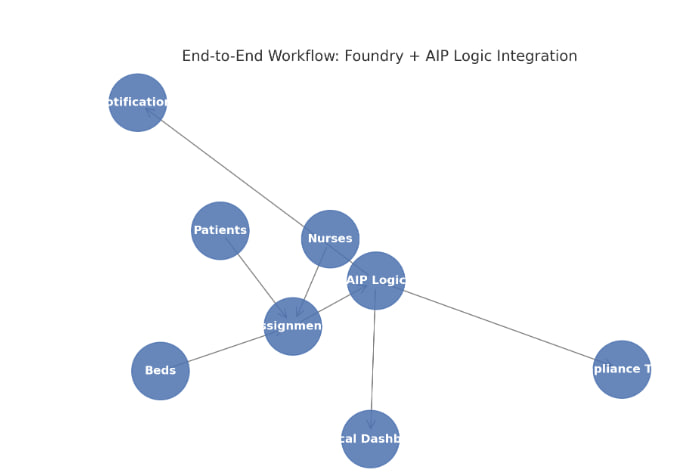
End-to-end workflow diagram
Foundry Datasets: Patients, Nurses, Beds → feed into Assignments.
AIP Logic Layer: consumes Assignments, applies decision logic.
Downstream Systems:
Notifications (alerts ops team)
Compliance Team (manual escalation)
Clinical Dashboard (real-time monitoring)
This shows how Foundry handles data orchestration while AIP Logic automates operational workflows.
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
import pandas as pd
# 온톨로지 데이터 정의 (간호사, 병상, 환자 객체)
nurses = [
{"id": "N001", "name": "Alice", "shift": "day", "availability": True, "hospital_id": "H001"},
{"id": "N002", "name": "Bob", "shift": "night", "availability": False, "hospital_id": "H001"},
]
beds = [
{"id": "B001", "hospital_id": "H001", "status": "available", "room": "ICU"},
{"id": "B002", "hospital_id": "H001", "status": "occupied", "room": "General"},
]
patients = [
{"id": "P001", "name": "John Doe", "condition": "critical", "admission_date": datetime(2025, 9, 15)},
{"id": "P002", "name": "Jane Smith", "condition": "stable", "admission_date": datetime(2025, 9, 16)},
]
# 온톨로지 관계 정의 (간호사-환자-병상)
def build_ontology():
ontology = {
"nurses": pd.DataFrame(nurses),
"beds": pd.DataFrame(beds),
"patients": pd.DataFrame(patients),
"relationships": [
{"nurse_id": "N001", "patient_id": "P001", "bed_id": "B001"},
]
}
return ontology
# AIP Logic: 간호사 스케줄링 및 병상 배치
def schedule_nurses_and_beds(ontology):
available_nurses = ontology["nurses"][ontology["nurses"]["availability"] == True]
available_beds = ontology["beds"][ontology["beds"]["status"] == "available"]
critical_patients = ontology["patients"][ontology["patients"]["condition"] == "critical"]
assignments = []
for _, patient in critical_patients.iterrows():
if not available_nurses.empty and not available_beds.empty:
nurse = available_nurses.iloc[0]
bed = available_beds.iloc[0]
assignments.append({
"patient_id": patient["id"],
"nurse_id": nurse["id"],
"bed_id": bed["id"],
"assignment_time": datetime.now()
})
# 업데이트: 간호사와 병상 상태 변경
ontology["nurses"].loc[ontology["nurses"]["id"] == nurse["id"], "availability"] = False
ontology["beds"].loc[ontology["beds"]["id"] == bed["id"], "status"] = "occupied"
return assignments, ontology
# AI 에이전트: 실시간 스케줄링 추천
def ai_agent_recommendation(ontology):
assignments, updated_ontology = schedule_nurses_and_beds(ontology)
recommendations = []
for assignment in assignments:
recommendation = (
f"Patient {assignment['patient_id']} assigned to Nurse {assignment['nurse_id']} "
f"and Bed {assignment['bed_id']} at {assignment['assignment_time']}"
)
recommendations.append(recommendation)
return recommendations
# 실행
ontology = build_ontology()
recommendations = ai_agent_recommendation(ontology)
for rec in recommendations:
print(rec)- Local (pandas/Python) execution for experimentation.
- Foundry (Spark/SQL-based) conversion for production pipelines.
