Sass
.list
width: 100px
float: left
li
color: red
background: url("./image.jpg")
&:last-child
margin-right: -10pxSCSS(css와 거의 같은 문법으로 Sass기능 지원함)
.list {
width: 100px;
float: left;
li {
color: red;
background: url("./image.jpg");
&:last-child {
margin-right: -10px;
}
}
}컴파일
1.SassMeister(https://www.sassmeister.com/)-사이트주소
vscode 플러그인
1.Sass 설치
2. Live Sass Compiler (sass 컴파일 자동으로 해주는 플러그인)
3.Sass Lint(sass문법 작성 플러그인)
[Watch Sass]를 누르면 [name.css] 생성
문법
Sass:
// 컴파일되지 않는 주석
/* 컴파일되는 주석 */
/* 컴파일되는
* 여러 줄
* 주석 */
// Error
/* 컴파일되는
* 여러 줄
* 주석 */
SCSS:
/*
컴파일되는
여러 줄
주석
*/데이터 종류
1. Numbers(숫자) 1, .82, 20px 2em
2. Strings(문자) bold, relative, "images/a.png"
3. Colors(색상 표현) red, blue, #ffffff
4. Booleans(논리) true, false
5. Nulls(아무것도 없음) null(컴파일 하지 않음)
6. Lists(공백이나 ,로 구분된 값의 목록) (apple, orange, banana), apple orange
( )를 붙이거나 붙이지 않는다.
7. Maps(Lists와 유사하나 값이 Key:Value형태) (apple: a, orange: o, banana: b)
( )를 꼭 붙여야한다
중첩
SCSS:
.section {
width: 100%;
.list {
padding: 20px;
li {
float: left;
}
}
}
Compiled to:
.section {
width: 100%;
}
.section .list {
padding: 20px;
}
.section .list li {
float: left;
}Ampersand (상위 선택자 참조) &
*중첩 안에서 &키워드는 상위(부모) 선택자를 참조하여 치환한다.
SCSS:
.btn {
position: absolute;
&.active {
color: red;
}
}
.list {
li {
&:last-child { //&이 바로 위 근처 부모 li로 치환된다
margin-right: 0;
}
}
}
Compiled to:
.btn {
position: absolute;
}
.btn.active {//일치선택자
color: red;
}
.list li:last-child {
margin-right: 0;
}
SCSS:
.fs {
&-small { font-size: 12px; }
&-medium { font-size: 14px; }
&-large { font-size: 16px; }
}
Compiled to:
.fs-small {
font-size: 12px;
}
.fs-medium {
font-size: 14px;
}
.fs-large {
font-size: 16px;
}
만약 &를 안쓰고 직접 부모선택자를 적게된다면,
.btn{
width:100px;
height:100px;
.btn.active{
color:red;
}
}
Compiled to:
.btn{
width:100px;
height:100px;
}
.btn .btn.active{
color:red;
}
@at-root (중첩 벗어나기)
*중첩에서 벗어나고 싶을 때 @at-root 키워드를 사용
(중첩 안에서 생성하되 중첩 밖에서 사용해야 경우에 유용하다.)
SCSS:
.list {
$w: 100px;
$h: 50px;
li {
width: $w;
height: $h;
}
@at-root .box { //부모안에 선언된 변수는 사용하고싶지만, 중첩시키고 싶지 않을때 붙힘.
width: $w;
height: $h;
}
}
Compiled to:
.list li {
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
}
.box {
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
}
중첩된 속성
SCSS:
.box {
font: {
weight: bold;
size: 10px;
family: sans-serif;
};
margin: {
top: 10px;
left: 20px;
};
padding: {
bottom: 40px;
right: 30px;
};
}
Compiled to:
.box {
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 10px;
font-family: sans-serif;
margin-top: 10px;
margin-left: 20px;
padding-bottom: 40px;
padding-right: 30px;
}
변수(Variables)
*반복적으로 사용되는 값을 변수로 지정
$변수이름: 속성값;
SCSS:
//선언하기
$color-primary: #e96900;
$url-images: "/assets/images/";
$w: 200px;
//작성하기
.box {
width: $w;
margin-left: $w;
background: $color-primary url($url-images + "bg.jpg");
}
//컴파일
Compiled to:
.box {
width: 200px;
margin-left: 200px;
background: #e96900 url("/assets/images/bg.jpg");
}
변수 유효범위(Variable Scope)
*선언된 블록({}) 내에서만 유효범위를 가진다.
.box1 {
$color: #111;//선언하기
background: $color; //사용하기
}
// Error
.box2 {
background: $color;//선언범위가 아니라서 사용안됨
}
//$color는 .box1의 블록 안에서 설정되었기 때문에, 블록 밖의 .box2에서는 사용할 수 없다.
변수 재 할당(Variable Reassignment)
*변수를 특정한 다른변수에 재사용
SCSS:
$red: #FF0000; //선언하기
$blue: #0000FF; //선언하기
$color-primary: $blue; //다시 할당
$color-danger: $red; //다시 할당
.box {
color: $color-primary;
background: $color-danger;
}
Compiled to:
.box {
color: #0000FF;
background: #FF0000;
}
!global (전역 설정)
*!global 플래그를 사용하면 변수의 유효범위를 전역(Global)로 설정할 수 있다.
