Chapter 1: 인텔리제이로 스프링 부트 시작하기
gradle 프로젝트를 스프링 부트 프로젝트로 변경하기
프로젝트의 플러그인 의존성 관리를 위한 설정
buildscript {
ext {
springBootVersion = '2.1.7.RELEASE'
}
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
classpath("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-gradle-plugin:${springBootVersion}")
}
}ext: build.gradle에서 사용하는 전역변수를 설정
자바와 스프링 부트를 사용하기 위한 필수 플러그인
plugins {
id 'org.springframework.boot' version '2.7.8'
id 'io.spring.dependency-management' version '1.1.0'
id 'java'
}io.spring.dependency-management: 스프링 부트의 의존성 관리 플러그인
repositories
각종 의존성(라이브러리)들을 어떤 원격 저장소에서 받을지 정함
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}dependencies
프로젝트 개발에 필요한 의존성들을 선언
dependencies {
testImplementation 'org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-api:5.8.1'
testRuntimeOnly 'org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-engine:5.8.1'
// 웹에 관련된 의존성 관리. json이나 tomcat 등이 들어있다.
implementation('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web')
// 테스트를 위한 라이브러리가 들어있다.
testImplementation('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test')
}전체 코드
buildscript {
ext {
springBootVersion = '2.1.7.RELEASE'
}
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
classpath("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-gradle-plugin:${springBootVersion}")
}
}
plugins {
id 'org.springframework.boot' version '2.7.8' // 스프링 부트 그레이들 플러그인
id 'io.spring.dependency-management' version '1.1.0'// 의존성 관리 플러그인 버전
id 'java'
}
group '---'
version '1.0-SNAPSHOT'
sourceCompatibility = '11'
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
testImplementation 'org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-api:5.8.1'
testRuntimeOnly 'org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-engine:5.8.1'
implementation('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web')
testImplementation('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test')
}
//Junit5를 사용하기 위해서는 필수로 선언
test {
useJUnitPlatform()
}
Chapter 2: 스프링 부트에서 테스트 코드를 작성하자
테스트 코드란?
TDD vs. 단위 테스트(Unit Test)
- TDD: 테스트가 주도하는 개발
- 단위 테스트: TDD의 첫번째 단계인 기능 단위의 테스트 코드를 작성하는 것
테스트 코드를 작성하여 얻는 이점
- 단위 테스트는 개발단계 초기에 문제를 발견하게 도와준다.
- 단위 테스트는 개발자가 나중에 코드를 리팩토링하거나 라이브러리 업그레이드 등에서 기존 기능이 올바르게 작동하는지 확인할 수 있다.
- 단위 테스트는 기능에 대한 불확실성을 감소시킬 수 있다.
- 단위 테스트는 시스템에 대한 실제 문서를 제공한다. 즉, 단위 테스트 자체가 문서로 사용될 수 있다.
- 피드백이 빠르다.
System.out.println()과 같이 눈으로 검증하는 방법을 더이상 사용하지 않고, 자동검증이 가능하다.- 개발자가 만든 기능을 안전하게 보호해준다.
테스트 코드 작성을 도와주는 프레임워크
가장 대중적인 프레임워크: 개발환경(x)에 따라 Unit 테스트를 도와주는 xUnit
- JUnit - Java >> 사용
- DBUnit - DB
- CppUnit - C++
- NUnit - .net
Hello Controler 테스트 코드 작성하기
- 일반적으로 패키지명은 웹 사이트 주소의 역순으로 짓는다.
ex) 웹 사이트 주소: admin.jojoldu.com -> 패키지명: com.jojoldu.admin - 일반적으로 테스트 클래스는 대상 클래스 이름에 Test를 붙인다.
1. src/main/java에서 'com.jojoldu.book.springboot' 패키지 생성
2. 이 패키지 아래에 Application 클래스 생성
앞으로 만들 클래스의 메인 클래스
package com.jojoldu.book.springboot;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
3. 이 패키지 하위에 web이라는 패키지 생성
컨트롤러와 관련된 클래스들을 담을 패키지
4. web 패키지에 HelloController 클래스 생성
package com.jojoldu.book.springboot.web;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "hello";
}
}@RestController: 컨트롤러를 JSON을 반환하는 컨트롤러로 만들어준다.
@GetMapping: HTTP GET Method의 요청을 받을 수 있는 API를 만들어준다.
5. src/test/java에서 'com.jojoldu.book.springboot' 패키지 생성
6. 이 패키지에 HelloControllerTest 클래스 생성
package com.jojoldu.book.springboot.web;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringExtension;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.get;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.content;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.status;
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@WebMvcTest(controllers = HelloController.class)
public class HelloControllerTest {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mvc;
@Test
public void hello가_리턴된다() throws Exception{
String hello = "hello";
mvc.perform(get("/hello"))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().string(hello));
}
}
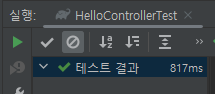
7. 테스트 코드 실행
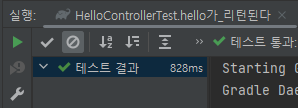
8. 메인 메소드 실행
Application 클래스
@SpringBootApplication이 있는 위치부터 설정을 읽어가기 때문에 항상 프로젝트의 최상단에 위치해야만 한다.
main 메소드에서 실행하는 SpringApplication.run으로 인해 내장 WAS(Web Application Server)를 실행한다.
