비동기 실습
비동기 실습 진행은 callback, promise, async/await, fetch을 사용한다.
실습을 본격적으로 하기 전, 내가 위에 있는 키워드를 정확하게 이해하고 넘어갔는지 체크포인트를 진행하였다.
👩🏻 CheckPoint
-
Promise 실행 함수가 가지고 있는 두 개의 파라미터 resolve와 reject는 각각 무엇을 의미하나요?
코드가 정상적으로 처리 되었을 때는
resolve함수를 호출하고,reject는 에러가 발생했을 경우 호출한다. 즉, 성공과 실패로 나눌 수 있다. -
resolve , reject 함수에는 전달인자를 넘길 수 있습니다. 이때 넘기는 전달인자는 어떻게 사용할 수 있나요?
성공했을 때는 promise에서
resolve(arg)가 실행되는데, 이때.then(arg)를 인자를 받을 수 있고, 실패했을 때는 promise에서reject(arg)가 실행되는데, 이때.catch(arg)를 이용해 인자를 받을 수 있다. -
new Promise() 를 통해 생성한 Promise 인스턴스에는 어떤 메서드가 존재하나요? 각각은 어떤 용도인가요?
생성된 Promise 인스턴스는
.catch,.then,.finally가 존재한다.- then : 콜백 함수(executor)에 작성했던 코드들이 정상적으로 처리가 되었다면 resolve 함수를 호출하고,
.then메서드로 접근할 수 있다. - catch : 콜백 함수(executor)에 작성했던 코드들이 에러가 발생할 경우에는 reject 함수를 호출하고 ca 메서드로 접근할 수 있다.
- finally : 콜백 함수(executor)에 작성했던 코드들의 정상 처리 여부와 상관없이
.finally메서드로 접근할 수 있다.
- then : 콜백 함수(executor)에 작성했던 코드들이 정상적으로 처리가 되었다면 resolve 함수를 호출하고,
-
Promise.prototype.then 메서드는 무엇을 리턴하나요?
then()메서드는 Promise를 리턴하고, 두 개의 콜백 함수를 인수로 받는다. 하나는 Promise가 이행했을 때, 다른 하나는 거부했을 때를 위한 콜백 함수다. -
Promise.prototype.catch 메서드는 무엇을 리턴하나요?
catch()메서드 Promise.prototype.then(undefined, onRejected)를 호출한다. 그리고 호출한 then의 반환값인 Promise를 리턴한다.
-
Promise의 세 가지 상태는 각각 무엇이며, 어떤 의미를 가지나요?
pending(대기) : 기본(초기) 상태
fulfilled(이행) : 비동기 처리를 수행할 콜백 함수가 정상적으로 작동했을 경우
rejected(거부) : 비동기 처리를 수행할 콜백 함수가 에러가 발생했을 경우 -
await 키워드 다음에 등장하는 함수 실행은 어떤 타입을 리턴할 경우에만 의미가 있나요?
해당 함수가 Promise 타입을 리턴한 경우에만 의미가 있다.
await은 Promise가 수행되거나 성공될 때까지async함수의 실행을 일시 정지하고, Promise가 수행되면async함수를 일시 정지한 부분부터 실행한다. -
await 키워드를 사용할 경우, 어떤 값이 리턴되나요?
await키워드는async키워드가 붙어있는 함수 내부에서만 사용할 수 있으며, 비동기 함수가 리턴하는 Promise로 부터 result 값을 추출해준다.즉,
await키워드를 사용하면 일반 비동기처럼 바로 실행이 다음 라인으로 넘어가는 것이 아니라 결과값을 얻을 수 있을 때까지 기다려 준다.
-
Promise.all의 전달인자는 어떤 형태인가요?
Promise.all은 여러 개의 비동기 작업을 동시에 처리하고 싶을 때 사용하므로 순회 가능한 객체에 주어져야 한다. 즉, 전달인자는 Promise가 담겨 있는 배열 등의 이터러블(interable)의 형태다. -
Promise.all 을 사용할 경우에 then 메서드의 매개변수는 어떠한 형태인가요?
then 메서드를 실행한다는 것은 콜백함수에 작성했던 코드들이 정상적으로 처리가 되었다는 것이다.
Promise.all의 첫 번째 Promise는 가장 늦게 이행되더라도 처리 결과는 배열의 첫 번째 요소로 저장된다. 요소 전체가 promise인 배열(이터러블 객체)을 받고 새로운 promise를 반환한다.
-
Promise.all 에 두 개의 Promise 요청이 전달되고, 만일 그중 하나가 rejected 상태가 되는 경우, then 메서드, catch 메서드 중 어떤 메서드를 따라갈까요?
