Table of Contents
- 상속
- 포함
- 오버라이딩
- super
- super()
상속
-기존의 클래스로 새로운 클래스를 작성하는 것
-두 클래스를 부모와 자식으로 관계를 맺어줌
-새로운 클래스 extends 이미 존재하는 클래스
-단일 상속만 가능, 다중 상속 지원X
-상속의 최상위 조상 클래스는 java.lang.Object 클래스
-자식의 변경은 부모에게 아무런 영향을 끼치지 않음

package packTest;
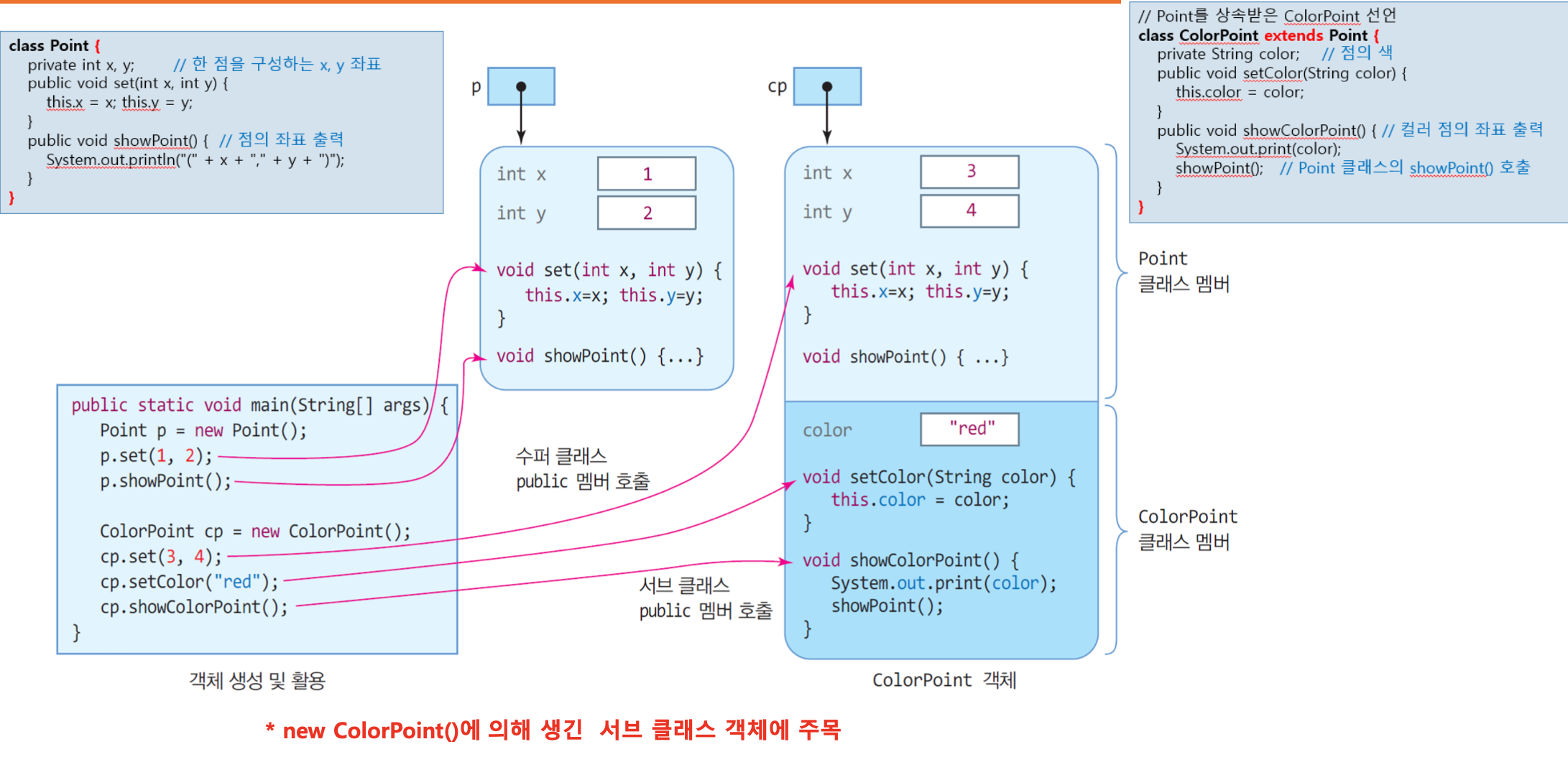
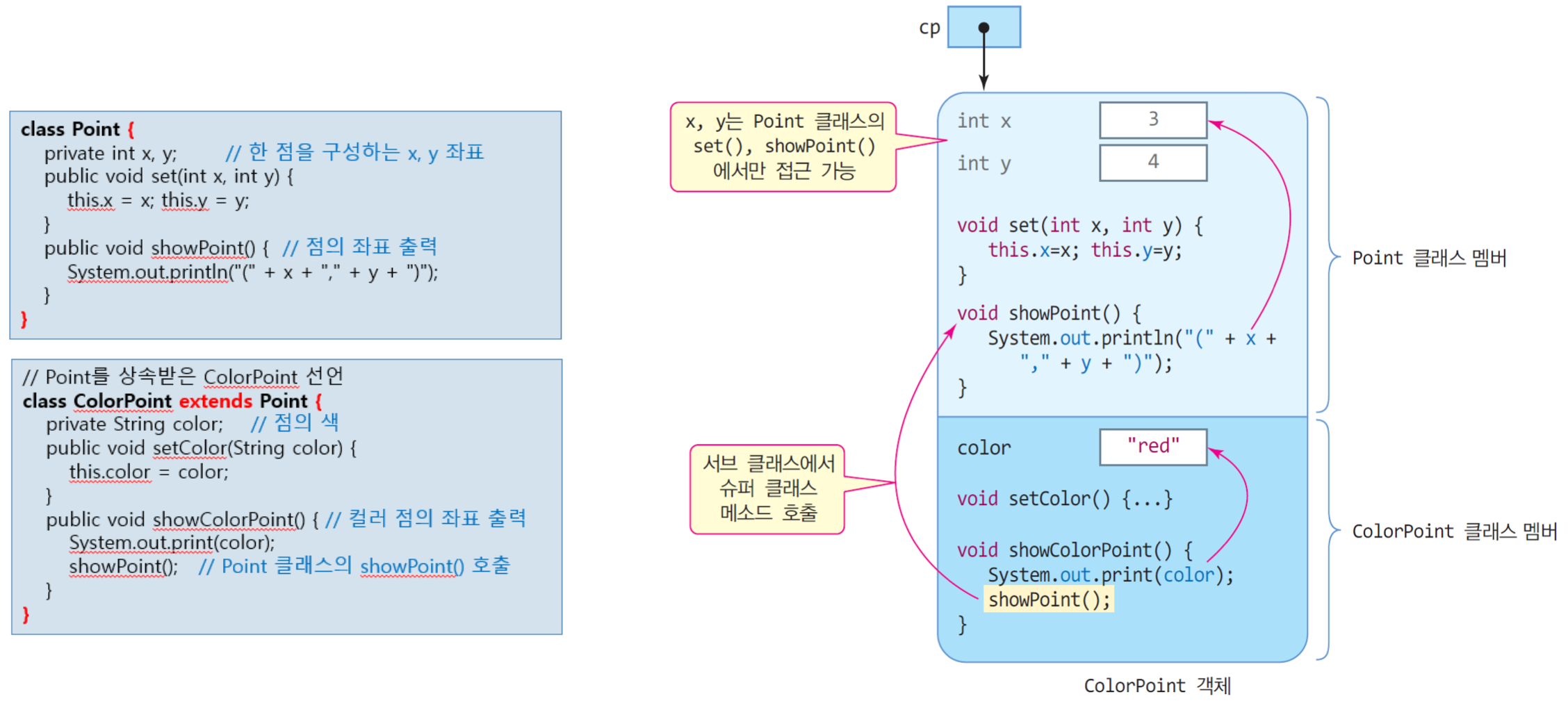
class Point{
private int x, y;
public void set(int x, int y){
this.x = x; this.y = y;
}
public void showPoint(){
System.out.println("(" + x + "," + y + ")");
}
}
class ColorPoint extends Point{
private String color;
public void setColor(String color){
this.color = color;
}
public void showColorPoint(){
System.out.printf(color);
showPoint();
}
}
public class ColorPointEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Point p = new Point();
p.set(1,2);
p.showPoint();
ColorPoint cp = new ColorPoint();
cp.set(3,4);
cp.setColor("red");
cp.showColorPoint();
}
}
