
}
}
▼ 실행결과
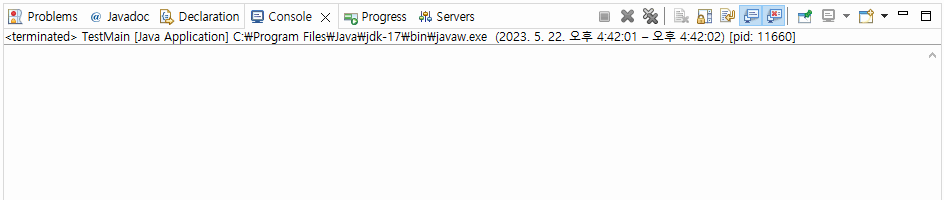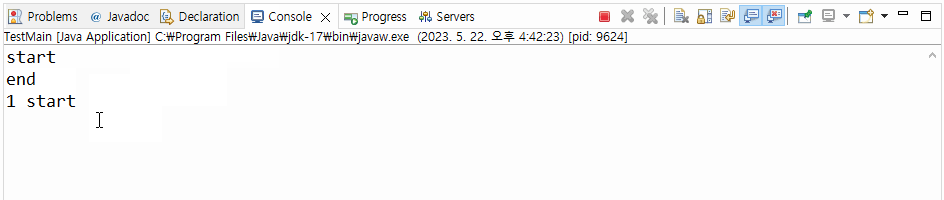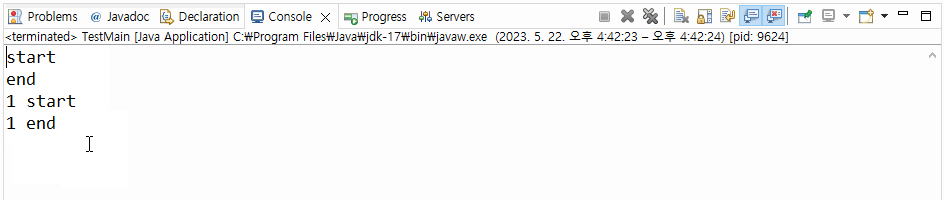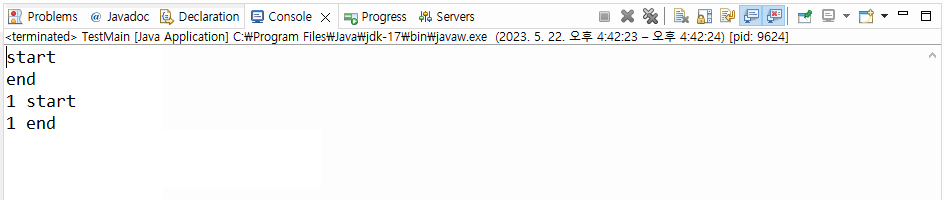
>>> 출력문 1 end는 2초 뒤에 출력되는 결과를 볼 수 있다.
🔥Runnable 인터페이스를 구현하는 경우 !!!
public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("start");
for(int i=1; i<=10; i++) {
//Runnable 인터페이스 구현 객체
SampleRunnable sr = new SampleRunnable(i);
Thread th = new Thread(sr); //SampleRunnable을 주입시킨 Thread 객체로 생성해주어야 스레드를 생성할 수 있다.
th.start();
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
//Runnable 인터페이스 구현
class SampleRunnable implements Runnable{
