1. 단체 채팅 서버 구현
1. 구현 방안
1. 구현 조건
- 채팅 클라이언트는 nc 로 대신
- 서버 프로그램 실행 후 클라이언트 접속
- 클라이언트가 접속 시 서버는 Welcome 메시지 전송
- 한 클라이언트에서 메시지 전송 시 다른 클라이언트 모두 출력
2. 구현 팁
- 서버는 각 클라이언트가 접속 시 해당 정보를 배열에 저장
- select() 함수를 사용하여 여러개의 소켓을 감시
- 하나의 소켓에서 입력이 들어오면 클라이언트 배열에 저장된 다른 소켓으로 그 내용을 그대로 출력
2. 구현
1. chatsrv.c
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <netdb.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define BUFSIZE 100
void error_handling(char *message);
void CutTokens(char* str);
void display();
void Forward(char *str, int sender) ;
int GetEmptySlot();
char tokens[3][100];
#define MAXCLIENT (16)
int peertcpSocket[MAXCLIENT];
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
int tcpServ_sock;
int slot;
struct sockaddr_in tcpServer_addr;
struct sockaddr_in tcpClient_addr;
struct sockaddr_in newTcp_addr;
for(int i = 0; i < MAXCLIENT; i++) {
peertcpSocket[i] = -1;;
}
socklen_t clnt_len;
fd_set reads, temps;
int fd_max;
char *tcpport = NULL;
char str[BUFSIZE];
int option = 2;
if(argc != 2) {
printf("Usage : %s <tcpport> \n", argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
tcpport = argv[1];
display();
tcpServ_sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if(tcpServ_sock == -1)
error_handling("socket() error");
memset(&tcpServer_addr, 0 , sizeof(tcpServer_addr));
tcpServer_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