내장 WAS: 별도로 외부에 WAS를 두지 않고 어플리케이션을 실행할 때 내부에서 WAS를 실행하는 것, 항상 서버에 톰캣을 설치할 필요가 없게 되고 스프링 부트로 만들어진 Jar 파일로 실행하면 된다.
스프링 부트는 언제 어디서나 같은 환경에서 스프링 부트를 배포하기 위해 내장 WAS를 사용하는 것을 권장한다.
롬복
롬복이란?
자바 개발 시 자주 사용하는 코드 Getter, Setter, 기본생성자, toString 등을 어노테이션으로 자동 생성해준다.
프로젝트에 롬복 추가
build.gradle에 다음 코드를 추가한다.
!!! gradle 7.5.1 버전 !!!
dependencies {
...
// 롬복 추가
compileOnly 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
annotationProcessor 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
...
}롬복 플러그인 설치
플러그인 설치 후 Setting > Build > Compiler > Annotation Processors에서 Enable annotation processing을 체크한다.
Hello Controller 코드를 롬복으로 전환하기
1. src/main/java/com.jojoldu.book.springboot.web 패키지에 dto 패키지 생성
앞으로 모든 응답 Dto는 dto 패키지에 추가한다.
2. 이 패키지에 HelloResponseDto 클래스 생성
package com.jojoldu.book.springboot.web.dto;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
@Getter
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class HelloResponseDto {
private final String name;
private final int amount;
}@Getter: 선언된 모든 필드의 get 메소드를 생성해준다.
@RequiredArgsConstructor: 선언된 모든 final 필드가 포함된 생성자를 생성해준다. (final이 없는 필드는 생성자에 포함되지 않는다.)
3. src/test/java/com.jojoldu.book.springboot.web 패키지에 dto 패키지 생성
4. 이 패키지에 HelloResponseDtoTest 클래스 생성
package com.jojoldu.book.springboot.web.dto;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
public class HelloResponseDtoTest {
@Test
public void 롬복_기능_테스트(){
//given
String name = "test";
int amount = 1000;
//when
HelloResponseDto dto = new HelloResponseDto(name, amount);
//then
assertThat(dto.getName()).isEqualTo(name);
assertThat(dto.getAmount()).isEqualTo(amount);
}
}@assertThat: assertj라는 테스트 검증 라이브러리의 검증 메소드로, 검증하고 싶은 대상을 메소드 인자로 받으며, 메소드 체이닝이 지원되어 isEqualTo와 같은 메소드를 이어서 사용할 수 있다.
@isEqualTo: assertj의 동등 비교 메소드로, assertThat에 있는 값과 isEqualTo의 값을 비교해서 같을 때만 성공이다.
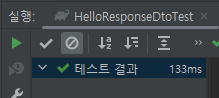
5. 테스트 메소드 실행
6. HelloController에 새로 만든 ResponseDto를 사용하는 코드 추가
package com.jojoldu.book.springboot.web;
import com.jojoldu.book.springboot.web.dto.HelloResponseDto;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "hello";
}
// 이하 추가
@GetMapping("/hello/dto")
public HelloResponseDto helloDto(@RequestParam("name") String name, @RequestParam("amount") int amount){
return new HelloResponseDto(name, amount);
}
}@RequestParam: 외부에서 API로 넘긴 파라미터를 가져오는 어노테이션으로, 여기에서는 외부에서 name이라는 이름으로 넘긴 파라미터를 메소드 파라미터 name(String name)에 저장하게 된다.
7. HelloControllerTest에 새로운 코드 추가
package com.jojoldu.book.springboot.web;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringExtension;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.is;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.get;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.content;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.status;
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@WebMvcTest(controllers = HelloController.class)
public class HelloControllerTest {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mvc;
@Test
public void hello가_리턴된다() throws Exception{
String hello = "hello";
mvc.perform(get("/hello"))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().string(hello));
}
@Test
public void helloDto가_리턴된다() throws Exception{
String name = "hello";
int amount = 1000;
mvc.perform(
get("/hello/dto")
.param("name", name)
.param("amount", String.valueOf(amount)))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.name", is(name)))
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.amount", is(amount)));
}
}param: API 테스트 시 사용될 요청 파라미터를 설정하며, String 값만 허용된다.
jsonPath: JSON 응답값을 필드별로 검증할 수 있는 메소드로, $를 기준으로 필드명을 명시한다.
8. 테스트 코드 실행