오버라이딩과 다형성
메서드 오버라이딩(overridind)
- 상위 클래스에 정의된 메서드 중 하위 클래스와 기능이 맞지 않거나 추가 기능이 필요한 경우에 같은 이름과 매개변수로 하위 클래스에서 재정의 하는 것
Customer 클래스(상위 클래스)와 VIPCustomer 클래스(하위 클래스)에 가격을 매개변수로 받는 calcPrice() 메서드를 이름은 동일하지만 return 값은 다르게 추가하여 확인해보겠다.
public class Customer {
public int calcPrice(int price) {
bonusPoint += price * bonusRatio;
return price;
}
}public class VIPCustomer extends Customer{
public int calcPrice(int price) {
bonusPoint += price * bonusRatio;
return price - (int)(price * saleRatio);
}
}main 함수에서 Customer 객체와 VIPCustomer 객체를 생성하여 출력해보면 calcPrice 메서드는 overriding 되어 VIPCustomer 클래스의 calcPrice 메서드가 적용된다.
public class OverridingTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
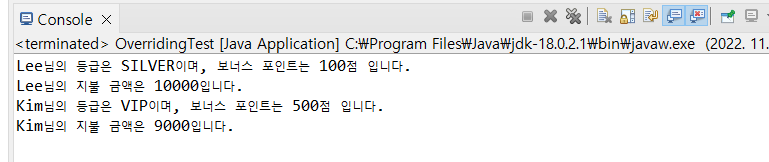
Customer customerLee = new Customer(100010, "Lee");
int price = customerLee.calcPrice(10000);
customerLee.showCustomerInfo();
System.out.println(customerLee.getCustomerName() + "님의 지불 금액은 " + price1 + "입니다.");
VIPCustomer customerKim = new VIPCustomer(100020, "Kim", 100);
price = customerKim.calcPrice(10000);
customerKim.showCustomerInfo();
System.out.println(customerKim.getCustomerName() + "님의 지불 금액은 " + price2 + "입니다.");
}
}
전체코드
Customer 클래스
package inheritance;
public class Customer {
protected int customerID; // protected = 상속 관계에서만 public으로 보이게 해주는 기능
protected String customerName;
protected String customerGrade;
int bonusPoint;
protected double bonusRatio;
/*public Customer() {
customerGrade = "SILVER";
bonusRatio = 0.01;
}*/
public Customer(int customerID, String customerName) {
this.customerID = customerID;
this.customerName = customerName;
customerGrade = "SILVER";
bonusRatio = 0.01;
}
public int calcPrice(int price) {
bonusPoint += price * bonusRatio;
return price;
}
public void showCustomerInfo() {
System.out.println(/*"지불 금액은 " + price + "원이고, " +*/ customerName + "님의 등급은 " + customerGrade + "이며, 보너스 포인트는 " + bonusPoint + "점 입니다.");
}
public int getCustomerID() {
return customerID;
}
public int getBonusPoint() {
return bonusPoint;
}
public void setBonusPoint(int bonusPoint) {
this.bonusPoint = bonusPoint;
}
public void setCustomerID(int customerID) {
this.customerID = customerID;
}
public String getCustomerName() {
return customerName;
}
public void setCustomerName(String customerName) {
this.customerName = customerName;
}
public String getCustomerGrade() {
return customerGrade;
}
public void setCustomerGrade(String customerGrade) {
this.customerGrade = customerGrade;
}
}VIPCustomer 클래스
package inheritance;
public class VIPCustomer extends Customer{
private int agentID;
private double saleRatio;
/*public VIPCustomer() {
customerGrade = "VIP";
bonusRatio = 0.05;
saleRatio = 0.1;
}*/
public VIPCustomer(int customerID, String customerName, int agentID) {
super(customerID,customerName);
customerGrade = "VIP";
saleRatio = 0.1;
this.agentID = agentID;
bonusRatio = 0.05 ;
}
public int calcPrice(int price) {
bonusPoint += price * bonusRatio;
return price - (int)(price*saleRatio);
}
public int getAgentID() {
return agentID;
}
}main 클래스
package inheritance;
public class OverridingTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Customer customerLee = new Customer(100010, "Lee");
int price = customerLee.calcPrice(10000);
customerLee.showCustomerInfo();
System.out.println(customerLee.getCustomerName() + "님의 지불 금액은 " + price + "입니다.");
VIPCustomer customerKim = new VIPCustomer(100020, "Kim", 100);
price = customerKim.calcPrice(10000);
customerKim.showCustomerInfo();
System.out.println(customerKim.getCustomerName() + "님의 지불 금액은 " + price + "입니다.");
}
}
응용
지불금액도 showCustomerInfo안에 넣어주고 싶은데 자꾸 오류가 남.