class CellPhone {
String model;
String color;
//생성자 없음
//메소드
void powerOn() {
System.out.println("power on");
}
void powerOff() {
System.out.println("power off");
}
void bell() {
System.out.println("bellllll");
}
void sendVoice(String message) {
System.out.println("me: " + message);
}
void receiveVoice(String message) {
System.out.println("you: " + message);
}
void hangUp() {
System.out.println("hang up");
}
}
class DmbCellPhone extends CellPhone{
int channel;
//생성자
DmbCellPhone(String model, String color, int channel) {
this.model = model;
this.color = color;
this.channel = channel;
}
//메소드
void turnOnDmb() {
System.out.println("채널 " + channel + "번 DMB 방송 수신 시작");
}
void changeChannelDmb(int channel) {
this.channel = channel;
System.out.println("채널 " + channel + "번으로 바꿉니다");
}
void turnOffDmb(){
System.out.println("DMB 방송 수신을 멈춥니다");
}
}
public class DmCellPhoneEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DmbCellPhone dmbCellPhone = new DmbCellPhone("애플","블랙",10);
//CellPhone으로부터 상속받은 필드
System.out.println("모델: " + dmbCellPhone.model);
System.out.println("색상: " + dmbCellPhone.color);
//DmbCellphone의 필드
System.out.println("채널: " + dmbCellPhone.channel);
//CellPhone클래스로부터 상속받은 메소드
dmbCellPhone.powerOn();
dmbCellPhone.bell();
dmbCellPhone.sendVoice("준민아 안녕");
dmbCellPhone.receiveVoice("귀찮아 끊어");
dmbCellPhone.sendVoice("인성 무엇");
dmbCellPhone.hangUp();
//DmbCellPhone 메소드 호출
dmbCellPhone.turnOffDmb();
dmbCellPhone.changeChannelDmb(12);
dmbCellPhone.turnOffDmb();
}
}모델: 애플
색상: 블랙
채널: 10
power on
bellllll
me: 준민아 안녕
you: 귀찮아 끊어
me: 인성 무엇
hang up
DMB 방송 수신을 멈춥니다
채널 12번으로 바꿉니다
DMB 방송 수신을 멈춥니다포함
-클래스의 멤버로 참조변수를 선언하는 것
Point클래스와 Circle클래스가 있다고 하자.
class Point{
int x;
int y;
}class Circle{
int x;
int y;
int r;
}이 경우에 포함관계를 통해 Point를 재사용하면 다음과 같다.
class Circle{
Point c= new Point();