SCSS:
.box1 {
$color: #111 !global;//전역 선언
background: $color; //선언사용
}
.box2 {
background: $color; //선언사용
}
Compiled to:
.box1 {
background: #111;
}
.box2 {
background: #111;
}
대신 기존에 사용하던 같은 이름의 변수가 있을 경우 값이 덮어져 사용될 수 있다.
SCSS:
$color: #000; //선언하기
.box1 {
$color: #111 !global; //전역선언
background: $color; //(전역으로 우선적용)
}
.box2 {
background: $color; //선언적용(전역으로 적용)
}
.box3 {
$color: #222; //동일한 변수 재 선언
background: $color; //(가장 가까운 해당 내 선언된 변수로 적용)
}
Compiled to:
.box1 {
background: #111;
}
.box2 {
background: #111;
}
.box3 {
background: #222;
}
//가장 가까운 곳에서 마지막에 선언된 것으로 적용된다.
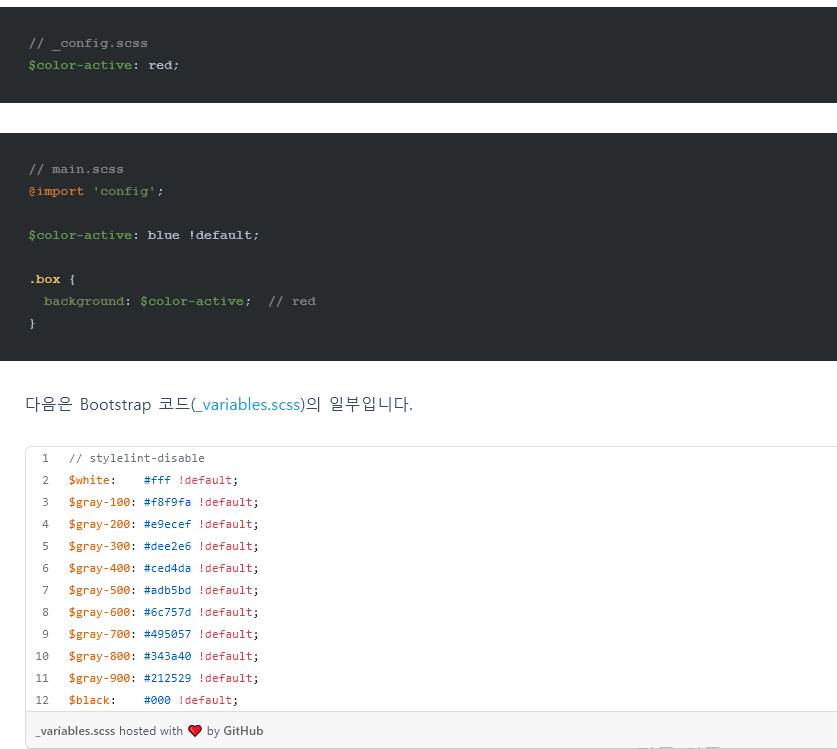
!default(초깃값 설정)
SCSS:
$color-primary: red;//전역으로 선언
.box {
$color-primary: blue !default; 부모안에서 선언을 했지만, 전역(초깃값)으로 적용
background: $color-primary;
}
Compiled to:
.box {
background: red;
}
‘변수와 값을 설정하겠지만, 혹시 기존 변수가 있을 경우는 현재 설정하는 변수의 값은 사용하지 않겠다’는 의미로 쓸 수 있다.
ex. 외부 라이브러리 연결했더니 변수이름이 같아 자신이 작성한 코드의 변수들이 덮어쓰기(Overwrite)된다면 문제가 된다.
이럴때, 라이브러리에 사용하는 변수에 !defult플래그가 있다면 기존 코드를overwrite 하지 않고 사용할 수 있다.
#{} (문자 보간)
#{}를 이용해서 코드의 어디든지 변수 값을 넣을 수 있다.
$family: unquote("Droid+Sans");
@import url("http://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=#{$family}");
@import url("http://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Droid+Sans");
Sass의 내장 함수 unquote()는 문자에서 따옴표를 제거한다.
가져오기(Import)
@import로 외부에서 가져온 Sass 파일은 모두 단일 CSS 출력 파일로 병합된다.
또한, 가져온 파일에 정의된 모든 변수 또는 Mixins 등을 주 파일에서 사용할 수 있다.
Sass @import는 기본적으로 Sass 파일을 가져오는데,
CSS @import 규칙으로 컴파일되는 몇 가지 상황이 있다.
- 파일 확장자가 .css일 때
- 파일 이름이 http://로 시작하는 경우
- url()이 붙었을 경우
- 미디어쿼리가 있는 경우
위의 경우 CSS @import 규칙대로 컴파일 됩니다.
@import "hello.css";
@import "http://hello.com/hello";
@import url(hello);
@import "hello" screen;여러 파일 가져오기
하나의 @import로 여러 파일을 가져올 수도 있다.(파일 이름은 ,로 구분한다.)