showCustomerInfo 출력문에 price를 넣어주면 showCustomerInfo가 Customer class에 있다 보니 main에서 계산된 price를 인식 못함..
bonusPoint도 같은 케이스 같은데 왜 bonusPoint되고 price는 안될까...모르겠음.
showCustomerInfo와 calcPric를 합치면 될 것 같긴한데...
각 메서드를 분리해두고 할 수 없을지 궁금함.
후에 더 고민해보기로...
- 오버라이딩으로 showinfo를 바꿔버리면 되지 않나?(근데 그럼 조삼모사..)
[리마인드] 형 변환
package inheritance;
public class OverridingTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
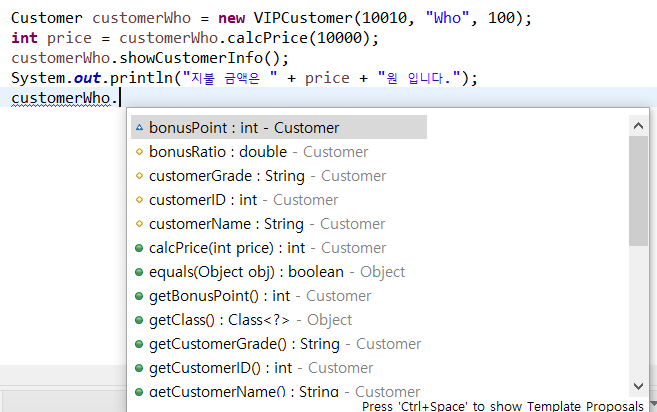
Customer customerWho = new VIPCustomer(10010, "Who", 100);
int price = customerWho.calcPrice(10000);
customerWho.showCustomerInfo();
System.out.println("지불 금액은 " + price + "원 입니다.");
}
}
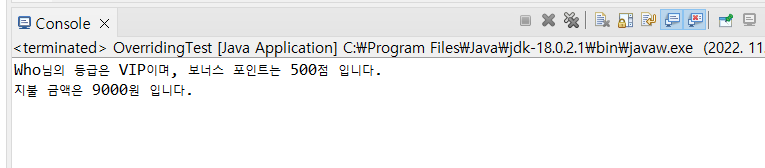
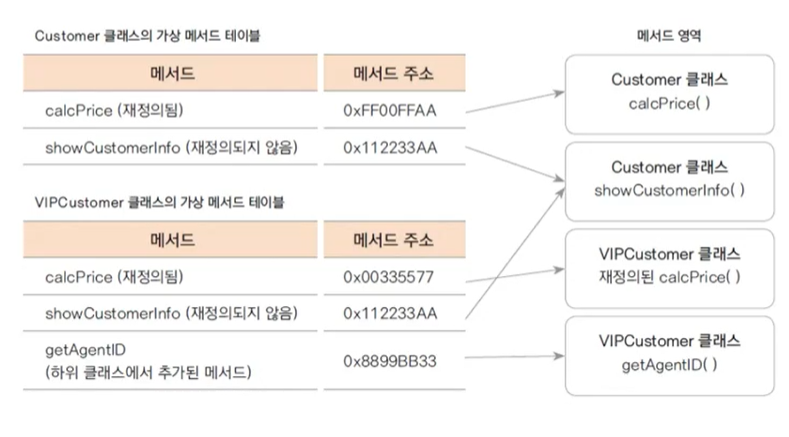
VIPCustomer() 생성자의 호출로 인스턴스는 모두 생성 되었지만
타입이 Customer이므로 접근 할 수 있는 변수나 메서드는 Customer의 변수와 메서드 임.
