쿼드 압축 후 개수 세기 68936
🎏 문제 설명
0과 1로 이루어진 2n x 2n 크기의 2차원 정수 배열 arr이 있습니다.
당신은 이 arr을 쿼드 트리와 같은 방식으로 압축하고자 합니다. 구체적인 방식은 다음과 같습니다.
1. 당신이 압축하고자 하는 특정 영역을 S라고 정의합니다.
2. 만약 S 내부에 있는 모든 수가 같은 값이라면, S를 해당 수 하나로 압축시킵니다.
3. 그렇지 않다면, S를 정확히 4개의 균일한 정사각형 영역(입출력 예를 참고해주시기 바랍니다.)으로 쪼갠 뒤, 각 정사각형 영역에 대해 같은 방식의 압축을 시도합니다.
arr이 매개변수로 주어집니다.
위와 같은 방식으로 arr을 압축했을 때, 배열에 최종적으로 남는 0의 개수와 1의 개수를 배열에 담아서 return 하도록 solution 함수를 완성해주세요.🔔 입출력 예시
다음 그림은 주어진 arr을 압축하는 과정을 나타낸 것입니다.
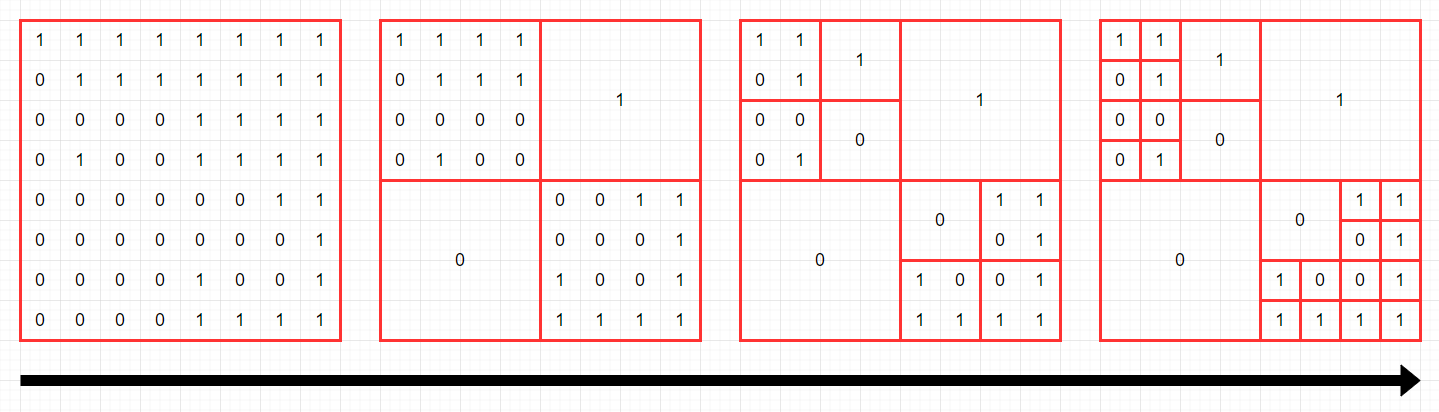
최종 압축 결과에 0이 10개, 1이 15개 있으므로, [10,15]를 return 해야 합니다.
🪁 제한사항
- arr의 행의 개수는 1 이상 1024 이하이며, 2의 거듭 제곱수 형태를 하고 있습니다. 즉, arr의 행의 개수는 1, 2, 4, 8, ..., 1024 중 하나입니다.
- arr의 각 행의 길이는 arr의 행의 개수와 같습니다. 즉, arr은 정사각형 배열입니다.
- arr의 각 행에 있는 모든 값은 0 또는 1 입니다.
🎺 풀이
DFS 로 접근해야 하나? 라고 생각은 했으나 다음과 같은 경우 4분할이 각각 크기가 다를 때에는 어떻게 하지? 라는 물음에 푸는데 어려움을 겪었다.
다음의 블로그를 참고하여 이해하려고 노력했고, 코드도 동일하게 작성했다!
참고 블로그 (^人^)
2^n X 2^n 의 사각형이기 때문에 분할시 무조건 4분할 하게 된다.
따라서 arr 을 4분할 하여 새로운 vector<int> tmp1 ~ tmp4 를 만들고 할당해 준다.
각 분할한 vector 들을 count 함수에 넣고 다시 압축할 수 있는지를 판단하기만 하면 된다.
긴 글 + 복잡한 과정을 그대로 작성할 수 있으면 된다..
