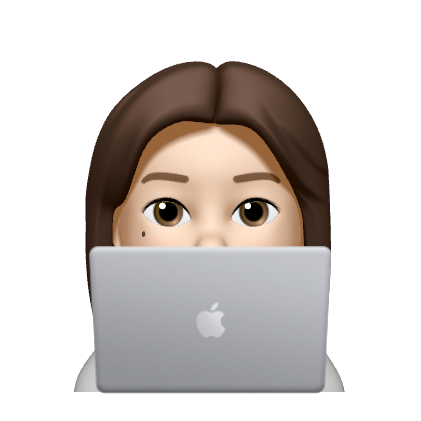
변수의 타입
기본형(Primitive Type)
- 오직 8개
- 실제 값을 저장

각 타입의 변수가 저장할 수 있는 값의 범위
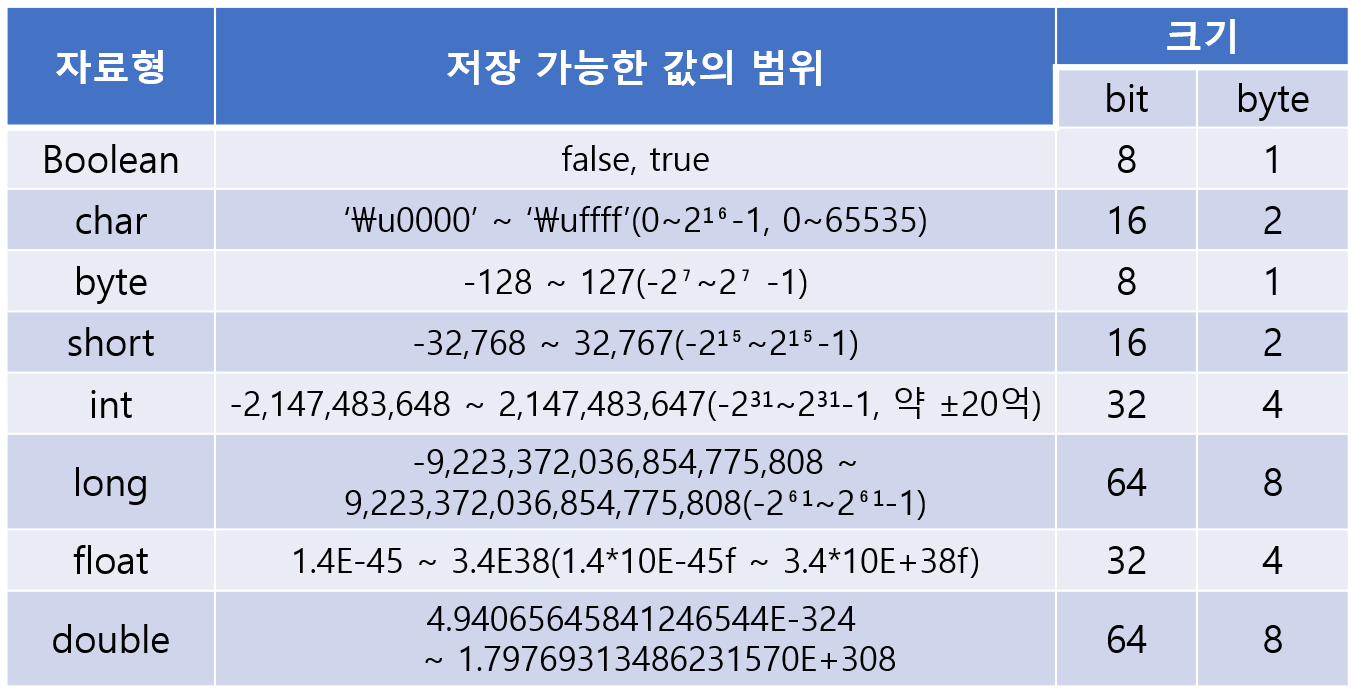
short와 char는 모두 같은 16비트로 약 6만개의 값을 표현할 수 있지만
short는 부호 있는 정수이고 char는 부호 없는 정수이다.