여기서 calcPrice를 참조했는데 불리는건 인스턴스께 불렸다. (=가상함수)
가상 메서드 (virtual method)
가상 메서드의 원리 =
프로그램에서 어떤 객체의 변수나 메서드의 참조는 그 타입에 따라 이루어짐
(가상 메서드의 경우는 타입과 상관없이 실제 생성된 인스턴스의 메서드가 호출되는 원리)
tip. JAVA에서는 모든 메서드가 가상 메서드다. (C++같은 곳에서는 가상 메서드 구분 해줘야함)
다형성 (polymorphism)
- 하나의 코드가 여러가지 자료형으로 구현되어 실행되는 것
- 정보은닉, 상속과 더불어 객체지향 프로그래밍의 가장 큰 특징 중 하나
- 객체지향 프로그래밍의 유연성, 재활용성, 유지보수성에 기본이 되는 특징임
다향성 구현하기
하나의 클래스를 상속 받은 여러 클래스가 있는 경우
각 클래스마다 같은 이름의 서로 다른 메서드를 재정의 함
상위 클래스 타입으로 선언된 하나의 변수가 여러 인스턴스에 대입되어 다양한 구현이 실행될 수 있음
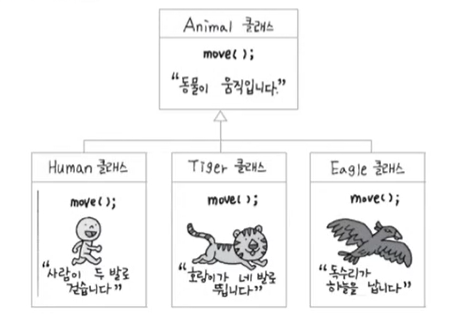
동일한 메서드를 호출하지만 다양한 구현을 가질 수 있다.
class Animal{
public void move() {
System.out.println("동물이 움직입니다.");
}
}
class Human extends Animal{
public void move() {
System.out.println("사람이 두발로 걷습니다.");
}
}
class Tiger extends Animal{
public void move() {
System.out.println("호랑이가 네발로 뜁니다.");
}
}
class Eagle extends Animal{
public void move() {
System.out.println("독수리가 하늘을 납니다.");
}
}
public class AnimalTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnimalTest test = new AnimalTest();
test.moveAnimal(new Human());
test.moveAnimal(new Tiger());
test.moveAnimal(new Eagle());
// Animal animal = new Human(); << 이거나 아래 moveAnimal(Animal animal)이나 똑같은거
}
public void moveAnimal(Animal animal) {
animal.move();
}
}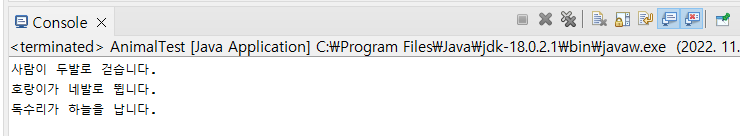
위 코드는 Animal 클래스를 상속받는 Human, Tiger, Eagle 클래스를 만들고
각각 move() 메서드를 통해 다른 메시지를 출력하도록 overriding 한 것이다.
Test 클래스에서는 moveAnimal() 메서드에서 animal(매개변수)를 받으면 해당 객체의 move() 메서드를 호출하게 만들었고, main 함수에서 각각 Human, Tiger, Eagle 인스턴스를 생성하여 매개변수로 moveAnimal(Animal animal)에 넣어주었다.
moveAnimal() 메서드에서는 animal.move(); 라는 코드 한 줄이 쓰여있지만 실제 구현될 때는 여러 결과가 나타나게 되고, 이것을 다형성이라고 한다.