@import "header", "footer";파일 분할(Partials)
프로젝트 규모가 커지면 파일들을 header나 side-menu 같이 각 기능과 부분으로 나눠 유지보수가 쉽도록 관리하게 된다.
이 경우 파일이 점점 많아지는데, 모든 파일이 컴파일 시 각각의 ~.css 파일로 나눠서 저장된다면 관리나 성능 차원에서 문제가 될 수 있다.
파일 이름 앞에 _를 붙여(_header.scss와 같이) @import로 가져오면 컴파일 시 ~.css 파일로 컴파일하지 않는다.
Sass-App
# ...
├─scss
│ ├─header.scss
│ ├─side-menu.scss
│ └─main.scss
# ...
main.scss로 나머지 ~.scss 파일을 가져온다.
// main.scss
@import "header", "side-menu";그리고 이 파일들을 css/디렉토리로 컴파일합니다.
(컴파일은 위에서 설명한 node-sass로 진행합니다.)
# `scss`디렉토리에 있는 파일들을 `css`디렉토리로 컴파일
$ node-sass scss --output css컴파일 후 확인하면 아래와 같이 scss/에 있던 파일들이 css/ 안에 각 하나씩의 파일로 컴파일된다.
Sass-App
# ...
├─css
│ ├─header.css
│ ├─side-menu.css
│ └─main.css
├─scss
│ ├─header.scss
│ ├─side-menu.scss
│ └─main.scss
# ...👉가져올 파일 이름에 _를 붙힌다면
(메인파일main.scss에서는 를사용하지 않고)
Sass-App
# ...
├─scss
│ ├─_header.scss
│ ├─_side-menu.scss
│ └─main.scss
# ...
// main.scss
@import "header", "side-menu";
Compiled to:
$ node-sass scss --output css
아래처럼 별도의 파일로 컴파일되지 않고 사용됩니다.
Sass-App
# ...
├─css
│ └─main.css # main + header + side-menu
├─scss
│ ├─header.scss
│ ├─side-menu.scss
│ └─main.scss
# ...연산(Operations)
✍산술 연산자:
| 종류 | 설명 | 주의사항 |
|---|---|---|
| + | 더하기 | |
| - | 빼기 | |
| * | 곱하기 | 하나 이상의 값이 반드시 숫자 |
| / | 나누기 | 오른쪽 값이 반드시 숫자 |
| % | 나머지 |
✍비교 연산자:
| 종류 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| == | 동등 |
| != | 부등 |
| < | 대소/보다 작은 |
| > | 대소/보다 큰 |
| <= | 대소 및 동등 /보다 작거나 같은 |
| >= | 대소 및 동등 /보다 크거나 같은 |
✍논리(불린, Boolean) 연산자:
| 종류 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| and | 그리고 |
| or | 또는 |
| not | 부정 |
숫자(Numbers)
상대적 단위 연산
-일반적으론 절댓값을 나타내는 px 단위로 연산을 합니다만, 상대적 단위(%, em, vw 등)의 연산의 경우 CSS calc()로 연산해야 합니다.
width: 50% - 20px; // 단위 모순 에러(Incompatible units error)
width: calc(50% - 20px); // 연산 가능나누기 연산의 주의사항
-CSS는 속성 값의 숫자를 분리하는 방법으로 /를 허용하기 때문에 /가 나누기 연산으로 사용되지 않을 수 있다.
예를 들어, font: 16px / 22px serif; 같은 경우 font-size: 16px와 line-height: 22px의 속성값 분리를 위해서 /를 사용한다.
아래 예제를 보면 나누기 연산자만 연산 되지 않고 그대로 컴파일됩니다.
SCSS:
div {
width: 20px + 20px; // 더하기
height: 40px - 10px; // 빼기
font-size: 10px * 2; // 곱하기
margin: 30px / 2; // 나누기
}
Compiled to:
div {
width: 40px; /* OK */
height: 30px; /* OK */
font-size: 20px; /* OK */
margin: 30px / 2; /* ?? */
}
/를 나누기 연산 기능으로 사용하려면 다음과 같은 조건을 충족해야 합니다.
- 값 또는 그 일부가 변수에 저장되거나 함수에 의해 반환되는 경우
- 값이 ()로 묶여있는 경우
- 값이 다른 산술 표현식의 일부로 사용되는 경우
SCSS:
div {
$x: 100px;
width: $x / 2; // 변수에 저장된 값을 나누기
height: (100px / 2); // 괄호로 묶어서 나누기
font-size: 10px + 12px / 3; // 더하기 연산과 같이 사용
}
Compiled to:
div {
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
font-size: 14px;
}
문자(Strings) 주의사항
문자 연산에는 +가 사용된다.
문자 연산의 결과는 첫 번째 피연산자를 기준으로 한다.
첫 번째 피연산자에 따옴표가(" ") 붙어잇으면, 연산 결과를 따옴표로 묶는다.
반대로 첫번째 피연산자에 따옴표가(" ") 붙어있지 않으면, 연산 결과도 따옴표 처리를 하지 않는다.