tcpServer_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
tcpServer_addr.sin_port = htons(atoi(tcpport));
setsockopt(tcpServ_sock, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, (const void *)&option, sizeof(int));
setsockopt(tcpServ_sock, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEPORT, (const void *)&option, sizeof(int));
if( bind(tcpServ_sock, (struct sockaddr *) &tcpServer_addr, sizeof(tcpServer_addr)) == -1 )
error_handling("bind() error");
if(listen(tcpServ_sock, 5)==-1)
error_handling("listen() error");
FD_ZERO(&reads);
FD_SET(tcpServ_sock, &reads);
fd_max = tcpServ_sock;
while(1) {
int nfound = 0;
temps = reads;
nfound = select(fd_max+1, &temps, 0, 0, NULL);
if(FD_ISSET(tcpServ_sock, &temps)) {
FD_CLR(tcpServ_sock, &temps);
clnt_len = sizeof(newTcp_addr);
slot = GetEmptySlot();
peertcpSocket[slot] = accept(tcpServ_sock,
(struct sockaddr *)&newTcp_addr, &clnt_len);
printf("connection from host %s, port %d, socket %d slot %d\n",
inet_ntoa(newTcp_addr.sin_addr),
ntohs(newTcp_addr.sin_port), peertcpSocket[slot], slot);
sprintf(str, "Welcome: host %s, port %d\n",
inet_ntoa(newTcp_addr.sin_addr), ntohs(newTcp_addr.sin_port));
write(peertcpSocket[slot], str, strlen(str));
FD_SET(peertcpSocket[slot], &reads);
if(fd_max < peertcpSocket[slot])
fd_max = peertcpSocket[slot];