참조형(Reference Type)
- 기본형을 제외한 나머지 (String, System 등)
- 기본형은 8개로 고정되어 있지만, 참조형은 직접 작성이 가능해 개수 제한 없음
- 메모리 주소를 저장 ( 32bit: 4byte, 64bit: 8byte)
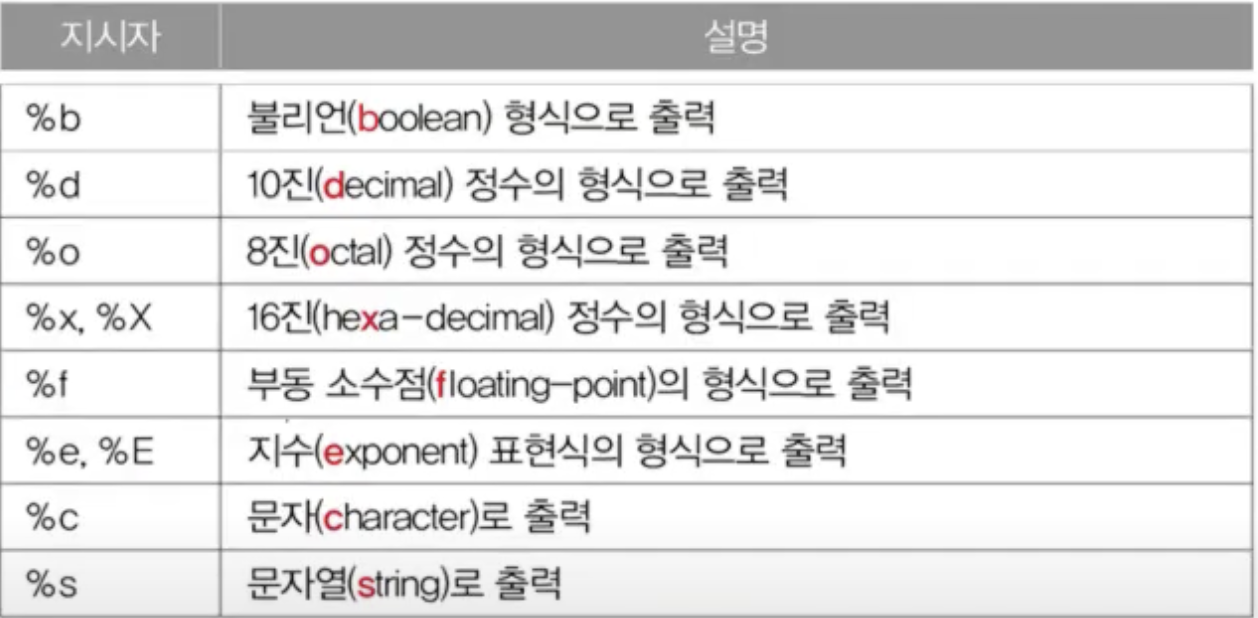
지시자(Specifier)와 변수 출력
-
print: 줄바꿈 없음, () 안 내용을 출력만 함
-
println: ""안의 값을 출력하고 줄바꿈, 출력 형태 지정 불가, 10진수만 출력됨.
public class Ex6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(10/3); //정수 나누기 정수라서 정수 출력
System.out.println(10/3.0);
System.out.println(10.0/3);
System.out.println(10.0/3.0);
//소수점 n자리만 출력하려면?
