이번 챕터 내용
- 순열, 조합
- 빈도계산
- 덱
- 우선순위 큐
1. 순열, 조합
1-1. 순수한 방법
- nC2 는 가능
- nC3 nC4 등은 for문으로 한계가 있음
''' nC2 구하기 ''' N = 5 cnt = 0 for i in range(N-1): for j in range(i+1, N): print(i, j) cnt += 1 print("5C2 = ", cnt)
1-2. 조합 combinations (중복 없이 출력)
from itertools import combinations # 조합# 4C3 출력
print(list(combinations([1, 2, 3, 4], 3)))
# 첫 번째 인자 = 리스트, 두 번째 인자 = nCm일 경우, m
print("* 4C3 = ", len(list(combinations([1,2,3,4], 3))))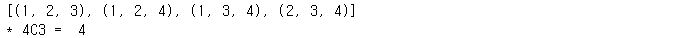
# 5C2
print(list(combinations([0,1,2,3,4], 2)))
print("* 5C2 = ", len(list(combinations([0,1,2,3,4], 2))))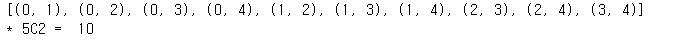
''' 백준 15650 - 내가 푼(블로그 참고) '''
from itertools import combinations # iter tools의 조합(콤비네이션s)
n, m = map(int, input().split())
# 리스트를 따로 만들지 않고 한줄에 해줬으며, (중요) 이때 각 원소를 str()로 변환해줘야 함
result = list(combinations([str(i) for i in range(1, n+1)], m))
for i in result:
print(" ".join(i))
# 첫 번째 인자 = 리스트, 두 번째 인자 = nCm일 경우, m
1-3. 순열 permutations (중복 포함 모든 경우의 수 출력)
''' 백준 15649 - 내가 푼(블로그 참고) '''
from itertools import permutations # iter tools의 순열 (<--> 조합 combinations)
n, m = map(int, input().split())
# 리스트를 따로 만들지 않고 한줄에 해줬으며, (중요) 이때 각 원소를 str()로 변환해줘야 함
result = list(permutations([str(i) for i in range(1, n+1)], m))
for i in result:
print(" ".join(i))
# 첫 번째 인자 = 리스트, 두 번째 인자 = nCm일 경우, m
1-4. 순열과 조합 참고 팁
''' 중복 조합 '''
from itertools import combinations_with_replacement
''' 중복 순열 '''
from itertools import product2. 빈도계산
- (중요) 대부분 기업 코딩테스트에서 모르면 조금 고생하는 내용
- .count말고, "collections의 Counter함수" 활용
from collections import Counter''' 백준 2592 '''
''' 안썼을 경우 - 내가 품 '''
result = []
arr = [0]*100 # 10의 배수니까 1000개까지 필요없고, 100개만 만들어줬음(메모리 때문)
for i in range(10):
result.append(int(input()))
arr[result[i]//10] += 1 # 1000개 만들고 arr[result[i]] 로 해줘도 됨
print(sum(result)//10)
print(arr.index(max(arr))*10) # 인덱스값으로 가져옴
''' 썼을 경우 - 블로그 참고 '''
from collections import Counter
result = [int(input()) for _ in range(10)] # (중요)
print(sum(result)//10)
a = Counter(result).most_common() # 빈도순으로 새롭게 정렬을 시킨다!
print(a[0][0]) # a를 출력하면 튜플형태로 출력됨
print(a) #주의!! 이렇게 저장된다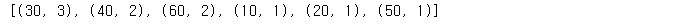
''' 백준 1157 _ 내가 품 '''
from collections import Counter
arr = input()
arr = arr.upper() # (중요) 결국 대문자만 사용하기 때문에 .upper() 사용함
result = Counter(arr).most_common() # 블로그로 공부한 Counter().most_common()를 활용
if len(result) == 1: # 단일 문자의 경우
print(result[0][0])
elif result[0][1] == result[1][1]: # 여러 개일 경우 = 2개 이상인 경우 = 맨 앞에만 체크하면 됨
print('?')
