앞전에 디스코드 봇 시작하기에서 작성해준 index.js 파일은 아래와 같이 생겼습니다.
index.js 파일에 명령어와 이벤트코드를 모두 작성하면 코드가 너무 길고 가독성이 떨어지기 때문에 분할해주도록 하겠습니다.
📁Folder Structure
dico-bot/
├── commands/
| ├── 명령어1.js
| ├── 명령어2.js
| └── 명령어3.js...
├── events/
| ├── interactionCreate/ // discord.js의 Events클래스의 하위클래스명으로 작성
| | ├──이벤트1.js
| | └──이벤트2.js
| ├── messsageCreate/
| | ├──이벤트1.js
| | └──이벤트2.js
| └── clientReady/
| ├──이벤트1.js
| └──이벤트2.js
├── node_modules/
├── config.json
├── index.js
├── package-lock.json
└── package.json
폴더구성은 다음과 같은 맥락으로 해주었습니다. (예시)
command는 각 파일당 하나의 명령어를 등록해주고
event는 봇의 기능이 많아져 수신할 이벤트가 많아질 경우 각각의 파일로도 코드가 길어져
2-deps폴더로 구성해두었습니다
🔔events
이벤트파일 코드구성은 다음과 같습니다.
module.exports = {
name: "이벤트명",
once: true 또는 false,
/**
*
* @param {import("discord.js").타입을 추론받고자하는 클래스} 변수명
*/
async execute(변수명) {
// 이벤트 수신시 실행할 코드
},
};이를 기반으로 기존의 코드를 다음과 같이 변경해줍니다
-
const { Events } = require('discord.js'); module.exports = { name: Events.ClientReady, once: true, /** * * @param {import("discord.js").Client} client */ async execute(client) { console.log(`${client.user.tag} 로그인`); }, };└ events/clientReady 폴더 밑에 원하는이름으로 js파일을 만들어 다음과 같이 작성합니다
-
const { Events } = require('discord.js'); module.exports = { name: Events.MessageCreate, once: false, /** * * @param {import("discord.js").Message} message */ async execute(message) { if (message.content === '안녕') { message.reply({ content: `**반갑습니다!**` }); } }, };└ events/messageCreate 폴더 밑에 마찬가지로 다음과 파일을 만들고 다음과 같이 작성합니다
📟commands
-
commands/ 폴더 밑에 ping.js라고 파일을 만들어 주겠습니다
const { SlashCommandBuilder } = require('discord.js'); module.exports = { data: new SlashCommandBuilder() .setName('ping') .setDescription('Replies with Pong!') }; -
events/interactionCreate/ 폴더 밑에 ping.js 에서 명령어 처리를 해주겠습니다
const { Events } = require('discord.js'); module.exports = { name: Events.InteractionCreate, once: false, /** * * @param {import("discord.js").CommandInteraction} interaction */ async execute(interaction) { if (interaction.commandName !== 'ping') return; // 이벤트가 모든 interactionCreate 파일에 대해 작동하기 떄문에 필터링이 필요합니다 await interaction.reply('Pong!'); }, }; -
discord js 공식가이드에서는 다음과 같이
const { SlashCommandBuilder } = require('discord.js'); module.exports = { data: new SlashCommandBuilder() .setName('ping') .setDescription('Replies with Pong!'), /** 상호작용 실행코드 */ async execute(interaction) { await interaction.reply('Pong!'); }, };실행코드를 같이 적어주지만 개인적으로 events 폴더에서 모두 처리를 해주는것이 통일성이있다고 생각합니다.
🟡index.js
index.js 코드를 다음과 같이 바꾸어줍니다
const { Client, Collection, REST, Routes, GatewayIntentBits } = require('discord.js');
require('dotenv').config();
const { env } = process;
const client = (module.exports = new Client({
intents: [
GatewayIntentBits.Guilds,
GatewayIntentBits.MessageContent,
GatewayIntentBits.GuildMessages,
],
}));
/** 이벤트 파일 등록 */
const fs = require('fs');
const eventFolders = fs.readdirSync('./events');
/** 폴더 loop */
for (const folder of eventFolders) {
const eventsPath = `./events/${folder}`;
const eventFiles = fs.readdirSync(eventsPath).filter(file => file.endsWith('.js'));
/** 파일 loop */
for (const file of eventFiles) {
const event = require(`./events/${folder}/${file}`);
if (event.once == true) {
client.once(event.name, (...args) => event.execute(...args));
} else {
client.on(event.name, (...args) => event.execute(...args));
}
}
}
/** 커맨드 파일 등록 */
client.commands = new Collection();
const commands_json = [];
const commandsFiles = fs
.readdirSync('./commands')
.filter(file => file.endsWith('.js'));
/** 파일 loop */
for (const file of commandsFiles) {
const command = require(`./commands/${file}`);
client.commands.set(command.data.name, command);
commands_json.push(command.data.toJSON());
}
const rest = new REST({ version: '10' }).setToken(env.TOKEN);
rest
.put(Routes.applicationCommands(env.ID), { body: commands_json })
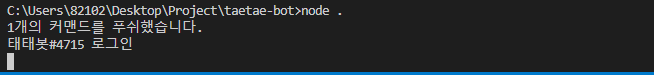
.then(command => console.log(`${command.length}개의 커맨드를 푸쉬했습니다.`))
.catch(console.error);
try {
client.login(env.TOKEN);
} catch (TOKEN_INVALID) {
console.log('An invalid token was provided');
}fs 파일입출력 모듈을 사용해 폴더를 순회하면서 command와 event들을 등록해줍니다
결과