System.out.println(0x1A); //26
}
}
- printf: 줄바꿈 없음, 텍스트출력형식 지정 가능
(줄 바꿈을 하려면 지시어 %n 또는 \n 추가)
public class Ex6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.printf("%.2f %n", 10.0 / 3); //3.3
System.out.printf("%d %n", 0x1A); //10진수 26
System.out.printf("%X %n", 0x1A); //16진수 1A
System.out.printf("%x %n",15); //f
System.out.printf("%o %n",15); //17
System.out.printf("%s %n",Integer.toBinaryString(15)); //2진수 변환 1111
//8진수와 16진수에 접두사 붙이기
System.out.printf("%#o %n",15); //017
System.out.printf("%#x %n",15); //0xf
System.out.printf("%#X %n",15); //0XF
//실수 출력을 위한 지시자 %f, 지수형식 %e, 간단한 형식 %g
float f = 123.4567890f;
System.out.printf("%f %n",f); //123.456787
System.out.printf("%e %n",f); //1.234568e+02
System.out.printf("%g %n",123.456789); //123.457
System.out.printf("%g %n",0.0000001); //1.00000e-07
}
}
public class Ex6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String url = "https://velog.io/@turningtwenty";
float f1 = .10f;
float f2 = 1e1f;
float f3 = 3.14e3f;
double d = 1.23456789;
System.out.printf("f1 = %f, %e, %g%n", f1,f1,f1);
System.out.printf("f2 = %f, %e, %g%n", f2,f2,f2);
System.out.printf("f3 = %f, %e, %g%n", f3,f3,f3);
System.out.printf("d=%f%n",d); //소수점 아래 6자리만
System.out.printf("d=%14.10f%n", d); //%전체자리.소수점 아래자리
System.out.printf("[%s]%n",url); //문자열의 길이만큼 출력공간 확보
System.out.printf("[%40s]%n",url); //최소40글자 출력공간 확보(우측정렬)
System.out.printf("[%-40s]%n",url); //(좌측정렬)
System.out.printf("[%.12s]%n",url); //왼쪽에서 12글자만 출력
System.out.printf("[%5d]%n",1234567); //7자리 모두 출력
}
}output
f1 = 0.100000, 1.000000e-01, 0.100000
f2 = 10.000000, 1.000000e+01, 10.0000
f3 = 3140.000000, 3.140000e+03, 3140.00
d=1.234568
d= 1.2345678900
[https://velog.io/@turningtwenty]
[ https://velog.io/@turningtwenty]
[https://velog.io/@turningtwenty ]
[https://velo]
[1234567]오버플로우(Overflow)
public class Over {
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte num1 = 127;
System.out.println("num1: " + num1);
num1++;
System.out.println("overflowed num1: " + num1);
byte num2 = -128;
System.out.println("num2: " + num2);
num2--;
System.out.println("overflowed num2: " + num2);
}
}output
num1: 127
overflowed num1: -128
num2: -128
overflowed num2: 127public class Over {
public static void main(String[] args) {
short sMin = -32768, sMax = 32767;
char cMin = 0, cMax = 65535;
System.out.println("sMin = " + sMin);
System.out.println("sMin-1 = " + (short) (sMin - 1));
System.out.println("sMax = " + sMax);
System.out.println("sMax+1 = " + (short) (sMax + 1));
System.out.println("cMin = " + (int) cMin);
System.out.println("cMin-1 = " + (int) --cMin);
System.out.println("cMax = " + (int) cMax);
System.out.println("cMax+1 = " + (int) ++cMax);
}
}output
sMin = -32768
sMin-1 = 32767
sMax = 32767
sMax+1 = -32768
cMin = 0
cMin-1 = 65535
cMax = 65535
cMax+1 = 0즉 최소값에서 1을 빼면 최대값이 되고
최대값에 1을 더하면 최소값이 된다.