int seq;
public SampleRunnable(int seq) {
this.seq = seq;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(seq + " runnable start");
try {
int sleepCount = ((int)(Math.random() * 2) + 1) * 1000;
Thread.sleep(sleepCount); //밀리초
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(seq + " runnable end");
}
}▼ 실행 결과
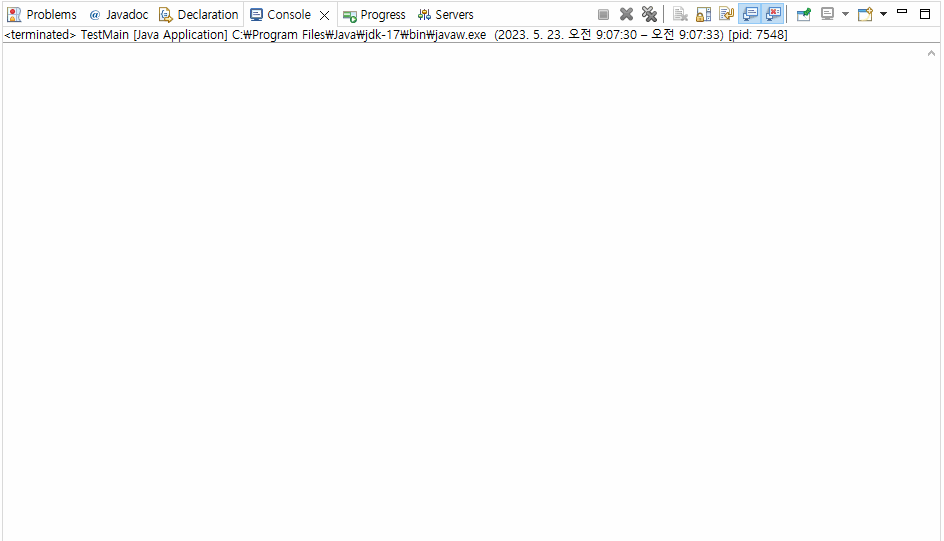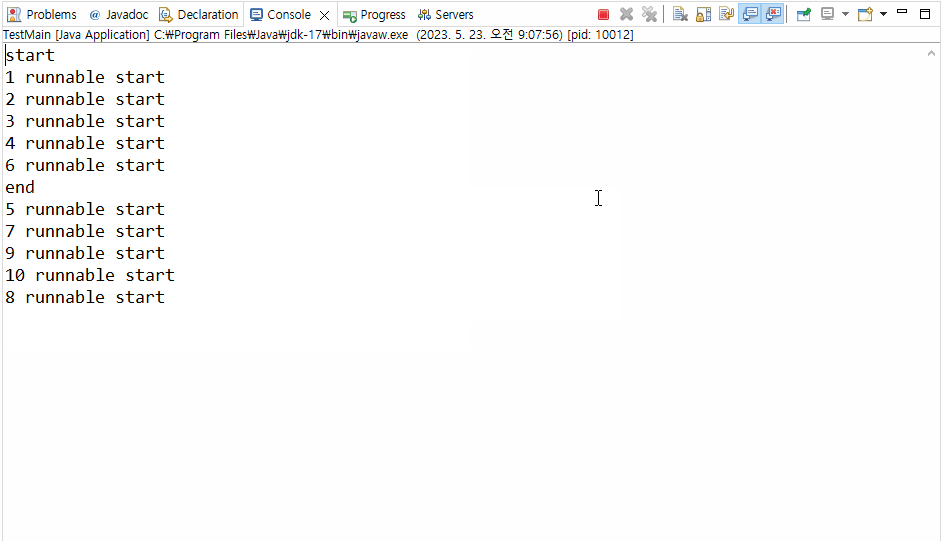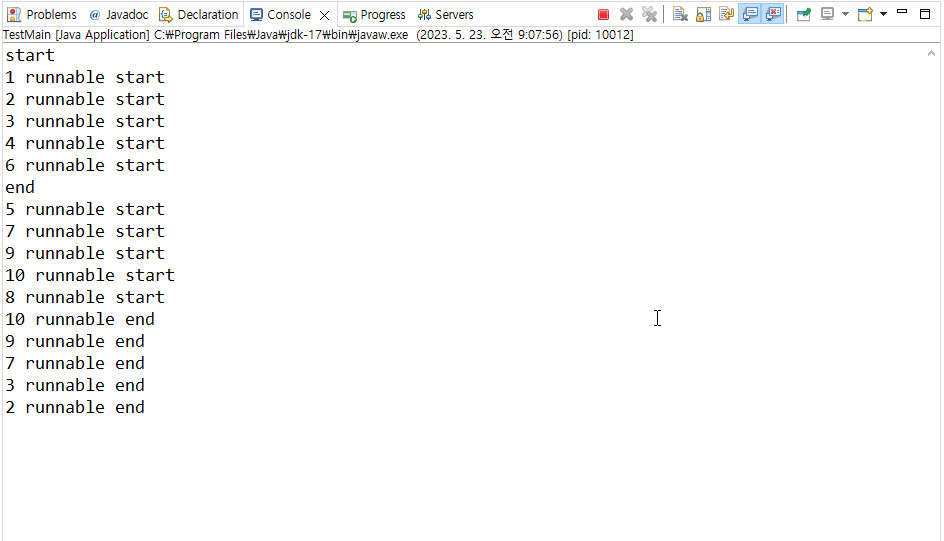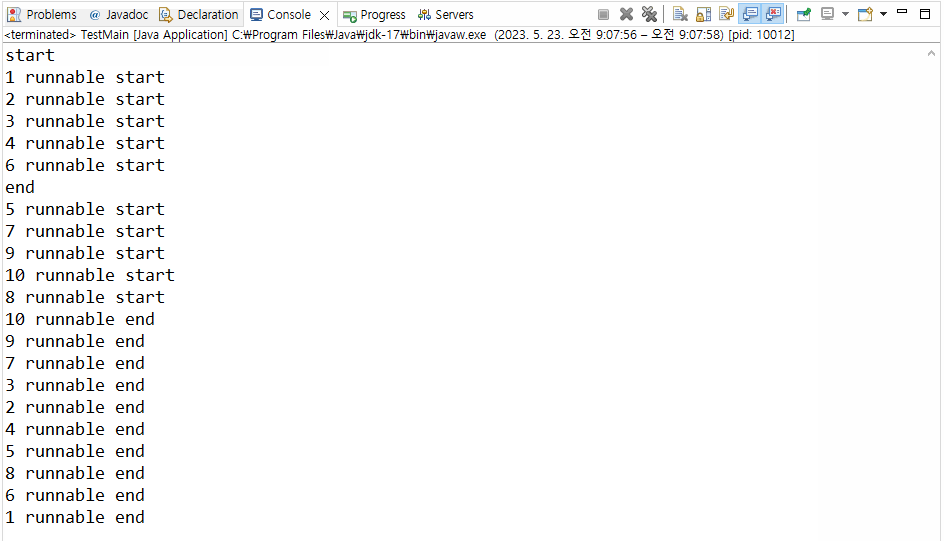
>>> Runnable 인터페이스를 구현한 클래스는 Thread 객체로 생성해주어야 스레드 생성이 가능하다!🔥
💡 join()