SCSS:
div::after {
content: "Hello " + World;
flex-flow: row + "-reverse" + " " + wrap
}
//Compiled to:
div::after {
content: "Hello World";
flex-flow: row-reverse wrap;
}
색상(Colors)
SCSS:
div {
color: #123456 + #345678;
// R: 12 + 34 = 46
// G: 34 + 56 = 8a
// B: 56 + 78 = ce
background: rgba(50, 100, 150, .5) + rgba(10, 20, 30, .5);
// R: 50 + 10 = 60
// G: 100 + 20 = 120
// B: 150 + 30 = 180
// A: Alpha channels must be equal
}
//Compiled to:
div {
color: #468ace;
background: rgba(60, 120, 180, 0.5);
}
RGBA에서 Alpha 값은 연산되지 않으며 서로 동일해야 다른 값의 연산이 가능하다.
Alpha 값을 연산하기 위한 다음과 같은 색상 함수(Color Functions)를 사용할 수 있다.
✍opacify(), transparentize()
SCSS:
$color: rgba(10, 20, 30, .5);
div {
color: opacify($color, .3); // 30% 더 불투명하게 / 0.5 + 0.3
background-color: transparentize($color, .2); // 20% 더 투명하게 / 0.5 - 0.2
}
//Compiled to:
div {
color: rgba(10, 20, 30, 0.8);
background-color: rgba(10, 20, 30, 0.3);
}논리(Boolean)
Sass의 @if 조건문에서 사용되는 논리(Boolean) 연산에는 ‘그리고’,’ 또는’, ‘부정’이 있다.
자바스크립트 문법에 &&, ||, !와 같은 기능으로 생각하면 된다.
| 종류 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| and | 그리고 |
| or | 또는 |
| not | 부정 |
SCSS:
$width: 90px;
div {
@if not ($width > 100px) {//width(90px)가 100px보다 크다면(not이니까 -> 크지 않다면
height: 300px;
}
}
//Compiled to:
div {
height: 300px;
}
-----------------------------------------------
SCSS:
$w: 100px
.item{
display:block;
@if ($w > 150px){(w(100px)가 50px보다 크다면)
width:400px;
}
}
//Compiled to:
.item{
display:block;
//$w가 150px보다 작기때문에 적용이 안된다.
}
-----------------------------------------------
SCSS:
$w: 100px
.item{
display:block;
@if ($w > 50px){(w(100px)가 50px보다 크다면)
width:400px;
}
}
//Compiled to:
.item{
display:block;
//$w가 150px보다 작기때문에 적용이 안된다.
}
-----------------------------------------------
SCSS:
$w: 100px
.item{
display:block;
@if ($w > 50px and $w << 90px ){//오류나서<<두개 표지 원래는 하나만.
//$w(100px)가 50px보다 크고, 90px보다 작으면)
width:400px;
}
}
//Compiled to:
.item{
display:block;
//$w가 50px보단 큭지만, 90px보다도 크기때문에 적용안됨
}재활용(Mixins)
스타일 시트 전체에서 재사용 할 CSS 선언 그룹 을 정의한다. 1. 선언하기(@mixin)
2. 포함하기(@include)
-만들어서(선언), 사용(포함)한다.
@mixin size($w: 100px, $h: 100px){
width:$w;
height:$h;
}
.box1{
@include size(100px, 100px);
}
.box2{
@include size;
}
.box3{
@include size(200px, 300px);
}
.box4{
@include size($h:300px);
}
//Compiled to:
.box1{
width:100px;
height:100px;
}
.box2{
width:100px;
height:100px;
}
.box3{
width:200px;
height:300px;
}
.box4{
width:100px;
height:300px;
}
✍@mixin
@mixin 지시어를 이용하여 스타일을 정의힌디/
// SCSS
@mixin 믹스인이름 {
스타일;
}
.
// Sass
=믹스인이름
스타일
// SCSS
@mixin large-text {
font-size: 22px;
font-weight: bold;
font-family: sans-serif;
color: orange;
}
// Sass
=large-text
font-size: 22px
font-weight: bold
font-family: sans-serif
color: orangeMixin은 선택자를 포함 가능하고 상위(부모) 요소 참조(& 같은)도 할 수 있다.
@mixin large-text {
font: {
size: 22px;
weight: bold;
family: sans-serif;
}
color: orange;
&::after {
content: "!!";
}
span.icon {
background: url("/images/icon.png");
}
}
.box1{
@include large-text;
}
//Compiled to:
.box1 {
font-size: 22px;
font-weight: bold;
font-family: sans-serif;
color: orange;
}
.box1::after {
content: "!!";
}
.box1 span.icon {
background: url("/images/icon.png");
}
✍@include
선언된 Mixin을 사용(포함)하기 위해서는 @include가 필요하다.
// SCSS
@include 믹스인이름;
.
// Sass
+믹스인이름
// SCSS
h1 {
@include large-text;
}
div {
@include large-text;
}
// Sass
h1
+large-text
div
+large-text
//Compiled to:
h1 {
font-size: 22px;
font-weight: bold;
font-family: sans-serif;
color: orange;
}
h1::after {
content: "!!";
}
h1 span.icon {
background: url("/images/icon.png");
}
div {
font-size: 22px;
font-weight: bold;
font-family: sans-serif;
color: orange;
}
div::after {
content: "!!";
}
div span.icon {
background: url("/images/icon.png");
}인수(Arguments)
Mixin은 함수(Functions)처럼 인수(Arguments)를 가질 수 있다.