문자열 자동 타입변환
public class Ex7_4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 7;
char ch = '1', ch2 = '8';
System.out.printf("7 + '1' = %d%n", num + ch);
System.out.printf("'8' - '1' = %d%n", ch2 - ch);
System.out.printf("숫자 + 빈 문자열: %s%n", 7 + "");
System.out.printf("문자 + 빈 문자열: %s%n", '7' + "");
num = Integer.parseInt("4000"); //문자열에서 int형으로 바꾸는 것
double pi = Double.parseDouble("3.14"); //문자열에서 double형으로 바꾸는 것
System.out.printf("문자열을 정수로 변환: %d%n", num);
System.out.printf("문자열을 실수로 변환: %f%n", pi);
String str = "CHAR";
System.out.printf("첫번째 문자: %c%n", str.charAt(0)); //문자열을 문자로 변환
System.out.printf("세번째 문자: %c%n", str.charAt(2)); //문자열을 문자로 변환
}
}output
7 + '1' = 56
'8' - '1' = 7
숫자 + 빈 문자열: 7
문자 + 빈 문자열: 7
문자열을 정수로 변환: 4000
문자열을 실수로 변환: 3.140000
첫번째 문자: C
세번째 문자: Apublic class Exchange {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int value1 = 3 + 7;
System.out.println(value1);
String str1 = "3" + 7;
System.out.println(str1);
String str2 = 3 + "7";
System.out.println(str2);
int value2 = 1 + 2 + 3;
System.out.println(value2);
String str3 = 1 + 2 + "3";
System.out.println(str3);
String str4 = 1 + "2" + 3;
System.out.println(str4);
String str5 = "1" + 2 + 3;
System.out.println(str5);
}
}output
10
37
37
6
33
123
123public class Exchange {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "3";
System.out.println(str.charAt(0) - '0'); //문자열을 문자로 변환->charAt(0)
System.out.println('3' - '0' + 1); //문자를 숫자로 변환(문자에서 '0' 뺀다
System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("3") + 1); //문자열을 문자로 변환 "3"->'3'
System.out.println("3" + 1);
System.out.println((char)(3 + '0')); //숫자를 문자로 변환(숫자에 '0' 더하기)
}
}output
3
4
4
31
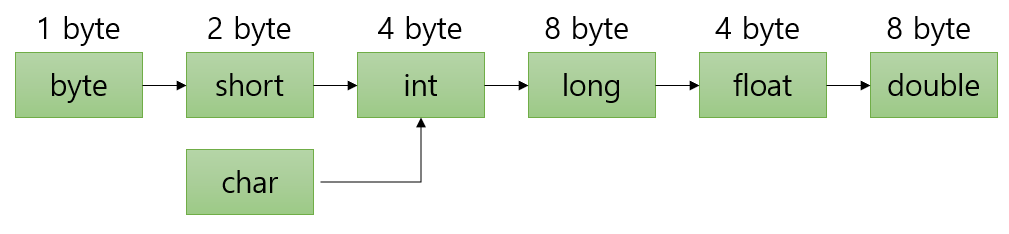
3자동 타입 변환
자바에서는 다음과 같은 방향으로 자동 형변환(Widening Casting)이 이루어진다. ->작은 타입에서 큰 타입으로!
public class Casting {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//작은 byte->큰 int
byte a = 10;
int b = a;
System.out.println("casting result: " + a); //output 10
System.out.println("casting result: " + b); //output 10
int myInt = 9;
double myDouble = myInt; // Automatic casting: int to double
System.out.println("casting result: " + myInt); // Output 9
System.out.println("casting result: " + myDouble); // Output 9.0
//큰 int->작은 byte
// int a = 10;
// byte b = a;
// System.out.println(b);
}
}강제 타입 변환
강제 형변환(Narrowing Casting)은 큰 타입을 작은 타입으로 변환한다.
public class Casting {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double d = 85.4;
int numd = (int)d;
System.out.println(numd); //85
char alpha = 'A';
int numalpha = (int)alpha;
System.out.println(numalpha); //65
int num = 65;
char alphanum = (char)num;
System.out.println(alphanum); //A
double myDouble = 9.78d;
int myInt = (int) myDouble;
System.out.println(myDouble); //9.78
System.out.println(myInt); //9
}
}public class Casting {
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte b = 127;
int i = 100;
System.out.println(b+i); //227
System.out.println(10/4); //2
System.out.println(10.0/4); //2.5
System.out.println((char)0x12340041); //char로 변환하면 0x0041로 문자A
System.out.println((byte)(b+i)); //227은 2진수 0xE3, 즉 -29
System.out.println((int)2.9+1.8); //3.8
System.out.println((int)(2.9+1.8)); //4
System.out.println((int)2.9 + (int)1.8); //3
}
}정수 연산에서 자동 타입 변환
피연산자의 타입이 int보다 작은 타입이면(byte,char,short) int로 변환된다.