다형성 활용하기
- 일반 고객과 VIP 고객의 중간 등급(Gold)의 고객을 생성
- 5명의 고객을 ArrayList에 생성하여 저장한 다음 (이건 다음시간에 이어서)
- 각 고객이 물건을 샀을 때의 가격과 보너스 포인트를 계산함
일단, GoldCustomer 클래스를 생성하여 Customer 클래스를 상속받도록 만들어준다.
public class GoldCustomer extends Customer{
public GoldCustomer(int customerID, String customerName) {
super(customerID, customerName);
customerGrade = "Gold";
bonusRatio = 0.05;
}
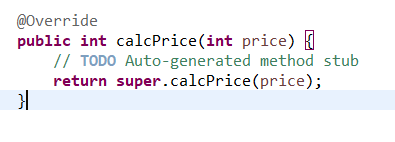
@Override
public int calcPrice(int price) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return super.calcPrice(price);
}
// 골드 등급의 지불 금액 해택은 없다고 설정했으니 바꿀게 없고 오버라이딩할 필요도 없다.
// 다만 이렇게 골드 등급의 지불 금액을 변경할 수 있다는 것을 나타내기 위해 쓴 거
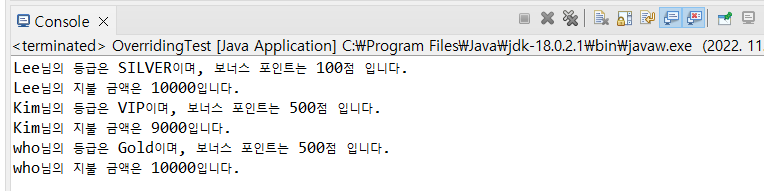
}main 함수가 있는 Test 클래스에서는 다형성을 활용하기 위해 InfoAndPrice() 메서드를 만들고 Customer 객체를 매개변수로 받는다.