📑 Technical Report
Title: Nurse Scheduling and Bed Assignment Workflow – Local Prototype and Foundry Production Conversion
1. Executive Summary
This report documents the design and implementation of a nurse scheduling and hospital bed assignment workflow.
The workflow was first developed locally using Python and pandas for rapid prototyping.
It was then converted into a Spark/SQL-based Foundry pipeline for production deployment, ensuring scalability, data lineage, and integration with operational dashboards.
2. Business Objective
Hospitals need automated, rule-based scheduling of nurses and bed assignments for patients, prioritizing critical cases.
The system must:
- Match available nurses and beds with patients in real time.
- Flag critical patients for immediate assignment.
- Update resource availability dynamically.
- Scale to enterprise-level datasets with auditability (Foundry).
3. Local Prototype (Python + pandas)
3.1 Environment
- Python ≥ 3.9
- pandas ≥ 1.5
3.2 Prototype Code
from datetime import datetime
import pandas as pd
# Ontology: Nurses, Beds, Patients
nurses = [
{"id": "N001", "name": "Alice", "shift": "day", "availability": True, "hospital_id": "H001"},
{"id": "N002", "name": "Bob", "shift": "night", "availability": False, "hospital_id": "H001"},
]
beds = [
{"id": "B001", "hospital_id": "H001", "status": "available", "room": "ICU"},
{"id": "B002", "hospital_id": "H001", "status": "occupied", "room": "General"},
]
patients = [
{"id": "P001", "name": "John Doe", "condition": "critical", "admission_date": datetime(2025, 9, 15)},
{"id": "P002", "name": "Jane Smith", "condition": "stable", "admission_date": datetime(2025, 9, 16)},
]
# Build ontology
def build_ontology():
return {
"nurses": pd.DataFrame(nurses),
"beds": pd.DataFrame(beds),
"patients": pd.DataFrame(patients),
}
# Scheduling logic
def schedule(ontology):
available_nurses = ontology["nurses"][ontology["nurses"]["availability"] == True]
available_beds = ontology["beds"][ontology["beds"]["status"] == "available"]
critical_patients = ontology["patients"][ontology["patients"]["condition"] == "critical"]
assignments = []
for _, patient in critical_patients.iterrows():
if not available_nurses.empty and not available_beds.empty:
nurse = available_nurses.iloc[0]
bed = available_beds.iloc[0]
assignments.append({
"patient_id": patient["id"],
"nurse_id": nurse["id"],
"bed_id": bed["id"],
"assignment_time": datetime.now()
})
# update states
ontology["nurses"].loc[ontology["nurses"]["id"] == nurse["id"], "availability"] = False
ontology["beds"].loc[ontology["beds"]["id"] == bed["id"], "status"] = "occupied"
return assignments
# Run locally
ontology = build_ontology()
print(schedule(ontology))3.3 Outcome
- Outputs assignment records (patient → nurse → bed).
- Updates nurse and bed availability inline.
- Suitable for experimentation, not for scaling.
4. Foundry Production Conversion (Spark/SQL)
4.1 Rationale
Foundry transforms pandas prototypes into scalable Spark/SQL pipelines with:
- Large dataset handling.
- Governance and lineage.
- Integration with operational dashboards (e.g., Contour, Quiver, AIP).
4.2 Dataset Design
-
nurses_dataset
- Columns:
id, name, shift, availability, hospital_id
- Columns:
-
beds_dataset
- Columns:
id, hospital_id, status, room
- Columns:
-
patients_dataset
- Columns:
id, name, condition, admission_date
- Columns:
4.3 SQL Transform Example
-- Select available nurses
WITH available_nurses AS (
SELECT id as nurse_id, hospital_id
FROM nurses_dataset
WHERE availability = TRUE
),
-- Select available beds
available_beds AS (
SELECT id as bed_id, hospital_id
FROM beds_dataset
WHERE status = 'available'
),
-- Select critical patients
critical_patients AS (
SELECT id as patient_id, hospital_id
FROM patients_dataset
WHERE condition = 'critical'
),
-- Join for assignment
assignments AS (
SELECT
p.patient_id,
n.nurse_id,
b.bed_id,
CURRENT_TIMESTAMP() as assignment_time
FROM critical_patients p
JOIN available_nurses n ON p.hospital_id = n.hospital_id
JOIN available_beds b ON p.hospital_id = b.hospital_id
LIMIT 10
)
SELECT * FROM assignments;4.4 Foundry Operationalization
-
Pipeline Orchestration: Foundry transforms scheduled hourly/daily.