int r;
}오버라이딩
-상속받은 메서드의 내용을 상속받는 자식 클래스에 맞게 변형하는 것
-반환타입, 메서드 이름, 매개변수가 일치해야 함.
class Point{
int x;
int y;
String getLocation(){
return “x:” + x + “, y:” + y;
}
}class Point3D extends Point{
int z;
String getLocation(){
return “x:” + x + “, y:” + y + “z:” + z;
}
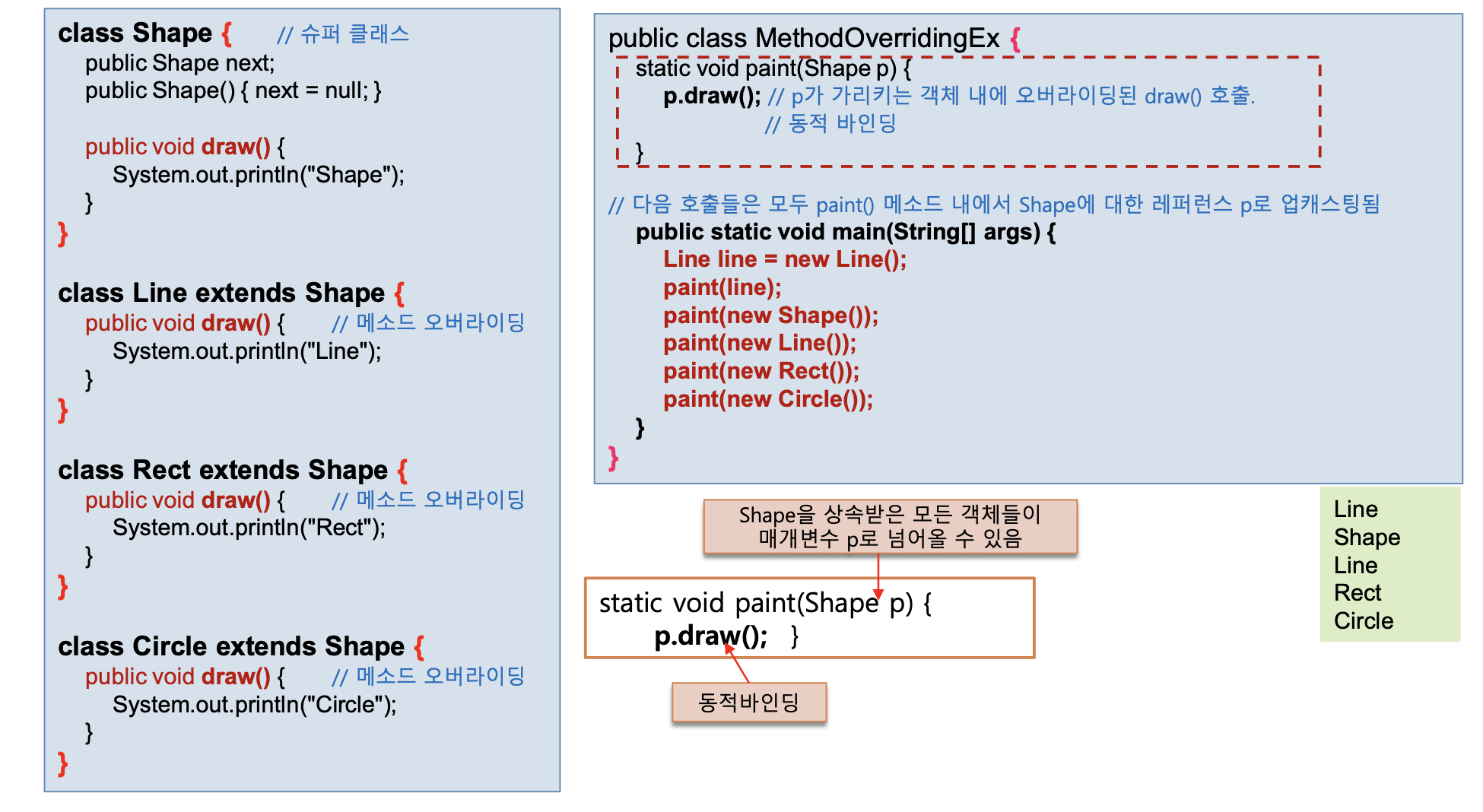
}class Shape {
public Shape next;
public Shape() {
next = null;
}
public void draw() {
System.out.println("shape");
}
}
class Line extends Shape {
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Line");
}
}
class Rect extends Shape {
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Rect");
}
}
class Circle extends Shape {
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Circle");
}
}
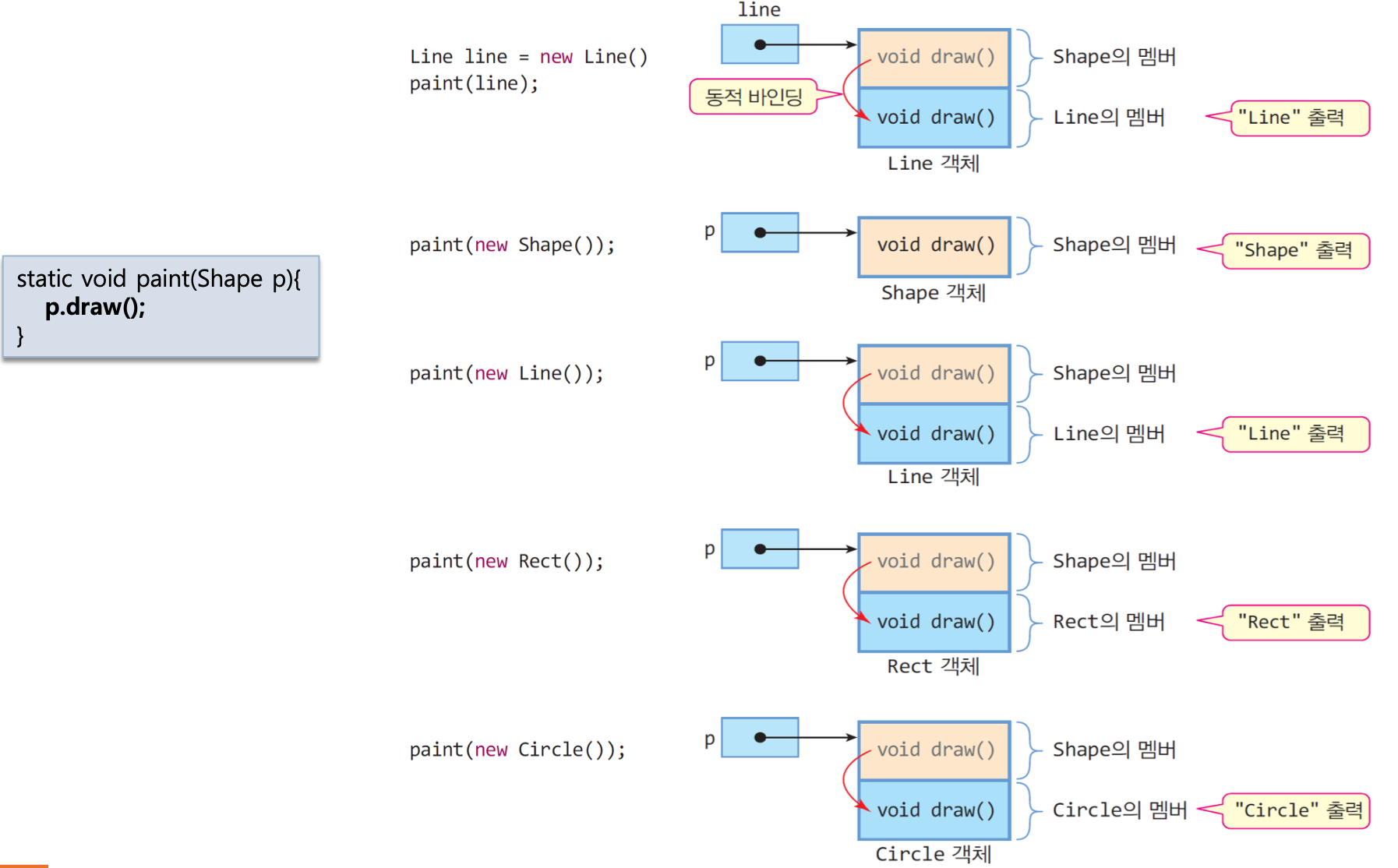
public class Overriding{
static void paint(Shape p) {
p.draw();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Line line = new Line();
paint(line);
paint(new Shape());
paint(new Line());
paint(new Rect());
paint(new Circle());
}
}
class Calculator{
double areaCircle(double r){
System.out.println("Calculator 객체의 areaCircle() 실행");
return 3.14159 * r * r;
}
}
class Computer extends Calculator{
double areaCircle(double r){ //오버라이딩
System.out.println("Computer 객체의 areaCircle() 실행");
return Math.PI * r * r;
}
}
public class ComputerEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int r = 10;
Calculator cal = new Calculator();
System.out.println("원 면적: " + cal.areaCircle(r));
System.out.println();
Computer com = new Computer();
System.out.println("원 면적: " + com.areaCircle(r));
}
}Calculator 객체의 areaCircle() 실행
원 면적: 314.159
Computer 객체의 areaCircle() 실행
원 면적: 314.1592653589793super
- 객체 자신을 가리키는 참조변수. 인스턴스 메서드(생성자)내에만 존재
- 부모 클래스의 멤버와 자식 클래스의 멤버를 구별할 때 사용
- 자식 클래스 내부에서 재정의(오버라이딩)된 부모 클래스의 메서드를 호출할 때 super 키워드를 붙여 부모 클래스를 호출한다.
