Daily Coding 24번
부분집합인지 여부를 리턴하라.
public boolean isSubsetOf(int[] base, int[] sample) {
boolean result = true;
List<Integer> baseList = Arrays.stream(base) // Array를 stream으로 변환
.boxed() // primitive(기본형) 타입을 wrapper 타입으로 박싱하여 반환
.collect(Collectors.toList()); // stream을 List로 변환
for(int o : sample){
if(!baseList.contains(o)) {
result = false;
break;
}
}
return result;
}[Spring MVC] 예외 처리
비즈니스 로직에대한 예외 처리
비즈니스적인 예외 던지기(throw) 및 예외 처리
개념정리
체크 예외
- 발생한 예외를 잡아서(catch) 체크한 후에 해당 예외를 복구 하든가 아니면 회피 하든가 등의 어떤 구체적인 처리를 해야 하는 예외
언체크 예외
- 잡아서(catch) 해당 예외에 대한 어떤 처리를 할 필요가 없는 예외
- ex)
NullPointerException,ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException등
코드를 잘못 작성해서 발생하는RuntimeException을 상속한 예외들RuntimeException을 이용해서 일부러 예외(Exception)를 만들어야 할 경우도 있다.
@ResponseStatus = 고정된 Exception(예외)를 처리할 경우에 사용
ResponseEntity = 다양한 유형의 Exception(예외)을 처리하고자 할 경우에 사용
Custom Exception(예외) 만들기
- 예외 상수를 정의
- Custom Exception에 사용할 ExceptionCode를 enum으로 정의
import lombok.Getter;
public enum ExceptionCode { // Custom 예외 정의하기 - 예외 멘트(상수) 정의
MEMBER_NOT_FOUND(404, "Member Not Found");
@Getter
private int status;
@Getter
private String message;
ExceptionCode(int status, String message) {
this.status = status;
this.message = message;
}
}
- Custom Exception 정의
import lombok.Getter;
public class BusinessLogicException extends RuntimeException{ // Custom Exception 정의
@Getter
private ExceptionCode exceptionCode;
public BusinessLogicException(ExceptionCode exceptionCode) {
super(exceptionCode.getMessage());
this.exceptionCode = exceptionCode;
}
}
이렇게 만든 Custom Exception을 아래와 같이 사용하면 된다.
@Service
public class MemberService {
~~~
public Member findMember(long memberId) {
~~~
if(a==0 ~~~)
throw new BusinessLogicException(ExceptionCode.MEMBER_NOT_FOUND);
}
}@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionAdvice {
~~~
@ExceptionHandler
public ResponseEntity handleBusinessLogicException(BusinessLogicException e) {
return new ResponseEntity(HttpStatus.valueOf(e.getExceptionCode().getStatus()));
}
}실습
ExceptionCode 클래스
- 커스텀 예외 상수 정의
import lombok.Getter;
public enum ExceptionCode {
MEMBER_NOT_FOUND(404, "Member Not Found"),
METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED(405, "Method Not Allowed"),
INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR(500, "Internal Server Error");
@Getter
private int status;
@Getter
private String message;
ExceptionCode(int code, String message) {
this.status = code;
this.message = message;
}
}
BusinessLogicException 클래스
- 커스텀 예외 정의
import lombok.Getter;
public class BusinessLogicException extends RuntimeException {
@Getter
private ExceptionCode exceptionCode;
public BusinessLogicException(ExceptionCode exceptionCode) {
super(exceptionCode.getMessage());
this.exceptionCode = exceptionCode;
}
}
ErrorResponse 클래스
- 예외별 응답을 간략화하는 클래스
@Getter
public class ErrorResponse {
private List<FieldError> fieldErrors;
private List<ConstraintViolationError> violationErrors;
private ServiceError serviceErrors;
private MethodNotAllowed methodErrors;
private ExceptionError exceptionError;
public ErrorResponse(List<FieldError> fieldErrors, List<ConstraintViolationError> violationErrors, ServiceError serviceErrors) {
this.fieldErrors = fieldErrors;
this.violationErrors = violationErrors;
this.serviceErrors = serviceErrors;
}
// public ErrorResponse(List<FieldError> fieldErrors, List<ConstraintViolationError> violationErrors, List<MethodNotAllowed> methodErrors) {
// this.fieldErrors = fieldErrors;
// this.violationErrors = violationErrors;
// this.methodErrors = methodErrors;
// } // 생성자 매개변수 갯수 똑같이 오버로딩하면 안됨
public ErrorResponse(List<FieldError> fieldErrors, List<ConstraintViolationError> violationErrors, ServiceError serviceErrors, MethodNotAllowed methodErrors) {
this.fieldErrors = fieldErrors;
this.violationErrors = violationErrors;
this.serviceErrors = serviceErrors;
this.methodErrors = methodErrors;
}
public ErrorResponse(List<FieldError> fieldErrors, List<ConstraintViolationError> violationErrors, ServiceError serviceErrors, MethodNotAllowed methodErrors, ExceptionError exceptionError) {