-
Lineage: assignments dataset is auditable and traceable.
-
Downstream Integration:
- Alerts to clinical dashboards.
- Triggers AIP Logic workflows for escalation (e.g., if beds < threshold).
5. Comparative View
| Aspect | Local (pandas) | Foundry (Spark/SQL) |
|---|---|---|
| Scale | Small datasets, prototyping | Large-scale hospital data |
| Execution | Manual / script | Automated pipelines, scheduling |
| Governance | None | Full lineage, versioning |
| Integration | Standalone | Dashboards, AIP, notifications |
| Deployment | Local environment | Production-grade Foundry pipelines |
6. Conclusion
- Local pandas code is ideal for testing logic quickly.
- Foundry Spark/SQL conversion enables scaling, governance, and enterprise integration.
- The combined approach supports rapid prototyping followed by enterprise deployment.
📑 Technical Report Addendum
Section: End-to-End Data Flow Narrative
1. Upstream Data Sources
-
Patients Dataset
Contains hospital admission records with patient ID, name, condition (critical/stable), and admission date.
Purpose: Identify which patients require immediate bed and nurse assignment. -
Nurses Dataset
Contains staff rosters with nurse ID, name, shift type, availability, and hospital ID.
Purpose: Filter for currently available nurses in the right hospital/shift. -
Beds Dataset
Contains bed inventory with bed ID, hospital ID, status (available/occupied), and room type (ICU/General).
Purpose: Filter for available beds that can be matched with patient needs.
2. Data Transformation in Foundry
-
Transform Step (Spark/SQL)
-
Join patients with available nurses and beds by
hospital_id. -
Filter for critical patients first to ensure priority assignment.
-
Generate an Assignments dataset containing:
patient_idnurse_idbed_idassignment_time
-
-
Output Dataset: Assignments
This dataset represents the authoritative record of nurse-patient-bed mappings.
It is versioned, auditable, and fully lineage-tracked in Foundry.
3. AIP Logic Layer
-
Trigger
The AIP workflow is triggered whenever the Assignments dataset is updated in Foundry. -
Logic Flow
- Fetch new assignment records.
- Perform rule-based or LLM-assisted risk assessment (e.g., validate nurse-patient ratios, ICU bed allocation).
- Route results to downstream systems.
4. Downstream Systems
-
Notifications
- Sends real-time alerts (Slack, email, SMS) to the operations team.
- Example: “Patient P001 assigned to Nurse N001 and Bed B001 at 2025-09-18 14:30.”
-
Compliance Team
- Receives flagged cases if assignment violates regulatory or hospital policy rules.
- Ensures accountability for critical decisions.
-
Clinical Dashboard
- Displays live assignments in an operational UI (e.g., Contour/Quiver in Foundry).
- Provides management with real-time visibility of resource allocation.
5. End-to-End Flow Summary
- Data ingestion into Foundry (Patients, Nurses, Beds).
- Transform pipeline produces Assignments dataset.
- AIP Logic consumes Assignments and applies business rules/AI.
- Downstream systems receive notifications, compliance alerts, and dashboard updates.
This integrated workflow ensures real-time hospital operations management with:
- Transparent lineage (Foundry).
- Scalable automation (Spark/SQL).
- Intelligent decision support (AIP Logic + LLM).
- Operational accountability (Notifications, Compliance, Dashboards).
Palantir의 AIP(Artificial Intelligence Platform): 기업이 실행형 AI 운영체제를 구축하도록 돕는 프로그램입니다. 이 과정은 문제 정의, 온톨로지 설계, 워크플로 자동화, AI 에이전트 배포를 체계적으로 진행하며, 실제 데이터를 기반으로 조직의 운영 방식을 재설계합니다. 아래는 각 단계에 대한 예시를 포함한 상세 과정입니다.
1. 문제 정의 (Use Case Definition)
- 목표: 조직의 핵심 문제를 식별하고, AI를 활용해 해결할 구체적인 사용 사례를 정의.
- 과정: 실무자, 관리자, IT팀이 함께 모여 조직의 주요 과제를 논의. 예를 들어, 제조업체가 공급망 지연 문제를 해결하려는 경우, "출하 지연 가능성을 예측하고 대응 방안을 제안"이라는 사용 사례를 설정.