} else {
for(int i = 0; i < MAXCLIENT; i++) {
if (FD_ISSET(peertcpSocket[i], &temps)) {
FD_CLR(peertcpSocket[i], &temps);
int bytesread = read(peertcpSocket[i], str, sizeof str - 1);
if (bytesread<0) {
perror("read");
}
if (bytesread <= 0) {
printf("Connection Closed %d slot %d\n",
peertcpSocket[i], i);
FD_CLR(peertcpSocket[i], &reads);
if (close(peertcpSocket[i])) perror("close");
peertcpSocket[i] = -1;
continue;
}
str[bytesread] = 0;
Forward(str, i);
}
}
}
}
}
void display() {
printf("Student ID : 01048028464 \n");
printf("Name : w10sim \n");
}
void error_handling(char *message) {
fputs(message, stderr);
fputc('\n', stderr);
perror("hi");
exit(1);
}
void CutTokens(char* str) {
char *pch;
int cnt = 0;
pch = strtok(str, " \r\n\t");
while(pch != NULL) {
strcpy(tokens[cnt++], pch);
pch = strtok(NULL, " ");
}
}
void Forward(char *str, int sender) {
for(int i = 0; i < MAXCLIENT; i++) {
if((peertcpSocket[i] != -1) && (i != sender)) {
write(peertcpSocket[i], str, strlen(str));
}
}
}
int GetEmptySlot() {
for(int i = 0; i < MAXCLIENT; i++) {
if(peertcpSocket[i] == -1) return i;
}
return -1;
}
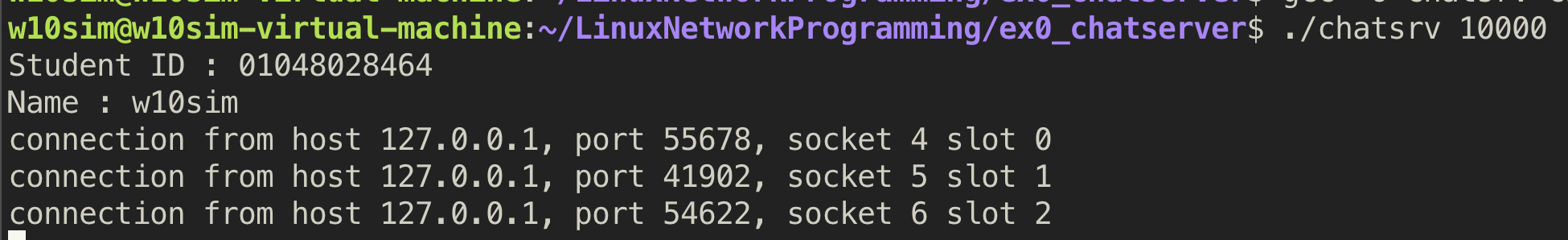
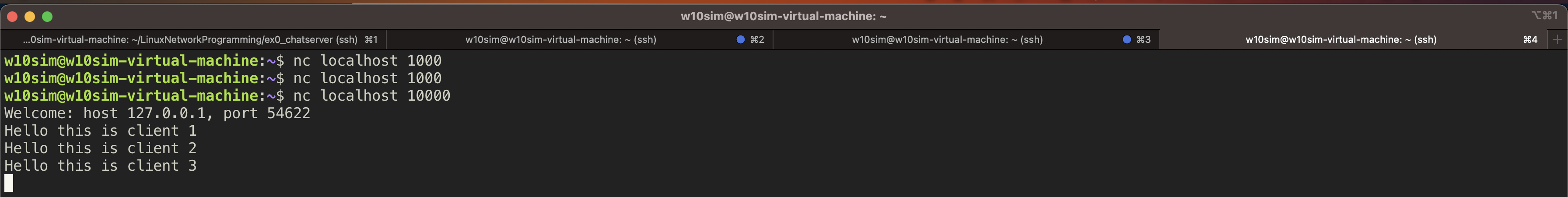
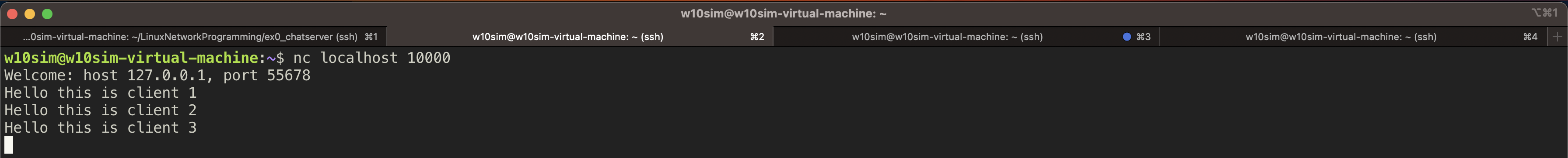
2. 동작 모습


2. 파일 서버 구현
1. 구현 방안
1. 구현 조건
- 파일 클라이언트는 nc로 대신
- 서버 프로그램 실행 후 클라이언트 접속
2. 기능
- 특정 확장자를 가진 파일 목록 다운로드