public class OverridingTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
OverridingTest test = new OverridingTest();
test.InfoAndPrice(new Customer(1001, "Lee"));
test.InfoAndPrice(new VIPCustomer(1002, "Kim", 100));
test.InfoAndPrice(new GoldCustomer(1003, "who"));
}
public void InfoAndPrice(Customer customer) {
int price = customer.calcPrice(10000);
customer.showCustomerInfo();
System.out.println(customer.getCustomerName() + "님의 지불 금액은 " + price + "입니다.");
}
}main함수에서 Customer, VIPCustomer, GoldCustomer 객체로 InfoAndPrice() 메서드를 호출하면 결과가 각각 출력된다. (하나의 메서드로 3개 구현)
overriding 편하게 하는 방법
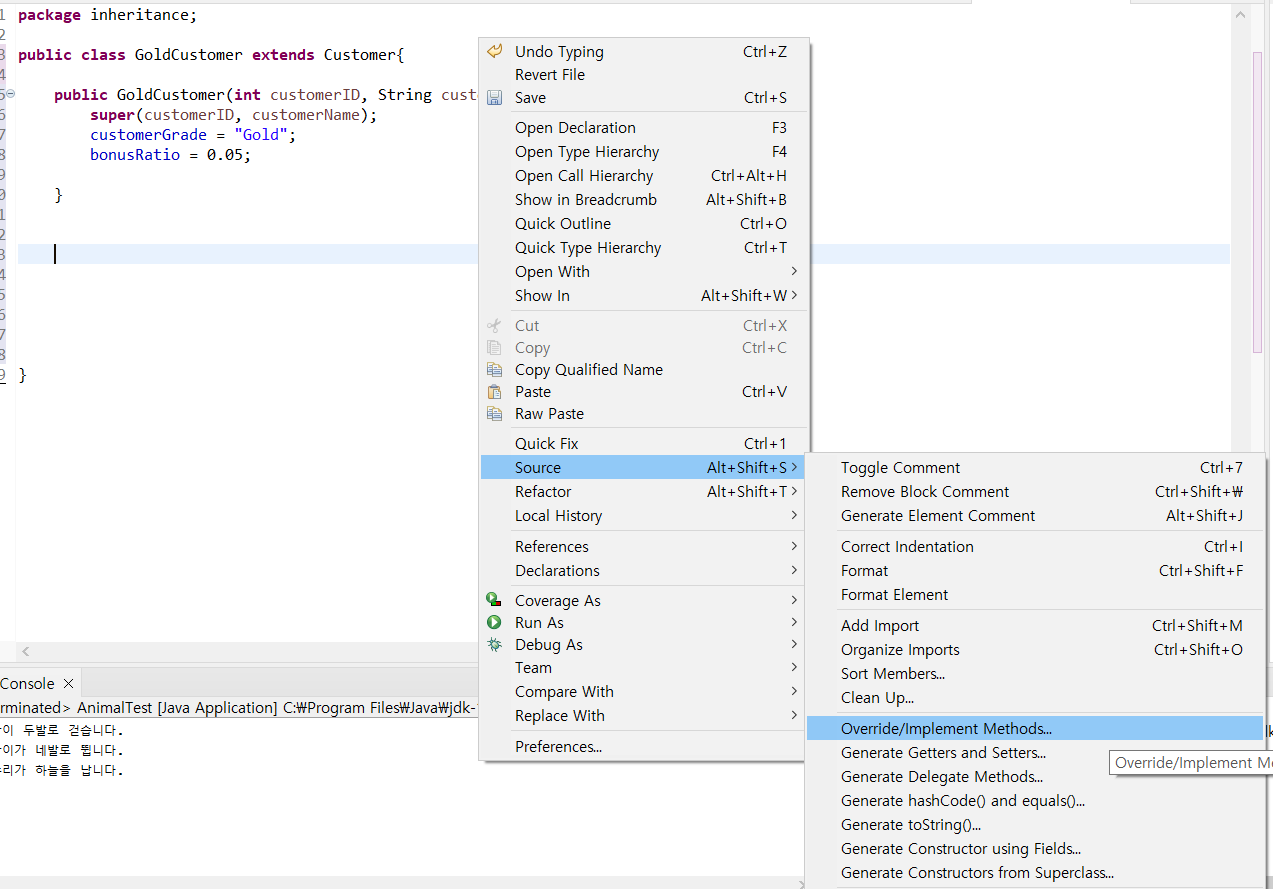
우클릭 -> Source -> Override/Implement Methods
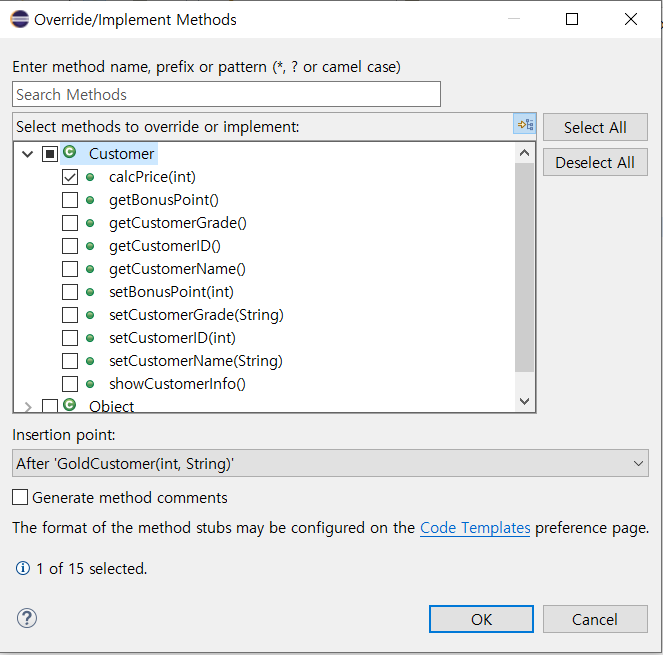
overriding할 메서드 선택