join()은 다른 스레드의 종료를 기다린다. 계산 작업을 하는 스레드가 모든 계산 작업을 마쳤을 때, 결과값을 받아 이용하는 경우 주로 사용한다. sleep()과 마찬가지로 try-catch로 감싸 사용한다.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class TestMain3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Thread> threadList = new ArrayList<Thread>();
System.out.println("main start");
for(int i=1; i<=10; i++) {
Thread th = new SampleThread(i);
th.start(); //스레드 생성 및 시작
threadList.add(th);
}
for(int i=0; i<threadList.size(); i++) {
try {
threadList.get(i).join(); //스레드 끝나는거 대기(기다리기)
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("main end");
}
}
class SampleThread2 extends Thread {
int seq;
public SampleThread2(int seq) {
this.seq = seq;
}
public void run() {
System.out.println(seq + " start");
try {
int sleepCount = ((int)(Math.random() * 2) + 1) * 1000;
Thread.sleep(sleepCount); //밀리초
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(seq + " end");
}
}▼ 실행결과
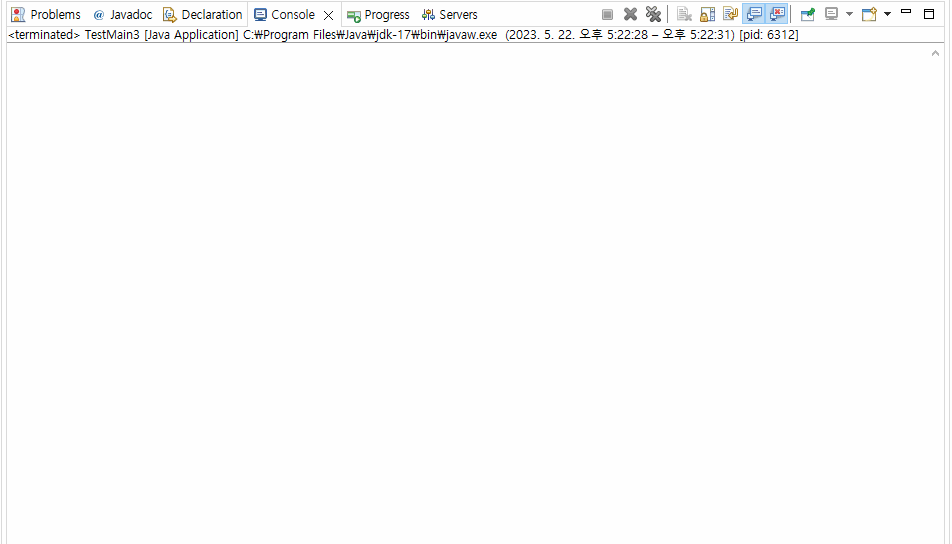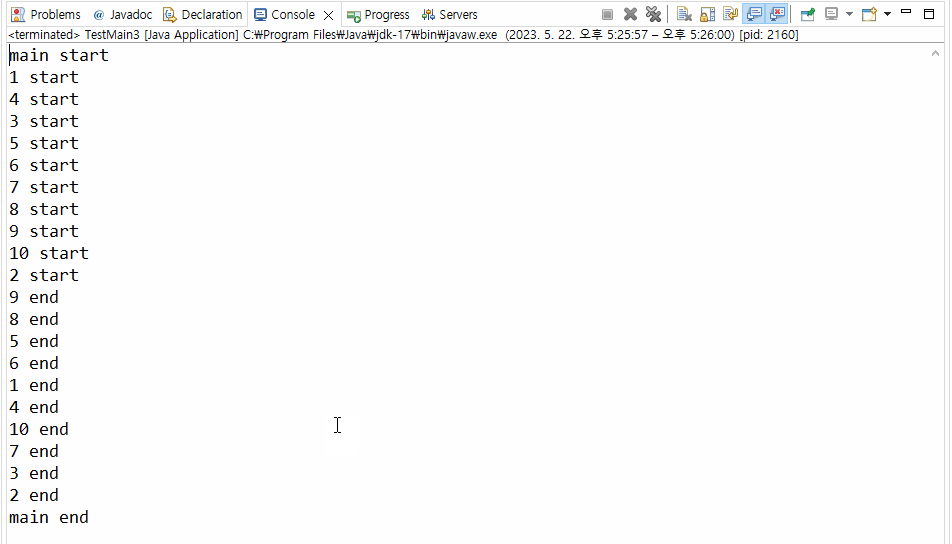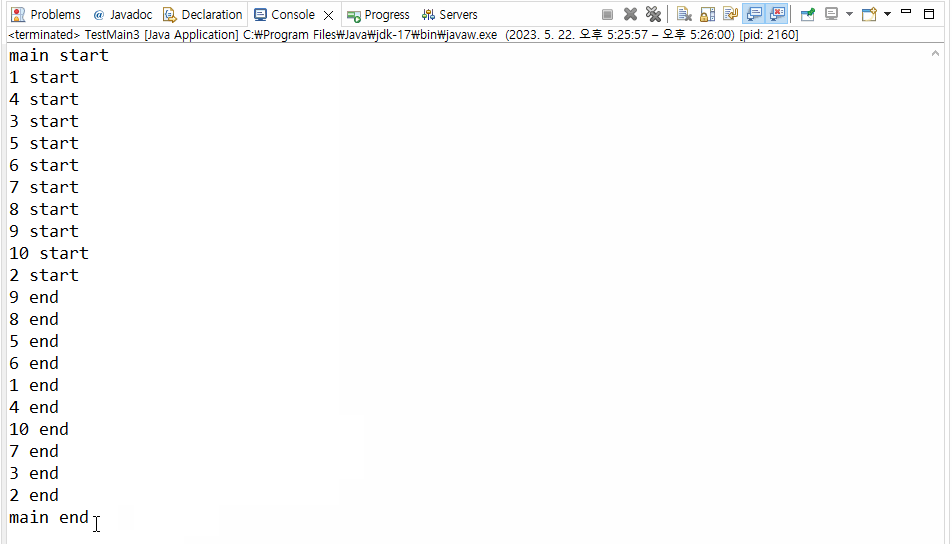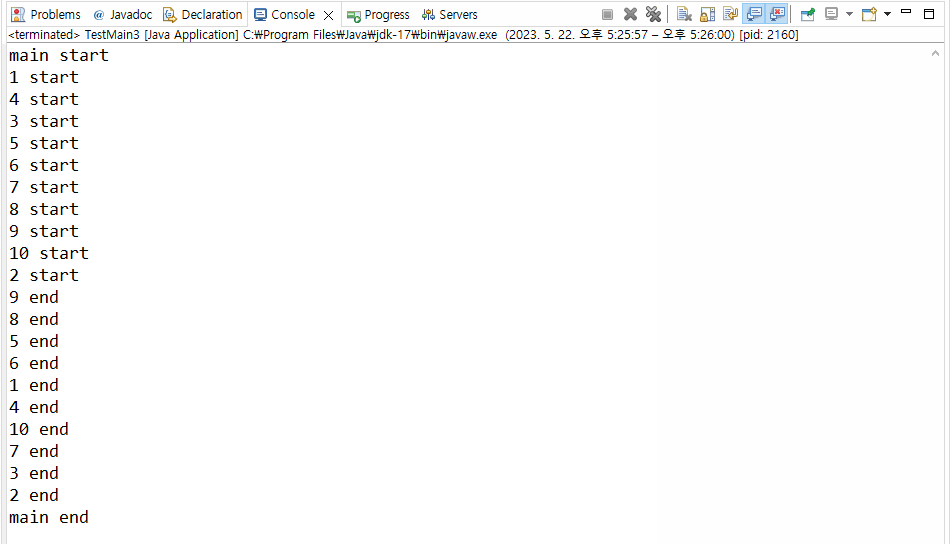
>>> join()의 결과로 출력문 main end가 제일 마지막에 출력되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
↓↓↓↓↓ join()을 사용하지 않았을 때

출력문 main end가 중간에 출력되는 것을 볼 수 있음!