- 예시:
- 문제: 특정 지역의 공급망 지연으로 인해 납품이 지연됨.
- 사용 사례: "이번 분기 출하 지연 가능성이 있는 품목을 식별하고 대응 방안을 제안."
- 활동: 팀은 ERP(전사적 자원 관리) 데이터, 물류 데이터, 외부 날씨 데이터를 연결해 분석 대상 데이터를 선정.
- 결과물: 명확한 문제 정의와 핵심 온톨로지 객체(예: 공급망, 품목, 리스크 요인) 선정.
2. 온톨로지 설계 (Ontology Modeling)
- 목표: 데이터, 사람, 시스템 간의 관계를 정의하는 의미 네트워크(온톨로지)를 구축.
- 과정: Palantir의 온톨로지는 데이터를 단순히 저장하는 것이 아니라, 조직의 의사결정 구조를 반영하도록 설계. 이를 위해 데이터를 개념화하고 계층 구조를 정의.
- 예시:
- 데이터 소스: ERP(재고 데이터), CRM(고객 데이터), 설비 센서(실시간 상태 데이터).
- 온톨로지 설계:
- 객체: "제품", "공급업체", "물류 경로".
- 관계: "제품은 공급업체로부터 공급받음", "물류 경로는 날씨 데이터와 연관됨".
- 속성: 제품의 재고 수준, 공급업체의 리드타임, 물류 경로의 지연 확률.
- 활동: Palantir 엔지니어와 함께 데이터를 통합하고, UI를 통해 시각적으로 온톨로지 모델을 구축. 예를 들어, "제품 A의 공급 지연 가능성"을 계산하는 논리 설정.
- 결과물: 조직의 운영을 반영하는 동적 온톨로지 모델.
3. 워크플로 자동화 (Workflow Automation with AIP Logic)
- 목표: AI를 활용해 반복적인 작업을 자동화하고, 의사결정을 지원하는 워크플로를 설계.
- 과정: AIP Logic 모듈을 사용해 코딩 없이 비즈니스 로직을 시각적으로 구성. 이를 통해 온톨로지 데이터를 기반으로 한 자동화된 워크플로를 구현.
- 예시:
- 시나리오: 공급망 지연 예측.
- AIP Logic 설정:
- 입력: 온톨로지에서 가져온 재고 수준, 공급업체 리드타임, 날씨 데이터.
- 로직: LLM(대규모 언어 모델)을 활용해 "지연 가능성 70% 이상인 품목"을 식별하고, 대체 공급업체를 추천.
- 출력: "제품 A는 지연 가능성 80%, 대체 공급업체 B로 전환 권장"이라는 알림.
- 활동: Palantir 플랫폼에서 실시간 시뮬레이션을 통해 워크플로 테스트. 예를 들어, 특정 품목의 지연이 감지되면 자동으로 발주 요청을 생성.
- 결과물: 자동화된 워크플로와 실시간 피드백 루프.
4. AI 에이전트 배포 (AI Agent Deployment)
- 목표: 설계된 온톨로지와 워크플로를 기반으로 AI 에이전트를 실제 운영 환경에 배포.
- 과정: AIP Agent Studio를 활용해 AI 에이전트를 구성하고, 실시간 의사결정을 지원하도록 배포. 에이전트는 온톨로지 데이터를 기반으로 사용자 질문을 처리하고 실행 가능한 결과를 제공.
- 예시:
- AI 에이전트 설정:
- 질문: "다음 주 출하 지연 가능성이 있는 품목은?"
- 응답: AIP Assist가 온톨로지 데이터를 분석해 "제품 A, C가 지연 가능성 75% 이상, 대체 경로 제안"과 같은 결과를 제공.
- 작업: AI 에이전트가 자동으로 경고를 생성하고, 사용자에게 대응 방안을 제안(예: 대체 공급업체로 발주 변경).
- 활동: 배포 후 사용자 피드백을 반영해 에이전트 성능을 최적화. 보안 및 권한 설정을 통해 민감 데이터 접근을 제어.
- AI 에이전트 설정:
- 결과물: 조직 내에서 실시간으로 작동하는 AI 에이전트와 이를 지원하는 보안 프레임워크.
5. 리더십 리뷰 및 확장 전략
- 목표: 부트캠프 결과를 검토하고, 조직 전체로 확장할 전략 수립.
- 과정: 마지막 날에는 임원진 앞에서 결과를 시연하고, ROI(투자수익률)를 시뮬레이션. 이후 AIP 도입 여부와 확장 계획을 결정.
