Kotlin Coroutine
kotlin은 1.3부터 코루틴을 구현할 수 있도록 언어에서 지원을 하기 시작했다.
'org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-android:$coroutine_version'을 통해 미리 만들어놓은 코루틴을 사용할 수 있다.
CoroutineScope
-
코루틴은 구조화된 동시성(structured concurrency) 를 통해서 CoroutineScope 안에서만 생성되어야 하고 scope은 coroutineContext를 통해 코루틴들을 관리한다.
-
CoroutineScope은 내부 코루틴들의 생명주기를 관리하고 에러사항을 처리해준다.
GlobalScope
- 앱이 실행되는 내내 코루틴을 실행시킬 수 있는 Scope이다.
- GlobalScope 내부 코루틴은 새로운 스레드를 생성해서 실행된다.
- 메인 스레드가 종료되면 코루틴도 종료되기 때문에 코루틴이 다 종료될 때까지 메인 스레드를 살려놔야 한다.
viewModelScope, lifecycleScope
- 각각 ViewModel과 Activity의 생명주기동안 실행
- ViewModel이나 Activity가 종료가 되면 scope이 취소가 되어 코루틴들을 다 종료한다.
CoroutineBuilder
- CoroutineBuilder를 통해서 코루틴을 만들 수 있다.
launch
- CoroutineScope의 확장함수
public fun CoroutineScope.launch(
context: CoroutineContext = EmptyCoroutineContext,
start: CoroutineStart = CoroutineStart.DEFAULT,
block: suspend CoroutineScope.() -> Unit
): Job {
}- Job을 리턴하며 CoroutineScope이 Job을 통해 코루틴을 관리한다.
async
- CoroutineScope의 확장함수
public fun <T> CoroutineScope.async(
context: CoroutineContext = EmptyCoroutineContext,
start: CoroutineStart = CoroutineStart.DEFAULT,
block: suspend CoroutineScope.() -> T
): Deferred<T> {
}- launch와 비슷하지만 Deferred를 리턴한다.
Deferred는 Job을 상속하기 때문에 결국은 Job을 리턴하는 것 - Deferred는 await()를 가지고 있어 코루틴의 종료까지 기다릴 수 있다.
runBlocking
- 일반함수 형태이고 매개변수로 CoroutineScope 수신객체 람다를 가진다.
public fun <T> runBlocking(context: CoroutineContext = EmptyCoroutineContext, block: suspend CoroutineScope.() -> T): T {
}- 코루틴이 다 실행될 때까지 runBlocking을 호출한 스레드를 blocking한다.
- 스레드는 비싼 자원이기 때문에 디버깅용 아니면 호출하지 않는게 좋다.
CoroutineContext
- 코루틴을 관리하기 위해 CoroutineScope이 가지고 있는 context
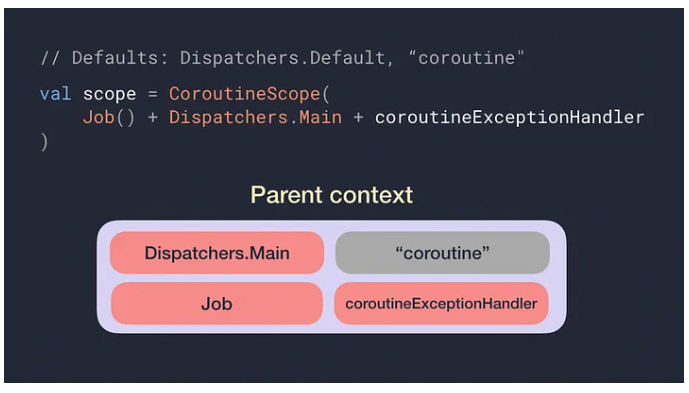
- Dispatcher, Coroutine Name, Job, ExceptionHandler로 구성되어 있다.
- scope.launch(Dispathcer.IO)로 선언한다면 scope의 context는 그대로 쓰되 Dispatcher만 오버라이드해서 사용하는 것
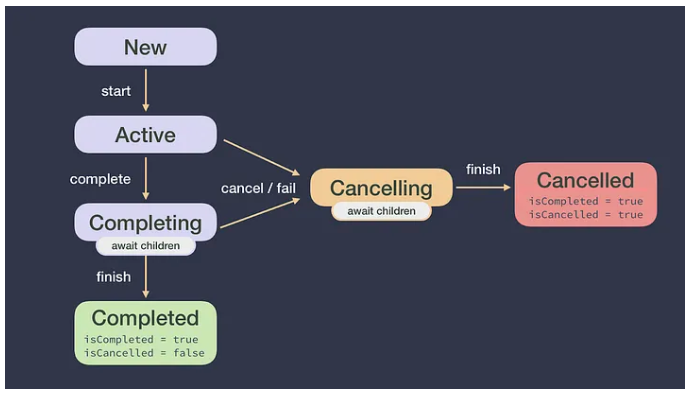
Job
- 코루틴들은 Job을 반환한다.
- CoroutineScope은 Job을 통해 코루틴 관리
- job lifecycle
Dispatcher
- 코루틴을 어떤 스레드나 스레드풀에서 동작시킬 것인지 결정하는 context
- Dispatchers.Main - 메인 스레드에서 작동
- Dispatchers.IO - IO 작업을 위한 스레드풀에서 코루틴 실행
- Dispatchers.Default - CPU 작업이 많이 필요한 경우에 이 스레드풀에서 실행
- Dispatchers.Unconfined - 특정 스레드에 국한되지 않고 스레드 실행
- newSingleThreadContext("MyOwnThread") - 새로운 스레드 만들어서 실행
CoroutineExceptionHandler
- coroutine은 취소될 수 있다.
val job1 = scope.launch { … }
val job2 = scope.launch { … }
scope.cancel()coroutineScope이 취소되면 child 코루틴들도 다 같이 취소가 된다.
val job1 = scope.launch { … }
val job2 = scope.launch { … }
// First coroutine will be cancelled and the other one won’t be affected
job1.cancel()- 하지만 child 코루틴 중 하나가 취소가 되어도 다른 child들은 영향을 받지 않는다.
- 그 이유는 SupervisorJob이기 때문이다.
- 일반 Job이었으면 child 코루틴이 취소가 되면 scope 자신 뿐만 아니라 다른 child들도 다 취소가 되고 scope을 호출한 스레드까지 에러가 전파된다.
- job.join() vs Deffered.await()
- 둘 다 코루틴의 동작이 종료될 때까지 기다린다.
- job.join()은 중간에 cancel되어도 다 완료할 때까지 기다린다.
- Deffered.await() Completed 상태로 종료되어 결과값을 반환해야 하기 때문에 중간에 cacnel이 되면 JobCancellationException 에러가 난다.