- 주어진 이름의 파일 다운로드
- 파일 업로드
2. 구현
1. filesrv.c
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <netdb.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <dirent.h>
int portnum = 0;
void SendFile(int new_sock, char *fname) {
char buf[BUFSIZ];
char msg[1024];
struct stat infobuf;
if ( stat(fname, &infobuf) == -1 ) {
printf("Server Error : No such file %s!\n", fname);
sprintf(msg, "FILE NOT FOUND\r\n");
infobuf.st_size = -1;
if (write(new_sock, msg, strlen(msg))!=strlen(msg))
perror("echo error");
} else {
if(infobuf.st_size != -1) {
int s = 0;
int num = 0;
FILE *fp1 = fopen(fname, "r");
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
while((num = fread( buf, sizeof( char ), BUFSIZ - 1, fp1 )) > 0) {
s += num;
if (write(new_sock, buf, num)!= num)
perror("send file error");
}
fclose(fp1);
printf("finish %d %d\n", s, (int)infobuf.st_size);
}
}
}
void SendDir(int new_sock, char *ext) {
char buf[BUFSIZ];
DIR *folder;
struct dirent *entry;
int num = 0;
int fcnt = 0;
folder = opendir(".");
if(folder == NULL) {
perror("Unable to read directory");
return;
}
while( (entry = readdir(folder)) ) {
char *p = strrchr(entry->d_name, '.');
if(p == NULL)
continue;
if (strcmp(p + 1, ext) != 0)
continue;
sprintf(buf, "%s\n", entry->d_name);
num = strlen(buf);
if (write(new_sock, buf, num) != num) {
perror("send ls error");