- 예시:
- 시연: 공급망 지연 예측 AI 에이전트가 실시간으로 경고를 생성하고, 대체 경로를 제안하는 모습 시연.
- ROI 계산: 지연 감소로 연간 500만 달러 비용 절감 예상.
- 확장 전략: 다른 사업부(예: 생산, 마케팅)로 온톨로지 및 AI 에이전트 확장.
- 결과물: AIP 도입 결정 및 장기 운영 전략.
실제 사례
- HCA Healthcare (헬스케어): Palantir AIP를 활용해 75개 병원, 4만 명 간호사의 스케줄링을 자동화. 온톨로지는 "간호사", "병상", "환자" 객체로 구성되었으며, AI 에이전트가 병상 배치와 스케줄링을 최적화해 대기 시간을 단축.
- 제조업: 공급망 리스크를 식별하고, 품질 이상을 자동 탐지하는 워크플로를 구축. 온톨로지는 설비 센서 데이터와 ERP 데이터를 통합해 실시간 분석을 지원.
요약
문제 정의 → 온톨로지 설계 → 워크플로 자동화 → AI 에이전트 배포를 통해 실행형 AI 운영체제를 구축합니다. 예를 들어, 공급망 지연 문제를 해결하기 위해 데이터를 통합하고, 온톨로지를 설계하며, AI 에이전트를 배포해 실시간 의사결정을 지원할 수 있습니다. 이 과정은 단순한 기술 도입이 아니라 조직의 사고방식과 운영 방식을 재설계하는 데 초점을 맞춥니다.
📘 Palantir Overview
Palantir은 데이터 통합, 분석, 의사결정을 지원하는 엔드투엔드 플랫폼을 제공합니다.
- Foundry: 데이터 통합·변환(ETL), 데이터 모델링, 분석 워크플로, 애플리케이션 개발을 지원. 주로 SQL/코드 기반 워크플로를 구성.
- AIP (Artificial Intelligence Platform): 대규모 언어모델(LLM)과 워크플로 자동화를 결합해, “Logic” 기능으로 정책·규칙 기반의 실행 흐름을 정의하고 운영팀이 AI와 상호작용하며 실행할 수 있게 함.
🔹 AIP Logic 워크플로 예제
AIP Logic은 비즈니스 규칙과 LLM 기반 에이전트의 액션을 연결하는 워크플로 언어입니다.
예제: 의료 데이터 접근 요청 자동화
workflow:
name: PatientDataAccessApproval
triggers:
- type: user_request
input: patient_id, requester_role
steps:
- name: ValidateRequester
action: check_role
params:
allowed_roles: ["doctor", "nurse", "researcher"]
- name: PHI_Check
action: query_data_classification
params:
dataset: patient_records
patient_id: $patient_id
- name: ApprovalLogic
action: conditional
conditions:
- if: requester_role in ["doctor","nurse"] and PHI_Check == "low"
then: auto_approve
- if: requester_role == "researcher"
then: route_to_compliance_team
- name: Notify
action: send_notification
params:
message: "Request for patient $patient_id processed. Status: $status"➡️ 설명:
- 트리거: 사용자가 특정 환자 데이터 접근을 요청
- 검증 단계: 요청자 역할(role) 확인
- 데이터 분류 확인: 민감도(PHI 여부) 체크
- 승인 로직: 조건에 따라 자동 승인/심사팀 라우팅
- 알림 발송: 최종 결과 통보
🔹 Foundry SQL 기반 워크플로 예제
Foundry는 데이터셋을 SQL Transform이나 코드 변환(Python, Spark)으로 정의합니다.