public class Casting {
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte x = 10;
byte y = 20;
// byte result = x+y; 컴파일에러
int result = x + y;
System.out.println(result);
}
}아니면 차라리..
public class Casting {
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte result = 10 + 20;
System.out.println(result);
}
}실수 연산에서 자동 타입 변환
피연산자 중 하나가 double타입이라면 다른 피연산자도 double타입으로 자동 타입 변환된다.
public class Casting {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int intval = 10;
double doubleval = 5.5;
double result = intval + doubleval;
System.out.println(result);
}
} 꼭 int타입으로 연산해야겠다면 double을 int로 강제 타입 변환하자.
public class Casting {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int intval = 10;
double doubleval = 5.5;
double result = intval + (int)doubleval;
System.out.println(result);
}
}1/2의 값은 0.5이다. 그러면 다음 코드의 결과값도 0.5일까?
int x = 1;
int y = 2;
double result = x/y;
System.out.println(result);이 경우에는
int x = 1;
int y = 2;
double result = (double)x/y;
System.out.println(result);또는
int x = 1;
int y = 2;
double result = x/(double)y;
System.out.println(result);또는
int x = 1;
int y = 2;
double result = (double)x/(double)y;
System.out.println(result);으로 수정해야한다.
public class Casting {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double avg = 90.5;
int score = (int) avg; //(int)생략 불가능
System.out.printf("avg: %f, score: %d%n", avg, score);
int ch = '0';
int temp = (int)ch; //(int)생략 가능
System.out.printf("ch: %c, tmp: %d%n", ch,temp);
double dAuto = 314; //(double)생략
double dManual = (double)314;
System.out.printf("자동 형변환 더블값: %f, 수동 형변환 더블값: %f%n", dAuto,dManual);
score = 400;
byte bScore = (byte)score; //큰 타입에서 작은 타입에서 수동 형변환, 값손실 발생
System.out.printf("int score: %d, 수동 형변환 bScore: %d%n", score, bScore);
}
}avg: 90.500000, score: 90
ch: 0, tmp: 48
자동 형변환 더블값: 314.000000, 수동 형변환 더블값: 314.000000
int score: 400, 수동 형변환 bScore: -112public class Ex{
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte a = 5, b = 10;
byte c = (byte) (a + b);
int iTemp = 200000;
long l = iTemp * iTemp;
System.out.println("20만 * 20만 형 변환 없을 때: " + l);
// long l2 = (long)iTemp * iTemp;
// long l2 = iTemp * (long)iTemp;
long l2 = (long)iTemp * (long)iTemp;
System.out.println("20만 * 20만 형 변환 후: " + l2);
System.out.println("int/int: " + 12/5);
System.out.println("int/double: " + 12/5.0);
System.out.println("double/int: " + 12.0/5);
int div = 10/7;
int mod = 10%7;
System.out.println("나누기 결과: " + div + " 나머지: " + mod);
a = 10; b = (byte) (a<<3);
System.out.printf("원래 수: %d, 시프트 연산 결과: %d%n", a,b);
float f = 0.1f;
double d = 0.1;
double d2 = (double)f; //(double) 생략 가능
System.out.printf("f의 값: " + f + " d의 값: " + d + " d2의 값: " + d2);
}
}output
20만 * 20만 형 변환 없을 때: 1345294336
20만 * 20만 형 변환 후: 40000000000
int/int: 2
int/double: 2.4
double/int: 2.4
나누기 결과: 1 나머지: 3
원래 수: 10, 시프트 연산 결과: 80
f의 값: 0.1 d의 값: 0.1 d2의 값: 0.10000000149011612