}
fcnt++;
}
if (fcnt == 0) {
sprintf(buf, "FILE NOT FOUND\r\n");
num = strlen(buf);
if (write(new_sock, buf, num) != num) {
perror("send ls error");
}
}
closedir(folder);
}
void StoreFile(FILE *fp, char *fname) {
char buf[BUFSIZ];
int num = 0;
FILE *fp1 = fopen(fname, "w");
printf("fopen %s\n", fname);
if (fp1 == NULL) {
printf("fopen error for %s\n", fname);
return;
}
while((num = fread( buf, sizeof( char ), BUFSIZ - 1, fp )) > 0) {
buf[num] = 0;
printf("%s\n", buf);
if (fwrite(buf, sizeof(char), num, fp1) != num) {
printf("write error %d\n", num);
fclose(fp1);
return;
}
}
fclose(fp1);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
struct sockaddr_in server, remote;
int request_sock, new_sock;
socklen_t addrlen;
char buf[BUFSIZ];
if (argc != 2) {
(void) fprintf(stderr,"usage: %s portnum \n",argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
portnum = atoi(argv[1]);
if ((request_sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP)) < 0) {
perror("socket create error");
exit(1);
}
printf("Student ID : 01048028464\n");
printf("Name : w10sim\n");
memset((void *) &server, 0, sizeof server);
server.sin_family = AF_INET;
server.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY;
server.sin_port = htons((u_short)portnum);
if (bind(request_sock, (struct sockaddr *)&server, sizeof server) < 0) {