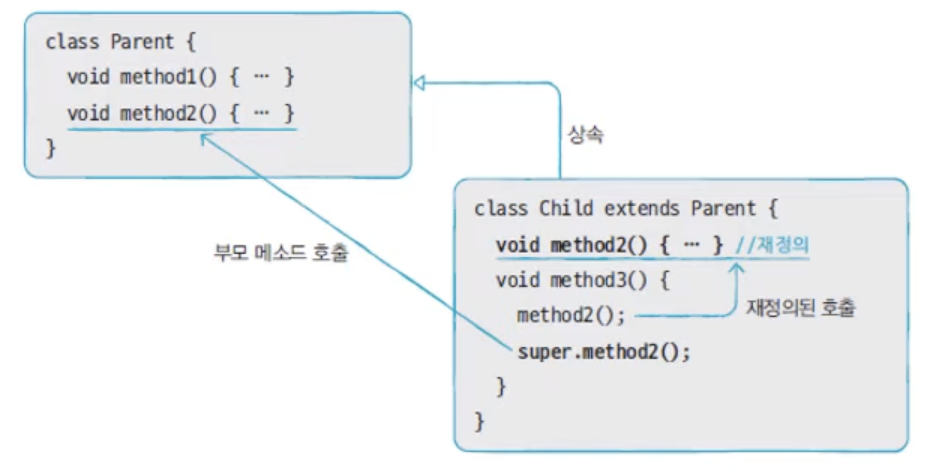
super vs this
- super는 조상멤버와 자신의 멤버를 구별할 때
- this는 lv와 iv를 구별할 때
class Parent {
int x = 10; //super.x
}
class Child extends Parent{
int x = 20; //this.x
void method(){
System.out.println("x="+x);
System.out.println("this.x="+this.x);
System.out.println("super.x="+super.x);
}
}
public class ExSuper {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Child c = new Child();
c.method();
}
}output
x=20
this.x=20
super.x=10이 예제에서 Child클래스의 멤버와 조상 Parent클래스의 멤버 x은 서로 이름이 같아 구분할 방법이 필요하다.
class Parent {
int x = 10; //super.x,this.x 모두 가능
}
class Child extends Parent{
void method(){
System.out.println("x="+x);
System.out.println("this.x="+this.x);
System.out.println("super.x="+super.x);
}
}
public class ExSuper {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Child c = new Child();
c.method();
}
}output
x=10
this.x=10
super.x=10class Airplane{
public void land(){
System.out.println("착륙");
}
public void fly() {
System.out.println("일반 비행");
}
public void takeOff(){
System.out.println("이륙");
}
}
class SupersonicAirplane extends Airplane{
public static final int NORMAL = 1;
public static final int SUPERSONIC = 2;
public int flyMode = NORMAL;
public void fly(){
if(flyMode == SUPERSONIC) {
System.out.println("초음속 비행");
}
else{
super.fly(); //Airplane 객체의 fly() 메서드 호출
}
}
}
public class SupersonicAirplaneEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SupersonicAirplane sa = new SupersonicAirplane();
sa.takeOff();
sa.fly();
sa.flyMode = SupersonicAirplane.SUPERSONIC;
sa.fly();
sa.flyMode = SupersonicAirplane.NORMAL;
sa.fly();
sa.land();
}
}이륙
일반 비행
초음속 비행
일반 비행
착륙super()
- 생성자와 초기화 블럭은 상속이 불가능
- 그래서 자식이 조상의 생성자를 호출할 때 사용
- 생성자의 첫 줄에 반드시 생성자를 호출해야 함 매우 중요.
class Point{
int x,y;
//조상의 생성자
Point(int x, int y){
//컴파일러가 super() 자동추가, 모든 생성자는 첫 줄에 생성자를 호출해야함!!!!
this.x = x; //iv 초기화
this.y = y; //iv 초기화
}
}