// SCSS
@mixin 믹스인이름($매개변수) {
스타일;
}
@include 믹스인이름(인수);
// Sass
=믹스인이름($매개변수)
스타일
+믹스인이름(인수)
매개변수(Parameters)란(dash-line) 변수의 한 종류로, 제공되는 여러 데이터 중 하나를 가리키기 위해 사용된다.
제공되는 여러 데이터들을 전달인수(Arguments) 라고 부른다.
w, $h). 값은 인수(자, ex. 1px, 3px)라고 한다.
@mixin dash-line($width, $color) {
border: $width dashed $color;
}
.box1 { @include dash-line(1px, red); }
.box2 { @include dash-line(4px, blue); }
//Compiled to:
.box1 {
border: 1px dashed red;
}
.box2 {
border: 4px dashed blue;
}
✍인수의 기본값 설정
인수(argument)는 기본값(default value)을 가질 수 있다.
@include 포함 단계에서 별도의 인수가 전달되지 않으면 기본값이 사용된다.
@mixin 믹스인이름($매개변수: 기본값) {
스타일;
}
@mixin dash-line($width: 1px, $color: black) {
border: $width dashed $color;
}
.box1 { @include dash-line; }
.box2 { @include dash-line(4px); }
//Compiled to:
.box1 {
border: 1px dashed black;
}
.box2 {
border: 4px dashed black;
}✍키워드 인수(Keyword Arguments)
Mixin에 전달할 인수를 입력할 때 명시적으로 키워드(변수)를 입력하여 작성할 수 있다.
별도의 인수 입력 순서를 필요로 하지 않아 편리하게 작성할 수 있다.
단, 작성하지 않은 인수가 적용될 수 있도록 기본값을 설정해 주는 것이 좋다.
@mixin 믹스인이름($매개변수A: 기본값, $매개변수B: 기본값) {
스타일;
}
@include 믹스인이름($매개변수B: 인수);
@mixin position(
$p: absolute,
$t: null,
$b: null,
$l: null,
$r: null
) {
position: $p;
top: $t;
bottom: $b;
left: $l;
right: $r;
}
.absolute {
// 키워드 인수로 설정할 값만 전달
@include position($b: 10px, $r: 20px);
}
.fixed {
// 인수가 많아짐에 따라 가독성을 확보하기 위해 줄바꿈
@include position(
fixed,
$t: 30px,
$r: 40px
);
}
.absolute {
position: absolute;
bottom: 10px;
right: 20px;
}
.fixed {
position: fixed;
top: 30px;
right: 40px;
}
✍가변 인수(Variable Arguments)
입력할 인수의 개수가 불확실한 경우가 있는데, 그럴때 사용한다.
가변 인수는 매개변수 뒤에 ...을 붙여준다.
@mixin 믹스인이름($매개변수...) {
스타일;
}
@include 믹스인이름(인수A, 인수B, 인수C);
// 인수를 순서대로 하나씩 전달 받다가, 3번째 매개변수($bg-values)는 인수의 개수에 상관없이 받음
@mixin bg($width, $height, $bg-values...) {
width: $width;
height: $height;
background: $bg-values;
}
div {
// 위의 Mixin(bg) 설정에 맞게 인수를 순서대로 전달하다가 3번째 이후부터는 개수에 상관없이 전달
@include bg(
100px,
200px,
url("/images/a.png") no-repeat 10px 20px,
url("/images/b.png") no-repeat,
url("/images/c.png")
);
}
div {
width: 100px;
height: 200px;
background: url("/images/a.png") no-repeat 10px 20px,
url("/images/b.png") no-repeat,
url("/images/c.png");
}
인수를 받는 매개변수에 ...을 사용하여 가변 인수를 활용했다.
반대로 가변 인수를 전달할 값으로 사용해 본다면,
@mixin font(
$style: normal,
$weight: normal,
$size: 16px,
$family: sans-serif
) {
font: {
style: $style;
weight: $weight;
size: $size;
family: $family;
}
}
div {
// 매개변수 순서와 개수에 맞게 전달
$font-values: italic, bold, 16px, sans-serif;
@include font($font-values...);
}
span {
// 필요한 값만 키워드 인수로 변수에 담아 전달
$font-values: (style: italic, size: 22px);
@include font($font-values...);
}
a {
// 필요한 값만 키워드 인수로 전달
@include font((weight: 900, family: monospace)...);
}
div {
font-style: italic;
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 16px;
font-family: sans-serif;
}
span {
font-style: italic;
font-weight: normal;
font-size: 22px;
font-family: sans-serif;
}
a {
font-style: normal;
font-weight: 900;
font-size: 16px;
font-family: monospace;
}@content
선언된 Mixin에 @content이 포함되어 있다면 해당 부분에 원하는 스타일 블록 을 전달할 수 있다.
이 방식을 사용하여 기존 Mixin이 가지고 있는 기능에 선택자나 속성 등을 추가할 수 있다.