perror("bind error");
exit(1);
}
if (listen(request_sock, SOMAXCONN) < 0) {
perror("listen error");
exit(1);
}
while(1) {
addrlen = sizeof(remote);
fflush(stdout);
new_sock = accept(request_sock,
(struct sockaddr *)&remote, &addrlen);
if (new_sock < 0) {
perror("accept error");
exit(1);
}
printf("Connection : Host IP %s, Port %d, socket %d\n",
inet_ntoa(remote.sin_addr), ntohs(remote.sin_port), new_sock);
FILE *fp = fdopen(new_sock, "r");
buf[0] = 0;
if (!fgets(buf, BUFSIZ - 1, fp)) {
printf("No Data: close connection");
fclose(fp);
if (close(new_sock)) perror("close error");
continue;
}
printf("%s", buf);
fflush(stdout);
char *command = strtok(buf, " \t\n\r");
char *filename = strtok(NULL, " \t\n\r");
if (strcmp(command, "GET") == 0) {
SendFile(new_sock, filename);
} else if (strcmp(command, "LS") == 0) {
SendDir(new_sock, filename);
} else if (strcmp(command, "PUT") == 0) {
StoreFile(fp, filename);
} else {
printf("Unknown Command %s\n", command);
}
if (close(new_sock))
perror("close error2");
}
}
2. 동작 모습
1. filesrv
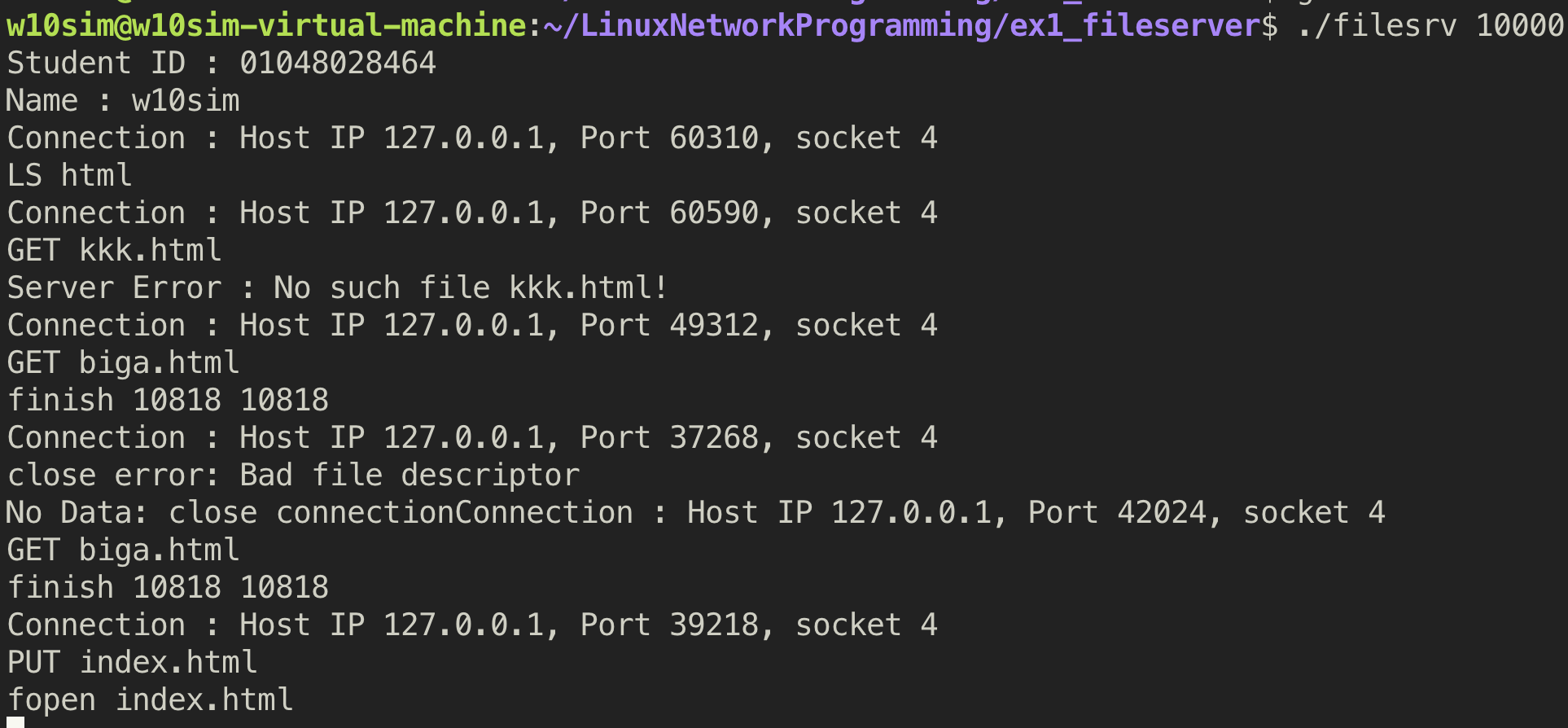
2. LS
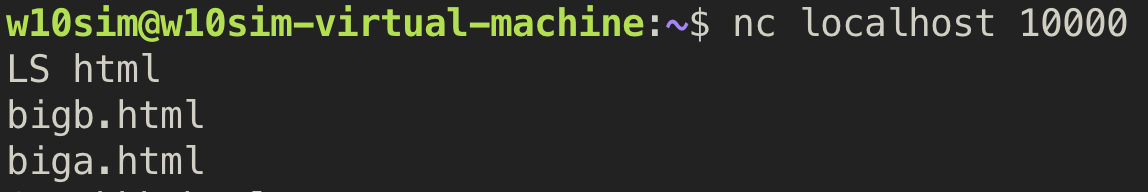
3. GET (not found)
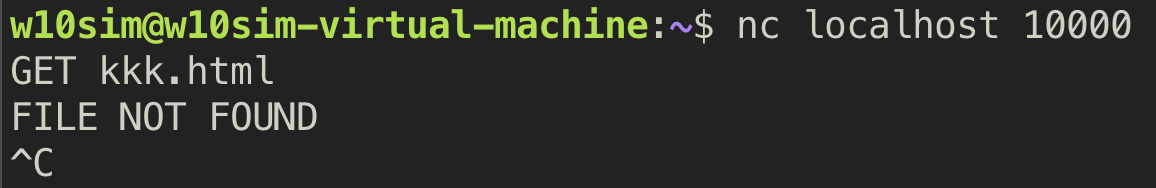
4. GET (found)
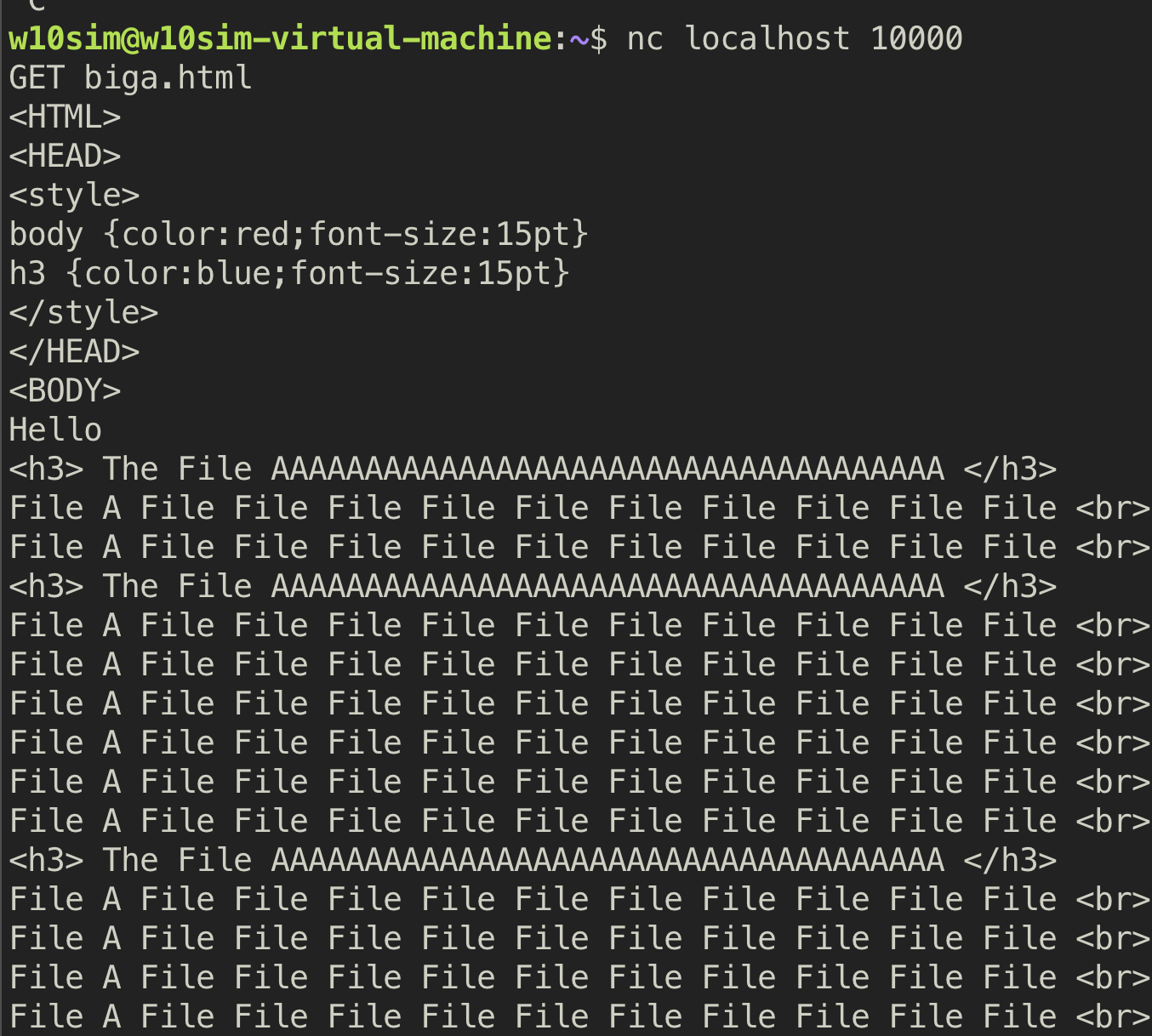
5. GET (redirect server to client)
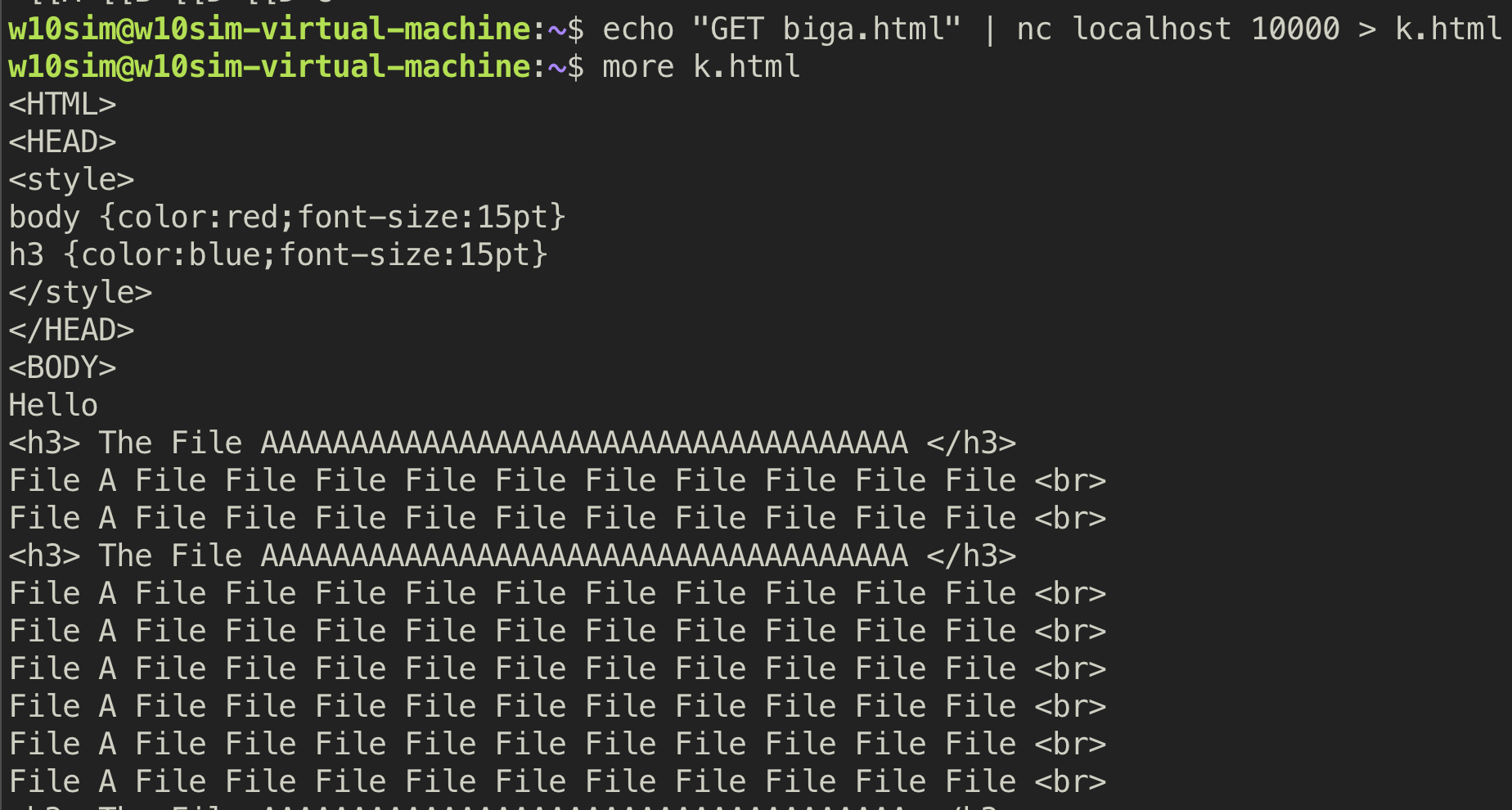
6. PUT (client to server)