🏒 코드
[C++]
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
bool is_equal_arr(vector<vector<int>> arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.size() - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.size() - 1; j++) {
if (arr[i][j] != arr[i][j + 1] || arr[i][j] != arr[i + 1][j] || arr[i][j] != arr[i + 1][j + 1]) return false;
}
}
return true;
}
vector<int> count(int size, vector<vector<int>> arr) {
vector<int> result(2, 0);
if (arr.size() == 1) {
result[arr[0][0]] += 1;
return result;
}
if (is_equal_arr(arr)) {
result[arr[0][0]] += 1;
return result;
}
else {
vector<vector<int>> tmp1(size / 2, vector<int>(size / 2, 0));
vector<vector<int>> tmp2(size / 2, vector<int>(size / 2, 0));
vector<vector<int>> tmp3(size / 2, vector<int>(size / 2, 0));
vector<vector<int>> tmp4(size / 2, vector<int>(size / 2, 0));
vector<int> result_tmp;
for (int i = 0; i < size / 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < size / 2; j++) {
tmp1[i][j] = arr[i][j];
tmp2[i][j] = arr[i][j + (size / 2)];
tmp3[i][j] = arr[i + (size / 2)][j];
tmp4[i][j] = arr[i + (size / 2)][j + (size / 2)];
}
}
result_tmp = count(size / 2, tmp1);
result[0] += result_tmp[0]; result[1] += result_tmp[1];
result_tmp = count(size / 2, tmp2);
result[0] += result_tmp[0]; result[1] += result_tmp[1];
result_tmp = count(size / 2, tmp3);
result[0] += result_tmp[0]; result[1] += result_tmp[1];
result_tmp = count(size / 2, tmp4);
result[0] += result_tmp[0]; result[1] += result_tmp[1];
return result;
}
}
vector<int> solution(vector<vector<int>> arr) {
vector<int> answer;
answer = count(arr.size(), arr);
return answer;
}[C]
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
bool is_equal_arr(int** arr, size_t arr_rows, size_t arr_cols) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr_rows - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr_cols - 1; j++) {
if (arr[i][j] != arr[i][j + 1] || arr[i][j] != arr[i + 1][j] || arr[i][j] != arr[i + 1][j + 1]) return false;
}
}
return true;
}
int* count(int** arr, size_t arr_rows, size_t arr_cols) {
int* result;
result = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 2);
result[0] = 0; result[1] = 0;
if (arr_rows == 1 && arr_cols == 1) {
result[arr[0][0]] += 1;
return result;
}
if (is_equal_arr(arr, arr_rows, arr_cols)) {
result[arr[0][0]] += 1;
return result;
}
else {
// setting tmp1~tmp4
int** tmp1 = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*) * (arr_rows / 2));
for (int i = 0; i < arr_rows / 2; i++) {
int* tmp_col = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * (arr_cols/2));
for (int j = 0; j < arr_cols / 2; j++) tmp_col[j] = 0;
tmp1[i] = tmp_col;
}
int** tmp2 = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*) * (arr_rows / 2));
for (int i = 0; i < arr_rows / 2; i++) {
int* tmp_col = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * (arr_cols/2));
for (int j = 0; j < arr_cols / 2; j++) tmp_col[j] = 0;
tmp2[i] = tmp_col;
}
int** tmp3 = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*) * (arr_rows / 2));
for (int i = 0; i < arr_rows / 2; i++) {
int* tmp_col = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * (arr_cols/2));
for (int j = 0; j < arr_cols / 2; j++) tmp_col[j] = 0;
tmp3[i] = tmp_col;
}
int** tmp4 = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*) * (arr_rows / 2));
for (int i = 0; i < arr_rows / 2; i++) {
int* tmp_col = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * (arr_cols/2));
for (int j = 0; j < arr_cols / 2; j++) tmp_col[j] = 0;
tmp4[i] = tmp_col;
}
int* tmp_result = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 2);
//init tmp1~tmp4
for (int i = 0; i < arr_rows / 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr_cols / 2; j++) {
tmp1[i][j] = arr[i][j];
tmp2[i][j] = arr[i][j + arr_cols / 2];
tmp3[i][j] = arr[i + arr_rows / 2][j];
tmp4[i][j] = arr[i + arr_rows / 2][j + arr_cols / 2];
}
}
tmp_result = count(tmp1, arr_rows / 2, arr_cols / 2);
result[0] += tmp_result[0]; result[1] += tmp_result[1];
tmp_result = count(tmp2, arr_rows / 2, arr_cols / 2);
result[0] += tmp_result[0]; result[1] += tmp_result[1];
tmp_result = count(tmp3, arr_rows / 2, arr_cols / 2);
result[0] += tmp_result[0]; result[1] += tmp_result[1];
tmp_result = count(tmp4, arr_rows / 2, arr_cols / 2);
result[0] += tmp_result[0]; result[1] += tmp_result[1];
return result;
}
}
// arr_rows는 2차원 배열 arr의 행 길이, arr_cols는 2차원 배열 arr의 열 길이입니다.
int* solution(int** arr, size_t arr_rows, size_t arr_cols) {
// return 값은 malloc 등 동적 할당을 사용해주세요. 할당 길이는 상황에 맞게 변경해주세요.
int* answer = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 2);
answer[0] = 0, answer[1] = 0;
answer = count(arr, arr_rows, arr_cols);
return answer;
}📻 어려웠던 점
- 어렵게 생각하지 말자 . . . . . . . .
분할정복을 좀 더 익숙해질 필요가 있는 것 같다.