@mixin 믹스인이름() {
스타일;
@content;
}
.
@include 믹스인이름() {
// 스타일 블록
스타일;
}
SCSS:
@mixin icon($url) {
&::after {
content: $url;
@content;
}
}
.icon1 {
// icon Mixin의 기존 기능만 사용
@include icon("/images/icon.png");
}
.icon2 {
// icon Mixin에 스타일 블록을 추가하여 사용
@include icon("/images/icon.png") {
position: absolute;
};
}
//Compiled to:
.icon1::after {
content: "/images/icon.png";
}
.icon2::after {
content: "/images/icon.png";
position: absolute;
}
//Mixin에게 전달된 스타일 블록은 Mixin의 범위가 아니라 스타일 블록이 정의된 범위에서 평가된다.
//Mixin의 매개변수는 전달된 스타일 블록 안에서 사용되지 않고 전역 값
//전역 변수(Global variables)와 지역 변수(Local variables)로 생각해보기
SCSS:
$color: red;
@mixin colors($color: blue) {
// Mixin의 범위
@content;
background-color: $color;
border-color: $color;
}
div {
@include colors() {
// 스타일 블록이 정의된 범위
color: $color;
}
}
//Compiled to:
div {
color: red;
background-color: blue;
border-color: blue;
}
확장(Extend)
특정 선택자가 다른 선택자의 모든 스타일을 가져야하는 경우
(선택자의 확장 기능을 사용)
@extend 선택자;
SCSS:
.btn {
padding: 10px;
margin: 10px;
background: blue;
}
.btn-danger {
@extend .btn;
background: red;
}
//Compiled to:
.btn, .btn-danger {
padding: 10px;
margin: 10px;
background: blue;
}
.btn-danger {
background: red;
}@extend 주의사항
- 내 현재 선택자(위 예제의 .btn-danger)가 어디에 첨부될 것인가?
- 원치 않는 부작용이 초래될 수도 있는가?
- 이 한 번의 확장으로 얼마나 큰 CSS가 생성되는가?
-확장은 사용 권장X, Mixin 권장
함수(Functions)
자신의 함수를 정의
함수와 Mixins은 거의 유사하지만 반환되는 내용이 다르다.
Mixin은 위에서 살펴본 대로 지정한 스타일(Style)을 반환하는 반면,
함수는 보통 연산된(Computed) 특정 값을 @return 지시어를 통해 반환한다.
// Mixins
@mixin 믹스인이름($매개변수) {
스타일;
}
// Functions
@function 함수이름($매개변수) {
@return 값
}Mixin은 @include 지시어를 사용하는 반면,
함수는 함수이름으로 바로 사용한다.
// Mixin
@include 믹스인이름(인수);
.
// Functions
함수이름(인수)
SCSS:
$max-width: 980px;
@function columns($number: 1, $columns: 12) {
@return $max-width * ($number / $columns)
}
.box_group {
width: $max-width;
.box1 {
width: columns(); // 1
}
.box2 {
width: columns(8);
}
.box3 {
width: columns(3);
}
}
//Compiled to:
.box_group {
/* 총 너비 */
width: 980px;
}
.box_group .box1 {
/* 총 너비의 약 8.3% */
width: 81.66667px;
}
.box_group .box2 {
/* 총 너비의 약 66.7% */
width: 653.33333px;
}
.box_group .box3 {
/* 총 너비의 25% */
width: 245px;
}@include 같은 별도의 지시어 없이 사용하기 때문에 내가 지정한 함수와 내장 함수(Built-in Functions)의 이름이 충돌할 수 있다.
따라서 내가 지정한 함수에는 별도의 접두어를 붙여주는 것이 좋다.
내장 함수란, 응용 프로그램에 내장되어 있으며 최종 사용자가 액세스 할 수 있는 기능
예를 들어, 대부분의 스프레드 시트 응용 프로그램은 행이나 열의 모든 셀을 추가하는 내장 SUM 함수를 지원한다.
예를 들어, 색의 빨강 성분을 가져오는 내장 함수로 이미 red()가 있습니다.
같은 이름을 사용하여 함수를 정의하면 이름이 충돌하기 때문에 별도의 접두어를 붙여 extract-red() 같은 이름을 만들 수 있습니다.
// 내가 정의한 함수
@function extract-red($color) {
// 내장 함수
@return rgb(red($color), 0, 0);
}
div {
color: extract-red(#D55A93);
}
//혹은 모든 내장 함수의 이름을 다 알고 있을 수 없기 때문에
특별한 이름을 접두어로 사용할 수도 있다.
my-custom-func-red()조건과 반복(Control Directives / Expressions)
✍ if (함수)
조건의 값(true, false)에 따라 두 개의 표현식 중 하나만 반환한다.
if(조건, 표현식1, 표현식2)
$width: 555px;
div {
width: if($width > 300px, $width, null);
}
//Compiled to:
div {
width: 555px;
}✍ @if (지시어)
@if 지시어는 조건에 따른 분기 처리가 가능하며, if 문(if statements)과 유사하다.
같이 사용할 수 있는 지시어는 @else, if
// @if
@if (조건) {
/ 조건이 참일 때 구문 /
}
.