예제: 의료 비용 이상 탐지 데이터셋 생성
-- Step 1: Join patient and claims data
SELECT
p.patient_id,
p.age,
c.claim_id,
c.procedure_code,
c.amount
FROM patients p
JOIN claims c
ON p.patient_id = c.patient_id;
-- Step 2: Flag abnormal claims (amount > 2 std dev from mean)
WITH claim_stats AS (
SELECT
procedure_code,
AVG(amount) as avg_amount,
STDDEV(amount) as std_amount
FROM claims
GROUP BY procedure_code
)
SELECT
c.claim_id,
c.patient_id,
c.procedure_code,
c.amount,
CASE
WHEN c.amount > cs.avg_amount + 2 * cs.std_amount
THEN 'abnormal'
ELSE 'normal'
END as claim_flag
FROM claims c
JOIN claim_stats cs
ON c.procedure_code = cs.procedure_code;➡️ 설명:
- Step 1: 환자와 청구 데이터 병합
- Step 2: 통계 기반 이상 탐지 (평균+2표준편차 초과 시 abnormal 플래그)
- 결과 데이터셋은 Foundry에서 다운스트림 앱이나 대시보드에 활용 가능
✨ 핵심 차이
- Foundry SQL 워크플로: 데이터 파이프라인 구축, 분석용 데이터셋 생성. (Data Engineering 중심)
- AIP Logic 워크플로: 규칙/조건 기반 + LLM 에이전트 자동화. (Operations + AI Agent 중심)
📘 End-to-End Workflow: 의료 청구 이상 탐지 및 자동 심사
1️⃣ Foundry SQL 워크플로 – 데이터 처리 및 이상 탐지
먼저 청구 데이터셋을 처리하고 이상 항목을 태깅합니다.
-- Step 1: Join patient and claims data
WITH joined AS (
SELECT
p.patient_id,
p.age,
c.claim_id,
c.procedure_code,
c.amount
FROM patients p
JOIN claims c
ON p.patient_id = c.patient_id
)
-- Step 2: Calculate stats by procedure
, claim_stats AS (
SELECT
procedure_code,
AVG(amount) as avg_amount,
STDDEV(amount) as std_amount
FROM joined
GROUP BY procedure_code
)
-- Step 3: Label abnormal claims
SELECT
j.claim_id,
j.patient_id,
j.procedure_code,
j.amount,
CASE
WHEN j.amount > cs.avg_amount + 2 * cs.std_amount
THEN 'abnormal'
ELSE 'normal'
END as claim_flag
FROM joined j
JOIN claim_stats cs
ON j.procedure_code = cs.procedure_code;➡️ Output dataset: claims_with_flags
- 각 청구 건은
normal또는abnormal로 표시 - 이 데이터셋은 Foundry Data Lineage를 통해 다운스트림에 연결
2️⃣ AIP Logic 워크플로 – 이상 청구 자동 심사 및 알림
Foundry에서 생성된 claims_with_flags 데이터셋을 기반으로 자동화 심사 로직을 실행합니다.
workflow:
name: AbnormalClaimReview
triggers:
- type: dataset_update
dataset: claims_with_flags
steps:
- name: FetchAbnormalClaims
action: query_dataset
params:
dataset: claims_with_flags
filter: claim_flag == "abnormal"
- name: RiskAssessment
action: llm_assist
params:
prompt: |
Analyze the claim for potential fraud indicators.
Consider patient age, procedure code, and claim amount.
input: $FetchAbnormalClaims
- name: Decision
action: conditional
conditions:
- if: RiskAssessment contains "high risk"
then: route_to_investigation_team
- if: RiskAssessment contains "low risk"
then: auto_approve
- name: Notify
action: send_notification
params:
message: |
Claim $claim_id has been reviewed.
Status: $status➡️ 설명:
- 트리거: Foundry 데이터셋 업데이트 시 자동 실행
- 데이터 추출:
abnormal청구 건만 가져옴 - LLM 보조: 이상 청구 건에 대해 LLM이 추가 위험 분석 수행
- 조건 분기: “high risk” → 조사팀 라우팅, “low risk” → 자동 승인
- 알림 발송: 심사 결과를 운영팀에 전송
3️⃣ 통합 시나리오 흐름
-
데이터 엔지니어링 (Foundry)
- 원시 환자/청구 데이터 → SQL 변환 →
claims_with_flags데이터셋 생성
- 원시 환자/청구 데이터 → SQL 변환 →
-
자동화 심사 (AIP Logic)
claims_with_flags가 업데이트되면 트리거 실행- LLM이 이상 청구에 대해 위험 분석 → 조건 분기 로직 처리
- 결과를 자동 승인하거나 조사팀으로 전달
-
운영/알림
- Slack/이메일/대시보드로 결과 통보
- 조사팀은 Foundry 앱에서 케이스를 추적
이렇게 하면 Foundry는 데이터 기반 이상 탐지를 담당하고,
AIP Logic은 운영 자동화와 LLM 보조 의사결정을 담당하는 엔드투엔드 AI-운영 파이프라인이 완성됩니다.