this.fieldErrors = fieldErrors;
this.violationErrors = violationErrors;
this.serviceErrors = serviceErrors;
this.methodErrors = methodErrors;
this.exceptionError = exceptionError;
}
public static ErrorResponse of(BindingResult bindingResult) {
return new ErrorResponse(FieldError.of1(bindingResult), null, null);
}
public static ErrorResponse of(Set<ConstraintViolation<?>> violations) {
return new ErrorResponse(null, ConstraintViolationError.of2(violations), null);
}
public static ErrorResponse of(ExceptionCode exceptionCode){
// return new ErrorResponse(null, null, new ArrayList<>((Collection) new ServiceError(exceptionCode.getStatus(), exceptionCode.getMessage())));
return new ErrorResponse(null, null, ServiceError.of3(exceptionCode));
}
public static ErrorResponse of(HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException e){
return new ErrorResponse(null, null, null, MethodNotAllowed.of4(e));
}
public static ErrorResponse of(Exception e){
return new ErrorResponse(null, null, null, null, ExceptionError.of5(e));
}
@Getter
private static class FieldError {
private String field;
private Object rejectedValue;
private String reason;
private FieldError(String field, Object rejectedValue, String reason) {
this.field = field;
this.rejectedValue = rejectedValue;
this.reason = reason;
}
private static List<FieldError> of1(BindingResult bindingResult) {
final List<org.springframework.validation.FieldError> fieldErrors =
bindingResult.getFieldErrors();
return fieldErrors.stream()
.map(error -> new FieldError(
error.getField(),
error.getRejectedValue() == null ?
"" : error.getRejectedValue().toString(),
error.getDefaultMessage()))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}
@Getter
private static class ConstraintViolationError {
private String propertyPath;
private Object rejectedValue;
private String reason;
private ConstraintViolationError(String propertyPath, Object rejectedValue,
String reason) {
this.propertyPath = propertyPath;
this.rejectedValue = rejectedValue;
this.reason = reason;
}
private static List<ConstraintViolationError> of2(
Set<ConstraintViolation<?>> constraintViolations) {
return constraintViolations.stream()
.map(constraintViolation -> new ConstraintViolationError(
constraintViolation.getPropertyPath().toString(),
constraintViolation.getInvalidValue().toString(),
constraintViolation.getMessage()
)).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}
@Getter
private static class ServiceError{
private int status;
private String message;
public ServiceError(int status, String message) {
this.status = status;
this.message = message;
}
private static ServiceError of3(ExceptionCode exceptionCode){
return new ServiceError(exceptionCode.getStatus(), exceptionCode.getMessage());
}
}
@Getter
private static class MethodNotAllowed{
private int status;
private String message;
public MethodNotAllowed(int status, String message) {
this.status = status;
this.message = message;
}
private static MethodNotAllowed of4(HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException e){
return new MethodNotAllowed(ExceptionCode.METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED.getStatus(), ExceptionCode.METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED.getMessage());
}
}
@Getter
private static class ExceptionError{
private int status;
private String message;
public ExceptionError(int status, String message) {
this.status = status;
this.message = message;
}
private static ExceptionError of5(Exception e){
return new ExceptionError(ExceptionCode.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.getStatus(), ExceptionCode.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.getMessage());
}
}
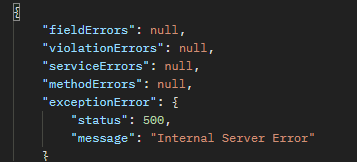
}아래 캡쳐본과 같이 발생하지 않은 예외도 확인가능하게 하려고 위와 같이 코드를 작성했지만 새로운 타입의 예외가 추가됨에 따라 생성자, 메서드, 멤버클래스 등 추가되는 코드의 양이 너무 많아진다.
멤버클래스를 사용하지 않으면 더 간단하게 메소드만으로 구현가능할 것 같다.