// @if @else
@if (조건) {
/ 조건이 참일 때 구문 /
} @else {
/ 조건이 거짓일 때 구문 /
}
.
// @if @else if
@if (조건1) {
/ 조건1이 참일 때 구문 /
} @else if (조건2) {
/ 조건2가 참일 때 구문 /
} @else {
/ 모두 거짓일 때 구문 /
}조건에 ()는 생략이 가능
$bg: true;
div {
@if $bg {
background: url("/images/a.jpg");
}
}
SCSS:
$color: orange;
div {
@if $color == strawberry {
color: #FE2E2E;
} @else if $color == orange {
color: #FE9A2E;
} @else if $color == banana {
color: #FFFF00;
} @else {
color: #2A1B0A;
}
}
//Compiled to:
div {
color: #FE9A2E;
}
조건에는 논리 연산자 and, or, not을 사용할 수 있다.
SCSS:
@function limitSize($size) {
@if $size >= 0 and $size <<= 200px {
@return 200px;
} @else {
@return 800px;
}
}
div {
width: limitSize(180px);
height: limitSize(340px);
}
//Compiled to:
div {
width: 200px;
height: 800px;
}Sass의 내장 함수 unitless()는 숫자에 단위가 있는지 여부를 반환한다.
SCSS:
@mixin pCenter($w, $h, $p: absolute) {
@if
$p == absolute
or $p == fixed
// or not $p == relative
// or not $p == static
{
width: if(unitless($w), #{$w}px, $w);
height: if(unitless($h), #{$h}px, $h);
position: $p;
top: 0;
bottom: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
margin: auto;
}
}
.box1 {
@include pCenter(10px, 20px);
}
.box2 {
@include pCenter(50, 50, fixed);
}
.box3 {
@include pCenter(100, 200, relative);
}
//Compiled to:
.box1 {
width: 10px;
height: 20px;
position: absolute;
top: 0;
bottom: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
margin: auto;
}
.box2 {
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
position: fixed;
top: 0;
bottom: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
margin: auto;
}✍ @for
@for는 스타일을 반복적으로 출력(for 문과 유사)
@for는 through를 사용하는 형식과 to를 사용하는 형식으로 나뉜다.
두 형식은 종료 조건이 해석되는 방식이 다르다.
// through
// 종료 만큼 반복
@for $변수 from 시작 through 종료 {
// 반복 내용
}
.
// to
// 종료 직전까지 반복
@for $변수 from 시작 to 종료 {
// 반복 내용
}
SCSS:
// 1부터 3번 반복
@for $i from 1 through 3 {
.through:nth-child(#{$i}) {
width : 20px * $i
}
}
// 1부터 3 직전까지만 반복(2번 반복)
@for $i from 1 to 3 {
.to:nth-child(#{$i}) {
width : 20px * $i
}
}
//Compiled to:
.through:nth-child(1) { width: 20px; }
.through:nth-child(2) { width: 40px; }
.through:nth-child(3) { width: 60px; }
.to:nth-child(1) { width: 20px; }
.to:nth-child(2) { width: 40px; }to는 주어진 값 직전까지만 반복해야할 경우 유용할 수 있다.
그러나 :nth-child()에서 특히 유용하게 사용되는 @for는 일반적으로 through를 사용하길 권장
✍ @each
@each는 List와 Map 데이터를 반복할 때 사용(for in 문과 유사)
@each $변수 in 데이터 {
// 반복 내용
}
List 데이터를 반복
SCSS:
// List Data
$fruits: (apple, orange, banana, mango);
.fruits {
@each $fruit in $fruits {
li.#{$fruit} {
background: url("/images/#{$fruit}.png");
}
}
}
//Compiled to:
.fruits li.apple {
background: url("/images/apple.png");
}
.fruits li.orange {
background: url("/images/orange.png");
}
.fruits li.banana {
background: url("/images/banana.png");
}
.fruits li.mango {
background: url("/images/mango.png");
}혹시 매번 반복마다 Index 값이 필요하다면 다음과 같이 index() 내장 함수를 사용할 수 있다.
SCSS:
$fruits: (apple, orange, banana, mango);
.fruits {
@each $fruit in $fruits {
$i: index($fruits, $fruit);
li:nth-child(#{$i}) {
left: 50px * $i;
}
}
}
//Compiled to:
.fruits li:nth-child(1) {
left: 50px;
}
.fruits li:nth-child(2) {
left: 100px;
}
.fruits li:nth-child(3) {
left: 150px;
}
.fruits li:nth-child(4) {
left: 200px;
}동시에 여러 개의 List 데이터를 반복 처리할 수도 있다.
단, 각 데이터의 Length가 같아야 함
SCSS:
$apple: (apple, korea);
$orange: (orange, china);
$banana: (banana, japan);
@each $fruit, $country in $apple, $orange, $banana {
.box-#{$fruit} {
background: url("/images/#{$country}.png");
}
}
//Compiled to:
.box-apple {
background: url("/images/korea.png");
}
.box-orange {
background: url("/images/china.png");
}
.box-banana {
background: url("/images/japan.png");
}Map 데이터를 반복할 경우 하나의 데이터에 두 개의 변수가 필요한다.
