01. List Methods
- Here are some other common list methods.
- list.append(elem) - adds a single element to the end of the list. Common error : does not return the new list, just modifies the original
- list.insert(index,elem) - inserts the element at the given index, shifting elements to the right.
- list.extend(list2) - adds the elements in list2 to the end of the list. Using + or += on a list is similar to using extend().
- list.index(elem) - searches for the given element from the start of the list and returns its index. Throws a ValueError if the element does not appear (use 'in" to check without a ValueError).
- list.remove(elem) - searches for the first instance of the given element and removes it (throws ValeError if not present)
- list.sort() 0 sorts the list in place (does not return it). (The sorted() function shown later is preferred.)
- list.reverse() - reverses the list in place (does not return it)
- list.pop(index) - removes and returns the element at the given index. Returns the rightmost element if index is omitted (roughly the opposite of append()).
02. black jack game
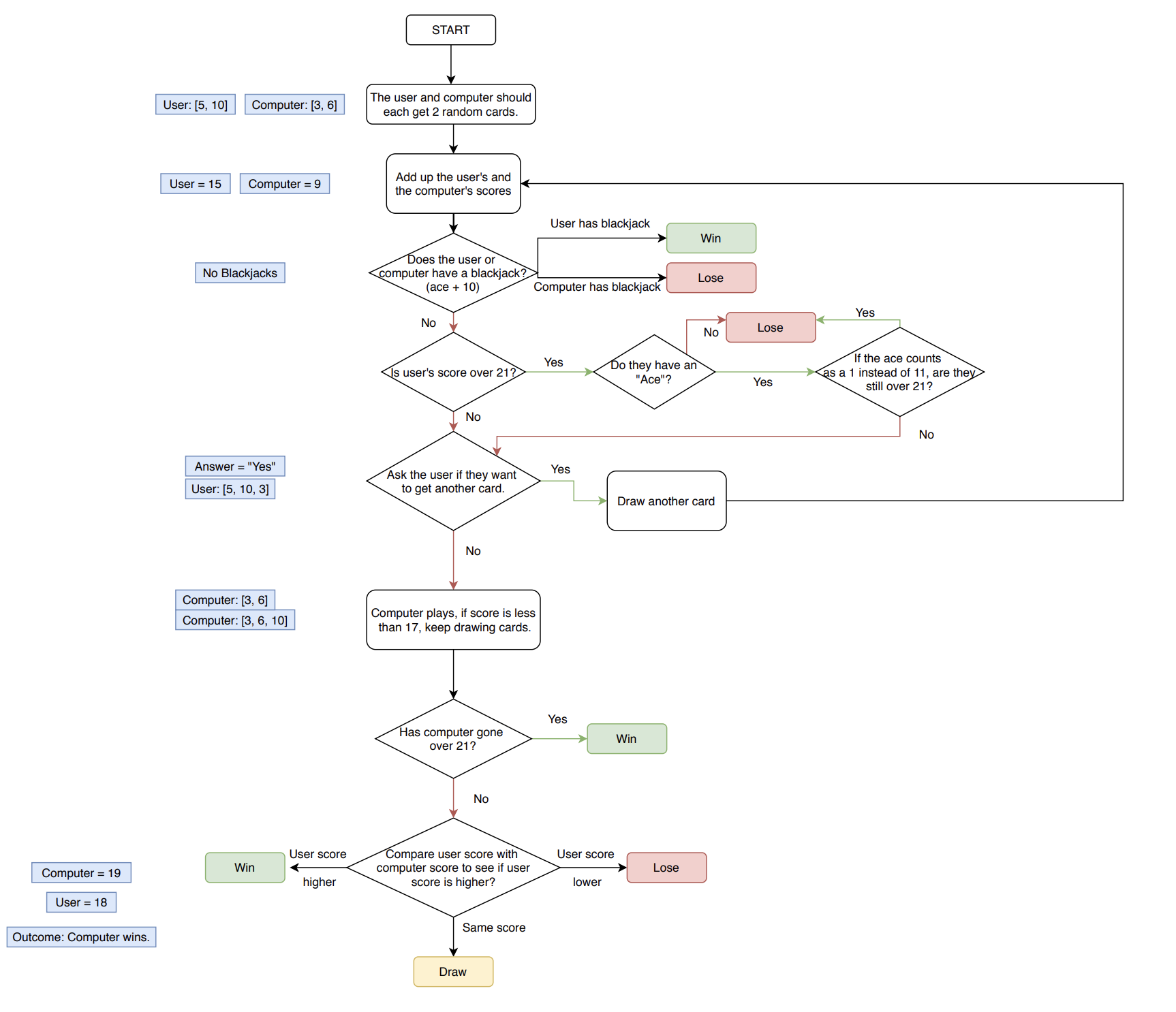
import random
from replit import clear
from art import logo
def deal_card():
"""Returns a random card from the deck."""
