개요
문제 파일은 다음 github 페이지에서 받을 수 있다.
문제

마찬가지로 루팅을 검사하며, 시리얼을 입력받는 앱이다.
풀이
소스 분석
uncracable::MainActivicty
package sg.vantagepoint.uncrackable2; import owasp.mstg.uncrackable2.R; import sg.vantagepoint.a.a; import sg.vantagepoint.a.b; public class MainActivity extends c { private CodeCheck m; static { System.loadLibrary("foo"); } /* access modifiers changed from: private */ public void a(String str) { AlertDialog create = new AlertDialog.Builder(this).create(); create.setTitle(str); create.setMessage("This is unacceptable. The app is now going to exit."); create.setButton(-3, "OK", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialogInterface, int i) { System.exit(0); } }); create.setCancelable(false); create.show(); } private native void init(); /* access modifiers changed from: protected */ public void onCreate(Bundle bundle) { init(); if (b.a() || b.b() || b.c()) { a("Root detected!"); } if (a.a(getApplicationContext())) { a("App is debuggable!"); } new AsyncTask<Void, String, String>() { /* access modifiers changed from: protected */ /* renamed from: a */ public String doInBackground(Void... voidArr) { while (!Debug.isDebuggerConnected()) { SystemClock.sleep(100); } return null; } /* access modifiers changed from: protected */ /* renamed from: a */ public void onPostExecute(String str) { MainActivity.this.a("Debugger detected!"); } }.execute(new Void[]{null, null, null}); this.m = new CodeCheck(); super.onCreate(bundle); setContentView((int) R.layout.activity_main); } public void verify(View view) { String str; String obj = ((EditText) findViewById(R.id.edit_text)).getText().toString(); AlertDialog create = new AlertDialog.Builder(this).create(); if (this.m.a(obj)) { create.setTitle("Success!"); str = "This is the correct secret."; } else { create.setTitle("Nope..."); str = "That's not it. Try again."; } create.setMessage(str); create.setButton(-3, "OK", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialogInterface, int i) { dialogInterface.dismiss(); } }); create.show(); } }
기존의 level1 소스와 비슷하다.
다른 점은 AsyncTask 클래스를 활용하여 디버깅을 검사하는 백그라운드 작업이 추가되었고, 시리얼을 검사하는 루틴이 CodeCheck 클래스의 a()를 호출하는 것으로 변경되었다는 것이다.
uncrackable::CodeCheck
public class CodeCheck { private native boolean bar(byte[] bArr); public boolean a(String str) { return bar(str.getBytes()); } }
CodeCheck 클래스를 확인해보면
전달받은 입력값을 인자로 해서, native method인 bar()를 호출하고 있다.
bar()가 내장된 라이브러리는 MainActivity 클래스에서 다음의 코드로 로드했었다.
uncracable::MainActivity
static { System.loadLibrary("foo"); }
native method
native method는 리눅스의 library인 .so파일을 로드해서 사용하는 것이다. 따라서 해당 코드는 IDA로 확인할 수 있다.
apk를 IDA에 로드시키면 아래와 같이 내장된 파일 목록이 출력되는데 여기서 foo.so를 찾을 수 있다.

시리얼 검사를 수행하는 함수를 확인해보자.
bar
int __cdecl Java_sg_vantagepoint_uncrackable2_CodeCheck_bar(int a1, int a2, int a3) { const char *v3; // esi@2 int result; // eax@4 signed int v5; // [sp+0h] [bp-2Ch]@2 signed int v6; // [sp+4h] [bp-28h]@2 signed int v7; // [sp+8h] [bp-24h]@2 signed int v8; // [sp+Ch] [bp-20h]@2 signed __int16 v9; // [sp+10h] [bp-1Ch]@2 signed int v10; // [sp+12h] [bp-1Ah]@2 signed __int16 v11; // [sp+16h] [bp-16h]@2 int v12; // [sp+18h] [bp-14h]@1 v12 = *MK_FP(__GS__, 20); result = 0; if ( byte_4008 == 1 ) { v5 = 'nahT'; v6 = 'f sk'; v7 = 'a ro'; v8 = 't ll'; v9 = 'eh'; v10 = 'sif '; v11 = 'h'; v3 = (const char *)(*(int (__cdecl **)(int, int, _DWORD))(*(_DWORD *)a1 + 736))(a1, a3, 0); if ( (*(int (__cdecl **)(int, int))(*(_DWORD *)a1 + 684))(a1, a3) == 23 && !strncmp(v3, (const char *)&v5, 0x17u) ) result = 1; } return result; }
result를 설정하는 조건문을 확인해보면 strncmp로 비교를 수행하고 있다.
시리얼로 추정되는 v5의 값은 어떤 문자열로 초기화되고 있다.
이 문자열을 거꾸로 정렬하면 정상적인 시리얼이 된다는 것을 유추할 수 있지만 후킹을 사용하여 풀이하는 것이 목적이므로 넘어가자.
v3는 입력값이며 v5인 시리얼과 비교 후 일치할 경우 True를 반환한다.
종료 우회
이전 문제와 동일하게 후킹 후 종료코드가 실행되지 않도록 만든다.
console.log("[*] Starting script");
Java.perform(function(){
console.log("[*] in perform");
var class_System = null;
class_System = Java.use("java.lang.System");
class_System.exit.implementation = function(){
console.log("[*] System.exit called!!");
}
});
"""시리얼 획득
후킹을 이용해 시리얼이 전달되는 strncmp의 인자를 확인하여 시리얼을 획득하자.
Interceptor.attach(Module.findExportByName('libfoo.so', 'strncmp'), {'onEnter': function(args){
if(args[2].toInt32() == 23){
console.log("serial: ", Memory.readUtf8String(args[1], 23));
}
}});주의
strcmp는 여러번 호출되기 때문에 시리얼을 인자로 전달하는 호출을 캡처하기 위해 조건을 잘 설정해야 한다.
Memory.readUtf8String()을 조건으로 넣을 경우, 여러번 호출되는 strcmp 중 String으로 읽을 수 없는 값을 인자로 전달하는 경우가 존재한다면 에러가 발생한다.
toInt32()는 메모리 값을 숫자 그대로 읽기 때문에 어떤 값이 오더라도 에러가 발생하지 않는다.
위 코드를 실행하고 아무 시리얼 값을 입력하면
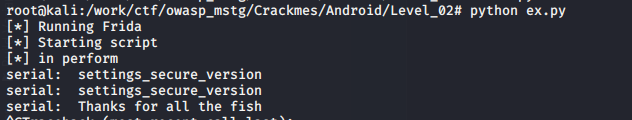
Thanks for all the fish라는 시리얼 값을 확인할 수 있다.
참조
https://secuinfo.tistory.com/entry/FRIDA-Frida%EB%A5%BC-%EC%9D%B4%EC%9A%A9%ED%95%9C-Native-Hooking