Promise.all은 배열 내 요소 중 어느 하나라도 거부하면 즉시 거부된다. 즉, 에러를 처리하는
catch()메서드를 실행한다.
Callback
파일 경로와 callback 을 이용하여 해결해야 하는 문제다.
파일을 불러오는 메서드인 fs.readFile의 공식 API 문서 를 참고해서 풀 수 있다.
const fs = require("fs");
const getDataFromFile = function (filePath, callback) {
fs.readFile(filePath, 'utf-8', (err, data) => {
if (err) {
callback(err, null);
} else {
callback(null, data);
}
});
}
getDataFromFile('README.md', (err, data) => {
console.log(data);
});
module.exports = {
getDataFromFile
};Promise
동일한 결과를 리턴해야하고, 위에서 사용했던 callback 대신 Promise의 resolve, reject 함수를 이용하는 문제다.
const fs = require("fs");
const getDataFromFilePromise = filePath => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fs.readFile(filePath, 'utf-8', (err, data) => {
if (err) {
reject(err);
} else {
resolve(data);
}
})
})
};
getDataFromFilePromise('README.md').then(data => {
console.log(data)
});
module.exports = {
getDataFromFilePromise
};
Promise chaining
앞서 작성한 getDataFromFilePromise 를 이용해서 해결해야하는 문제다.
[주어진 조건]
- fs 모듈을 직접 사용하면 안된다.
getDataFromFilePromise를 이용하여, 두 개의 json 파일을 불러오고, 두 파일을 합쳐서 최종적으로 두 객체가 담긴 배열을 만드는 것이다.
- 파일 경로를 찾을 때,
user1Path및user2Path를 이용할 수 있다.- 파일 읽기의 결과가 문자열이므로,
JSON.parse를 사용해야 한다.
const path = require('path');
const { getDataFromFilePromise } = require('./02_promiseConstructor');
const user1Path = path.join(__dirname, 'files/user1.json');
const user2Path = path.join(__dirname, 'files/user2.json');
// HINT: getDataFromFilePromise(user1Path) 및 getDataFromFilePromise(user2Path)를 이용해 작성합니다
const readAllUsersChaining = () => {
return getDataFromFilePromise(user1Path).then((user1) => {
return getDataFromFilePromise(user2Path).then((user2) => {
const user1Data = JSON.parse(user1);
const user2Data = JSON.parse(user2);
return [user1Data, user2Data];
});
});
}
readAllUsersChaining();
module.exports = {
readAllUsersChaining
}Promise.all
이 문제도 마찬가지로 readAllUsersChaining 과 정확히 같은 결과를 리턴해야 한다. 다만, Promise.all 을 반드시 사용해서 풀어야 한다.
const path = require('path');
const { getDataFromFilePromise } = require('./02_promiseConstructor');
const user1Path = path.join(__dirname, 'files/user1.json');
const user2Path = path.join(__dirname, 'files/user2.json');
const readAllUsers = () => {
return Promise.all([
getDataFromFilePromise(user1Path),
getDataFromFilePromise(user2Path)
]).then(([user1, user2]) => {
const user1Data = JSON.parse(user1);
const user2Data = JSON.parse(user2);
return [user1Data, user2Data];
});
;}
readAllUsers();
module.exports = {
readAllUsers
}Async/Await
위와 동일한 결과를 출력해야하지만, async/await 를 이용해야 한다.