GlobalExceptionAdvice 클래스
- 예외별 응답을 클라이언트에 보내주는 클래스
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionAdvice {
@ExceptionHandler
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
public ErrorResponse handleMethodArgumentNotValidException(
MethodArgumentNotValidException e) {
final ErrorResponse response = ErrorResponse.of(e.getBindingResult());
return response;
}
@ExceptionHandler
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
public ErrorResponse handleConstraintViolationException(
ConstraintViolationException e) {
final ErrorResponse response = ErrorResponse.of(e.getConstraintViolations());
return response;
}
@ExceptionHandler
public ResponseEntity handleBusinessLogicException(BusinessLogicException e) {
System.out.println(e.getExceptionCode().getStatus());
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
final ErrorResponse response = ErrorResponse.of(e.getExceptionCode());
return new ResponseEntity<>(response, HttpStatus.valueOf(e.getExceptionCode().getStatus()));
}
@ExceptionHandler
public ResponseEntity handleHttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException(HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException e){
final ErrorResponse response = ErrorResponse.of(e);
return new ResponseEntity(response, HttpStatus.METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED);
}
@ExceptionHandler
public ResponseEntity handleException(Exception e){
final ErrorResponse response = ErrorResponse.of(e);
return new ResponseEntity(response, HttpStatus.METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED);
}
}
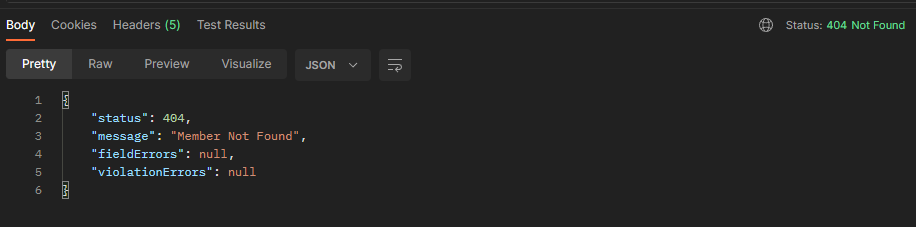
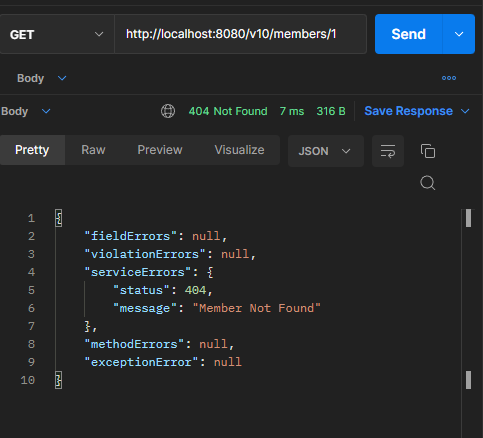
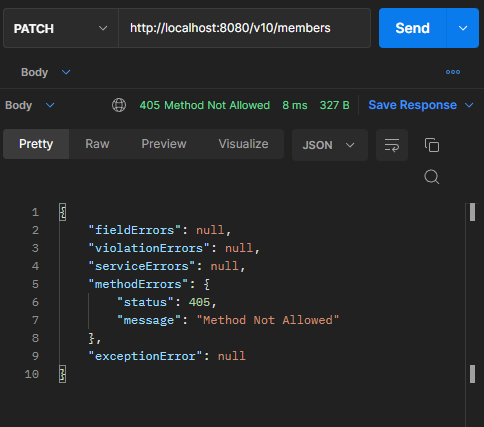
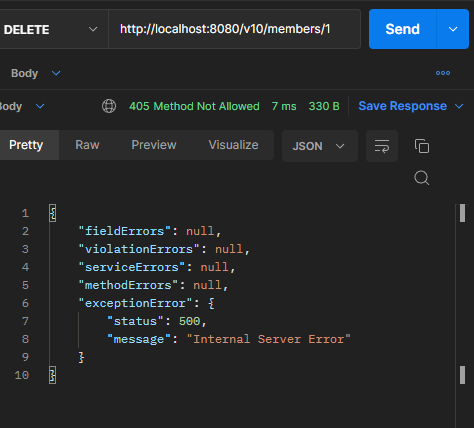
결과
없는 멤버요소를 찾으려 할 때
잘못된 형식의 요청을 보낼 때
- HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException 예외
서버 코드 오류일 떄
NullpointerException과 같은Exception예외들
이후에도 아래와 같은 과정을 통해 최적화(?)를 해봤다.
- 필요없는 생성자 삭제
- 일부 null응답하는 예외 클라이언트에서 안보이게하기
최적화(?) 코드는 링크를 참조
(풀코드는 아래 빨간 박스안에 있는 3가지 버전에서 확인 가능)
최적화(?)를 통해 아래 캡쳐본과 같이 클라이언트에서 나오는 출력을 바꿔봤다.