@each $key변수, $value변수 in 데이터 {
// 반복 내용
}
$fruits-data: (
apple: korea,
orange: china,
banana: japan
);
@each $fruit, $country in $fruits-data {
.box-#{$fruit} {
background: url("/images/#{$country}.png");
}
}
//Compiled to:
.box-apple {
background: url("/images/korea.png");
}
.box-orange {
background: url("/images/china.png");
}
.box-banana {
background: url("/images/japan.png");
}✍ @while
@while은 조건이 false로 평가될 때까지 내용을 반복
(while 문과 유사하게 잘못된 조건으로 인해 컴파일 중 무한 루프에 빠질 수 있음. 사용을 권장X)
@while 조건 {
// 반복 내용
}
$i: 6;
@while $i > 0 {
.item-#{$i} {
width: 2px * $i;
}
$i: $i - 2;
}
//Compiled to:
.item-6 { width: 12px; }
.item-4 { width: 8px; }
.item-2 { width: 4px; }내장 함수(Built-in Functions)
Sass Built-in Functions에서 모든 내장 함수를 확인할 수 있다.
- []는 선택 가능한 인수(argument)입니다.
- Zero-based numbering을 사용하지 않습니다.
✍ 색상(RGB / HSL / Opacity) 함수
mix($color1, $color2) : 두 개의 색을 섞습니다.
lighten($color, $amount) : 더 밝은색을 만듭니다.
darken($color, $amount) : 더 어두운색을 만듭니다.
saturate($color, $amount) : 색상의 채도를 올립니다.
desaturate($color, $amount) : 색상의 채도를 낮춥니다.
grayscale($color) : 색상을 회색으로 변환합니다.
invert($color) : 색상을 반전시킵니다.
rgba($color, $alpha) : 색상의 투명도를 변경합니다.
opacify(color, $amount) / fade-in(color, $amount) : 색상을 더 불투명하게 만듭니다.
transparentize(color, $amount) / fade-out(color, $amount) : 색상을 더 투명하게 만듭니다.
✍ 문자(String) 함수
unquote($string) : 문자에서 따옴표를 제거합니다.
quote($string) : 문자에 따옴표를 추가합니다.
str-insert($string, $insert, $index) : 문자의 index번째에 특정 문자를 삽입합니다.
str-index($string, $substring) : 문자에서 특정 문자의 첫 index를 반환합니다.
str-slice(string, $start-at, [end-at]) : 문자에서 특정 문자(몇 번째 글자부터 몇 번째 글자까지)를 추출합니다.
to-upper-case($string) : 문자를 대문자를 변환합니다.
to-lower-case($string) : 문자를 소문자로 변환합니다.
✍ 숫자(Number) 함수
percentage($number) : 숫자(단위 무시)를 백분율로 변환합니다.
round($number) : 정수로 반올림합니다.
ceil($number) : 정수로 올림합니다.
floor($number) : 정수로 내림(버림)합니다.
abs($number) : 숫자의 절대 값을 반환합니다.
min($numbers…) : 숫자 중 최소 값을 찾습니다.
max($numbers…) : 숫자 중 최대 값을 찾습니다.
random() : 0 부터 1 사이의 난수를 반환합니다.
✍ List 함수
모든 List 내장 함수는 기존 List 데이터를 갱신하지 않고 새 List 데이터를 반환합니다.
모든 List 내장 함수는 Map 데이터에서도 사용할 수 있습니다.
length($list) : List의 개수를 반환합니다.
nth($list, $n) : List에서 n번째 값을 반환합니다.
set-nth($list, $n, $value) : List에서 n번째 값을 다른 값으로 변경합니다.
join(list1, $list2, [separator]) : 두 개의 List를 하나로 결합합니다.
zip($lists…) : 여러 List들을 하나의 다차원 List로 결합합니다.
index($list, $value) : List에서 특정 값의 index를 반환합니다.
✍ Map 함수
모든 Map 내장 함수는 기존 Map 데이터를 갱신하지 않고 새 Map 데이터를 반환합니다.
map-get($map, $key) : Map에서 특정 key의 value를 반환합니다.
map-merge($map1, $map2) : 두 개의 Map을 병합하여 새로운 Map를 만듭니다.
map-keys($map) : Map에서 모든 key를 List로 반환합니다.
map-values($map) : Map에서 모든 value를 List로 반환합니다.
✍ 관리(Introspection) 함수
variable-exists(name) : 변수가 현재 범위에 존재하는지 여부를 반환합니다.(인수는 $없이 변수의 이름만 사용합니다.)
unit($number) : 숫자의 단위를 반환합니다.
unitless($number) : 숫자에 단위가 있는지 여부를 반환합니다.
comparable($number1, $number2) : 두 개의 숫자가 연산 가능한지 여부를 반환합니다.
참고 출처
https://heropy.blog/2018/01/31/sass/
참고 자료(References)
http://sass-lang.com/documentation
https://www.sitepoint.com/sass-basics-operators/
https://sass-guidelin.es/ko/
http://www.thesassway.com/