const path = require('path');
const { getDataFromFilePromise } = require('./02_promiseConstructor');
const user1Path = path.join(__dirname, 'files/user1.json');
const user2Path = path.join(__dirname, 'files/user2.json');
const readAllUsersAsyncAwait = async () => {
const user1Data = JSON.parse(await getDataFromFilePromise(user1Path));
const user2Data = JSON.parse(await getDataFromFilePromise(user2Path));
return [user1Data, user2Data];
}
readAllUsersAsyncAwait();
module.exports = {
readAllUsersAsyncAwait
}Fetch
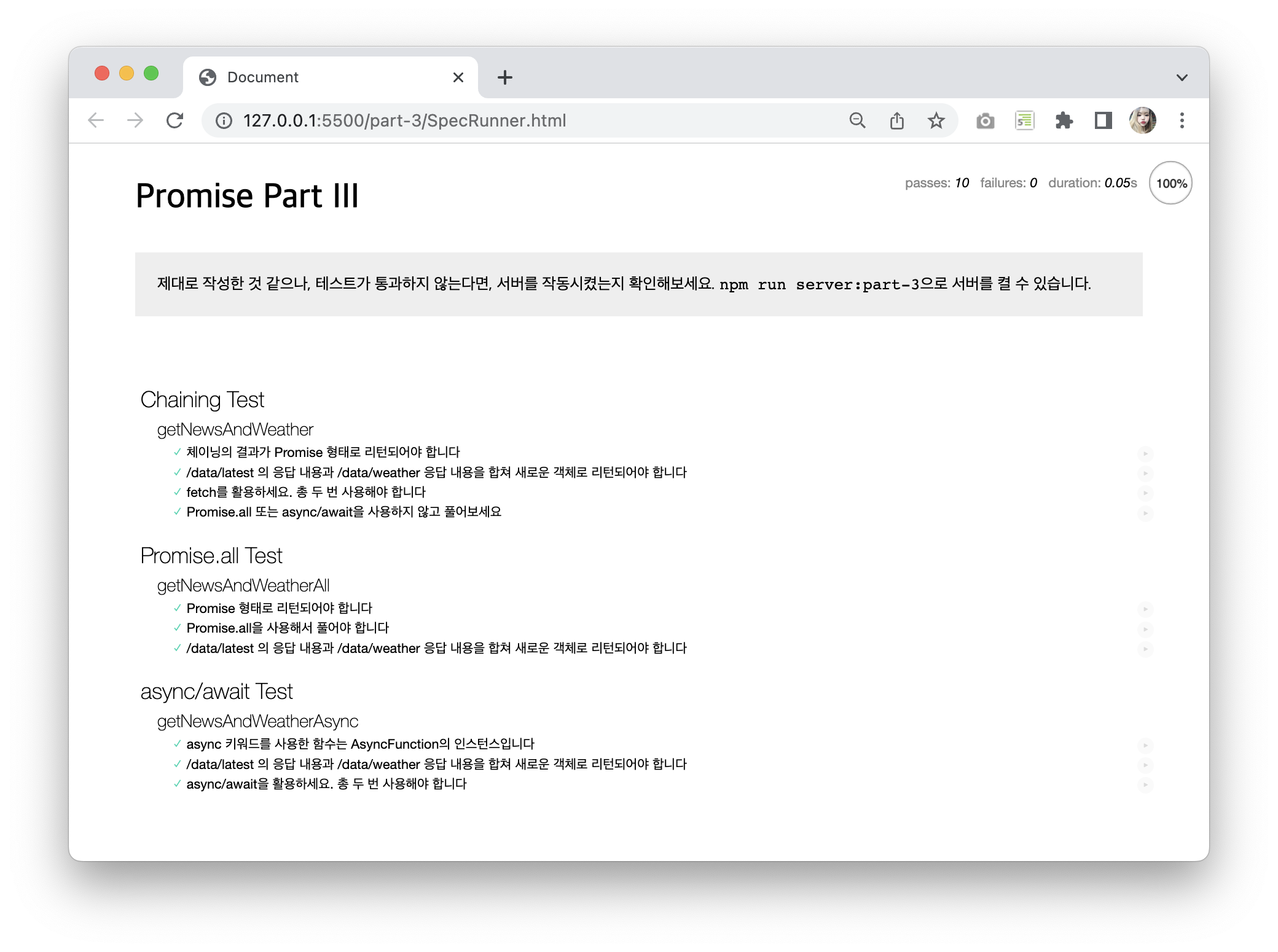
fetch를 이용하여 newsURL과 watherURL 요청의 결과를 하나의 객체로 합쳐야 한다.
const newsURL = 'news 주소';
const weatherURL = 'weather 주소';
const getNewsAndWeather = () => {
return fetch(newsURL)
.then(response => response.json())
.then(({ data: news }) => {
return fetch(weatherURL)
.then(response => response.json())
.then(weather => {
return {
news,
weather
};
});
});
}
if (typeof window === 'undefined') {
module.exports = {
getNewsAndWeather
}
}- 마찬가지로
getNewsAndWeather과 정확히 같은 결과를 리턴한다. 그러나 이번에는 반드시Promise.all을 사용해서 해결해야한다.
async function getNewsAndWeatherAll () {
return Promise.all([fetch(newsURL), fetch(weatherURL)])
.then(response => response.map(el => el.json()))
.then(jsonDatas => Promise.all(jsonDatas))
.then(data => {
let obj = {};
obj.news = data[0].data;
obj.weather = data[1];
return obj;
});
}
if (typeof window === 'undefined') {
module.exports = {
getNewsAndWeatherAll
}
}getNewsAndWeather,getNewsAndWeatherAll과 같은 결과를 리턴한다. 이번에는async및await키워드를 사용해야한다.
async function getNewsAndWeatherAsync () {
const { data: news } = await fetch(newsURL).then(response => response.json());
const weather = await fetch(weatherURL).then(response => response.json());
return { news, weather };
}
if (typeof window === 'undefined') {
module.exports = {
getNewsAndWeatherAsync
}
}Reference