else: # 나머지의 경우, 맨 앞에 데이터만 출력하면 됨
print(result[0][0])
3. 힙(Heap) =/= priority queue
3-1. 최소힙, 최대힙
- heap q : 기본적으로 최소힙이며, 최솟값은 0번 인덱스에 저장됨
- 최솟값 0은 이진트리 root에 위치함
- heapq.heappush()
- heapq.heappop()
- 정렬되어서 들어있는게 아니라, pop() 시 정렬된 순으로(작은/큰 순) 나오는 것!! <주의>
import heapq
heap = [] # 리스트이자 힙 생성 => 출력시 이진트리로 출력
heapq.heappush(heap, 3)
heapq.heappush(heap, 1)
heapq.heappush(heap,10)
heapq.heappush(heap, 5)
heapq.heappush(heap, 8)
print(heap) # 0번째 인덱스 = 가장 작은 값 = root node
print(heapq)
print("length = ", len(heap))
print(heapq.heappop(heap)) # pop 수행!
print(heap)
print(heapq.heappop(heap)) # pop 수행!
print(heap)
print(heapq.heappop(heap)) # pop 수행!
print(heap)
print(heapq.heappop(heap)) # pop 수행!
print(heap)
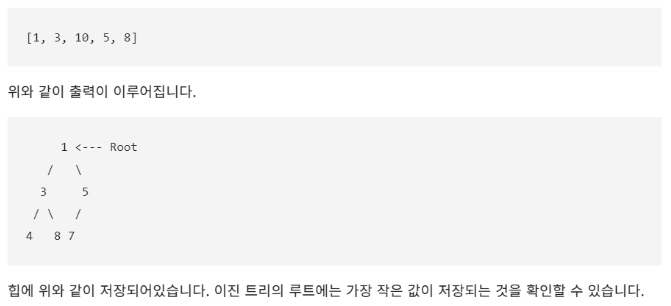
- (중요) 최대힙(max heapq)로 만드는 방법
- 데이터 넣을 때 -1 곱해서 넣고 (위에서 pop할 때 큰/작은 순으로 나온다고 했짢아)
- print()할 때 -1 곱해서 출력하면 큰순으로 나옴
''' 백준 11279 - jupyter라 input() 사용해서 시간초과 '''
import heapq
heap = []
for i in range(int(input())):
x = int(input()) * -1 # (중요) 최대힙(=역순)
if x == 0 and len(heap) == 0: # is empty
print(0)
elif x == 0:
print(heapq.heappop(heap) * -1) # (중요) 최대힙(=역순)
else:
heapq.heappush(heap, x)
''' 백준 11286 - 내가 품 - sys사용 (jupyter 실행 안됨) '''
import sys, heapq
heap = []
for i in range(int(sys.stdin.readline())):
x = int(sys.stdin.readline())
if x == 0 and len(heap) == 0: # is empty
print(0)
elif x == 0:
print(heapq.heappop(heap)[1]) # [0]을 기준으로 최소힙, 원래값인 [1]을 출력
else:
heapq.heappush(heap, (abs(x), x)) # (절댓값, 원래값) 최소힙 (이때 0번째 기준 정렬)

4. 덱(데크) Deque (중요 - 제일 다루기 시움)
- 큐(queue) 이다
- 양방향에서 데이터가 삽입 삭제
- 파이썬에서 스택 을 list 를 이용하기도 하지만, 시간초과 판정을 받을 때가 있음
- 파이썬에서 스택 문제 풀려면 deque를 사용해야 한다
from collections import deque # 힙은 그냥 import했다.
deq = deque() # 덱 초기화
print(deq)
deq1 = deque([1,2,3,4])
print(deq1)
deq2 = deque([i for i in range(1, 5)])
print(deq2)
4-1. append()와 appendleft()