cards = [11, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 10, 10, 10]
card = random.choice(cards)
return card
def calculate_score(cards):
"""Take a list of cards and return the score calculated from the cards"""
if sum(cards) == 21 and len(cards) == 2:
return 0
if 11 in cards and sum(cards) > 21:
cards.remove(11)
cards.append(1)
return sum(cards)
def compare(user_score, computer_score):
if user_score > 21 and computer_score > 21:
return "You went over. You lose 😤"
if user_score == computer_score:
return "Draw 🙃"
elif computer_score == 0:
return "Lose, opponent has Blackjack 😱"
elif user_score == 0:
return "Win with a Blackjack 😎"
elif user_score > 21:
return "You went over. You lose 😭"
elif computer_score > 21:
return "Opponent went over. You win 😁"
elif user_score > computer_score:
return "You win 😃"
else:
return "You lose 😤"
def play_game():
print(logo)
user_cards = []
computer_cards = []
is_game_over = False
for _ in range(2):
user_cards.append(deal_card())
computer_cards.append(deal_card())
while not is_game_over:
user_score = calculate_score(user_cards)
computer_score = calculate_score(computer_cards)
print(f" Your cards: {user_cards}, current score: {user_score}")
print(f" Computer's first card: {computer_cards[0]}")
if user_score == 0 or computer_score == 0 or user_score > 21:
is_game_over = True
else:
user_should_deal = input("Type 'y' to get another card, type 'n' to pass: ")
if user_should_deal == "y":
user_cards.append(deal_card())
else:
is_game_over = True
while computer_score != 0 and computer_score < 17:
computer_cards.append(deal_card())
computer_score = calculate_score(computer_cards)
print(f" Your final hand: {user_cards}, final score: {user_score}")
print(f" Computer's final hand: {computer_cards}, final score: {computer_score}")
print(compare(user_score, computer_score))
while input("Do you want to play a game of Blackjack? Type 'y' or 'n': ") == "y":
clear()
play_game()
import random
from replit import clear
from art import logo
def deal_card():
"""Returns a random card from the deck."""
cards = [11, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 10, 10, 10]
card = random.choice(cards)
return card
def calculate_score(cards):
"""Take a list of cards and return the score calculated from the cards"""
if sum(cards) == 21 and len(cards) == 2:
return 0
if 11 in cards and sum(cards) > 21:
cards.remove(11)
cards.append(1)
return sum(cards)
def compare(user_score, computer_score):
if user_score > 21 and computer_score > 21:
return "You went over. You lose 😤"
if user_score == computer_score:
return "Draw 🙃"
elif computer_score == 0:
return "Lose, opponent has Blackjack 😱"
elif user_score == 0:
return "Win with a Blackjack 😎"
elif user_score > 21:
return "You went over. You lose 😭"
elif computer_score > 21:
return "Opponent went over. You win 😁"
elif user_score > computer_score:
return "You win 😃"
else:
return "You lose 😤"
def play_game():
print(logo)
user_cards = []
computer_cards = []
is_game_over = False
for _ in range(2):
user_cards.append(deal_card())
computer_cards.append(deal_card())
while not is_game_over:
user_score = calculate_score(user_cards)
computer_score = calculate_score(computer_cards)
print(f" Your cards: {user_cards}, current score: {user_score}")
print(f" Computer's first card: {computer_cards[0]}")
if user_score == 0 or computer_score == 0 or user_score > 21:
is_game_over = True
else:
user_should_deal = input("Type 'y' to get another card, type 'n' to pass: ")
if user_should_deal == "y":
user_cards.append(deal_card())
else:
is_game_over = True
while computer_score != 0 and computer_score < 17:
computer_cards.append(deal_card())
computer_score = calculate_score(computer_cards)
print(f" Your final hand: {user_cards}, final score: {user_score}")
print(f" Computer's final hand: {computer_cards}, final score: {computer_score}")
print(compare(user_score, computer_score))
while input("Do you want to play a game of Blackjack? Type 'y' or 'n': ") == "y":
clear()
play_game()
- 너무 어려웠던 프로젝트, 강의 듣다가 다시 한 번 돌아와서 스스로 해낼 수 있기를!


Michael had always enjoyed playing card games with friends but had never ventured into the world of online gambling. On a whim, he https://pin-up-casino-az.online/ decided to try his luck at an online blackjack table after hearing about its simplicity and potential for big wins. The digital blackjack game featured sleek graphics and realistic dealer interactions, making it feel almost like a real casino experience. Michael started with low stakes, gradually becoming more confident as he familiarized himself with the game’s rules and strategies.