class Point3D extends Point{
int z;
Point3D(int x, int y, int z){
super(x,y); //조상의 생성자를 호출
this.z = z; //자신의 멤버 초기화
}
}
public class ColorPointEx{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Point3D p = new Point3D(1,2,3);
System.out.println("x=" + p.x + ",y=" + p.y + ",z=" + p.z);
}
}class A {
public A() {
System.out.println("생성자A");
}
public A(int x) {
System.out.println("매개변수 생성자 A" + x);
}
}
class B extends A{
public B() {
System.out.println("생성자B");
}
public B(int x){
super(x);
System.out.println("매개변수 생성자 B" + x);
}
}
public class ConstructorEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
B b;
b = new B(5);
}
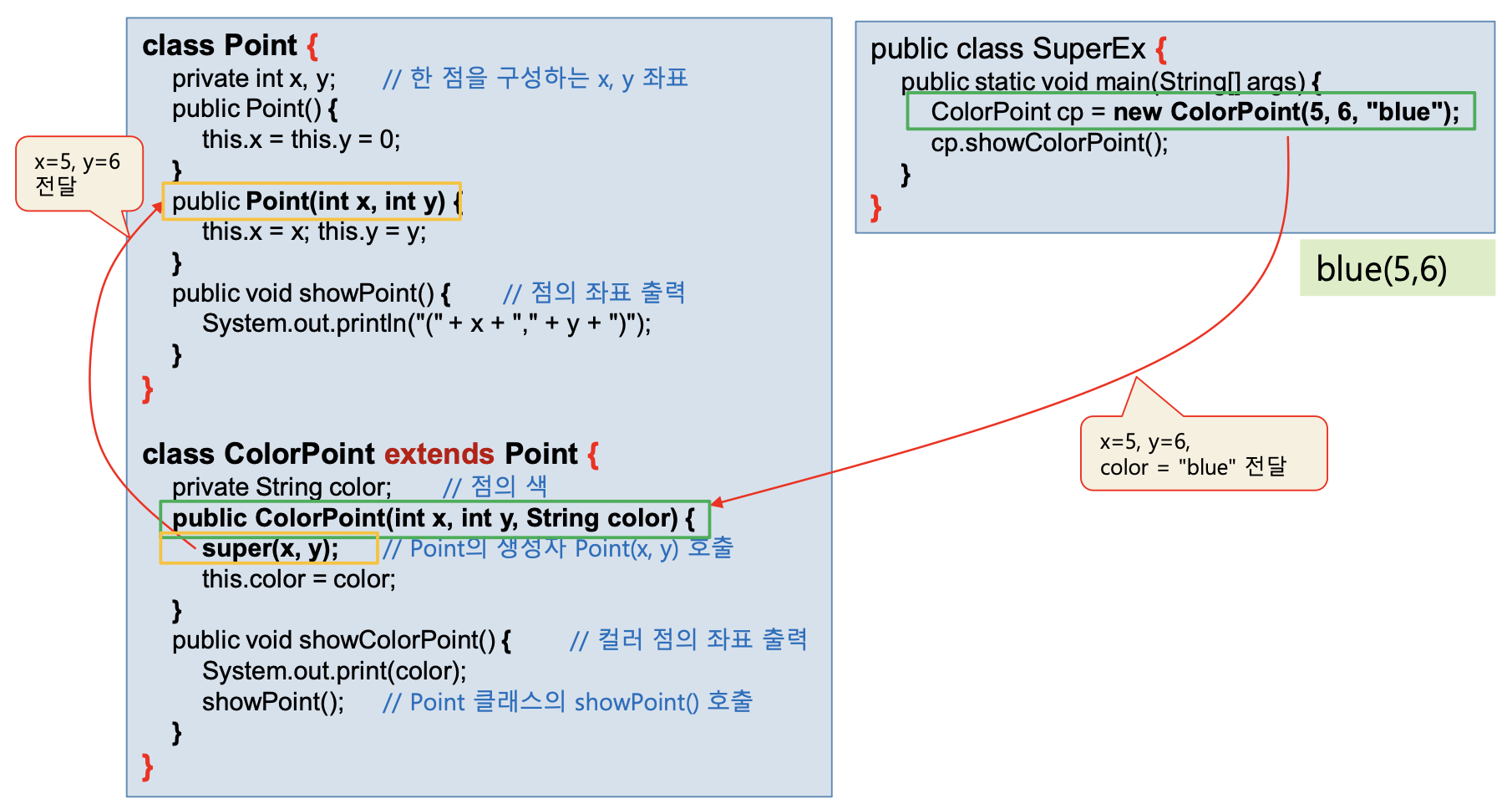
}class Point{
private int x,y;
public Point(){
this.x = this.y = 0;
}
public Point(int x, int y){
this.x = x; this.y = y;
}
public void showPoint(){
System.out.println("("+x+","+y+")");
}
}
class ColorPoint extends Point{
private String color;
public ColorPoint(int x, int y, String color){
super(x,y);
this.color = color;
}
public void showColorPoint() {
System.out.print(color);
showPoint();
}
}
public class SuperEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ColorPoint cp = new ColorPoint(5,6,"blue");
cp.showColorPoint();
}
}
class People{
public String name;
public String ssn;
//기본 생성자가 없고
public People(String name, String ssn){ //매개변수 생성자가 있다.
this.name = name;
this.ssn = ssn;
}
}
class Student extends People{
public int studentNo;
public Student(String name, String ssn, int studentNo){
super(name,ssn); //부모 생성자 People(String name, String ssn) 호출.
this.studentNo = studentNo;
}
}
public class StudentEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student = new Student("홍길동", "123456-1234567",1);
System.out.println("name : " + student.name);
System.out.println("ssn : " + student.ssn);
System.out.println("studentNo : " + student.studentNo);
}
}name : 홍길동
ssn : 123456-1234567
studentNo : 1
