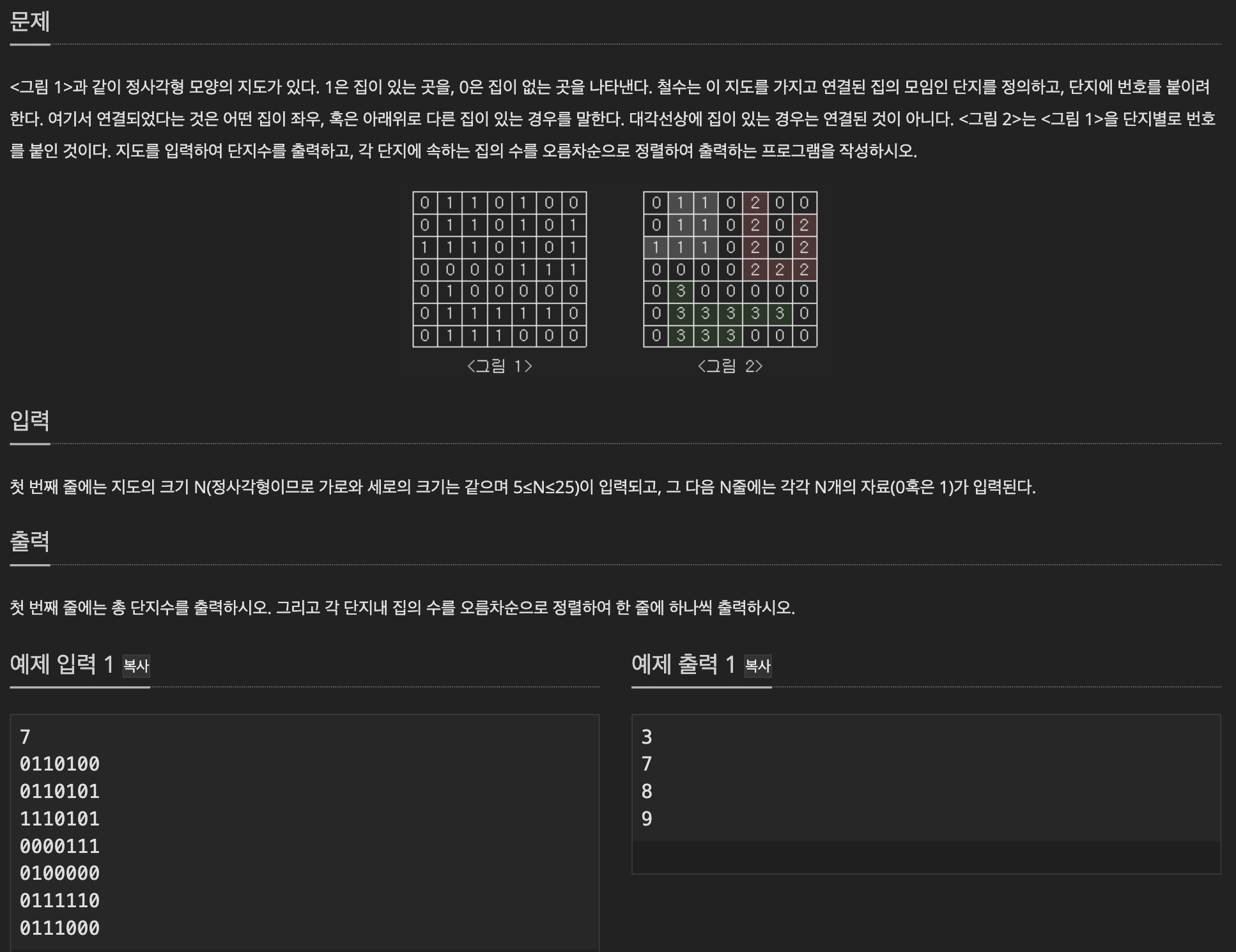
✅ 이전과 다른 점
시작이 0인 점
모든 배열에 대해 bfs를 실행해야 끊기지 않는다는 점
첫 시작이 0이므로 다음 bfs로 탐색한 배열의 수는 2가 아닌 1이 되어야 한다는 점bfs(0,0)에서 시작하면 다른 0을 만나면 끊긴다.
같은 단지가 다 다른 숫자로 바뀐다.
bfs(0, 0);
...
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int now[] = queue.poll();
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int nowX = now[0] + dx[k];
int nowY = now[1] + dy[k];
if (nowX >= 0 && nowY >= 0 && nowX < n && nowY < n) {
if (!visited[nowX][nowY] && A[nowX][nowY] == 1) {
visited[nowX][nowY] = true;
A[nowX][nowY] = A[now[0]][now[1]] + 1;
queue.add(new int[] {nowX, nowY});
}
}
}
}
bfs(i,j)에서 시작하면 전체 탐색은 된다.
하지만, 같은 단지가 다 다른 숫자로 바뀐다.
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
bfs(i, j);
}
System.out.println();
}
...
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int now[] = queue.poll();
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int nowX = now[0] + dx[k];
int nowY = now[1] + dy[k];
if (nowX >= 0 && nowY >= 0 && nowX < n && nowY < n) {
if (!visited[nowX][nowY] && A[nowX][nowY] == 1) {
visited[nowX][nowY] = true;
A[nowX][nowY] = A[now[0]][now[1]] + 1;
queue.add(new int[] {nowX, nowY});
}
}
}
}

✅ 필요한 것
bfs가 다시 시작되지 않고 계속 queue에서 게속될 때는 같은 단지라고 여긴다.
-> bfs가 실행될 때 dangi++한 후 몇 번이나 실행되었는지 count[dangi]++로 센다.✅ 코드
제일 처음 시작점 (1) 을 더해줘야 한다.
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(new int[] {x, y});
visited[x][y] = true;
count[danji]++;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Main {
static int[][] A;
static boolean[][] visited;
static int[] count;
static int danji = 0;
static int n = 0;
//우하좌상
static int[] dx = {0, 1, 0, -1}, dy = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
A = new int[n][n];
visited = new boolean[n][n];
count = new int[n * n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
String s = br.readLine();
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
A[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(s.substring(j, j + 1));
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (!visited[i][j] && A[i][j] == 1) {
danji++;
bfs(i, j);
}
}
}
Arrays.sort(count);
System.out.println(danji);
for (int n : count) {
if (n != 0) {
System.out.println(n);
}
}
}
private static void bfs(int x, int y) {
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(new int[] {x, y});
visited[x][y] = true;
count[danji]++;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int now[] = queue.poll();
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int nowX = now[0] + dx[k];
int nowY = now[1] + dy[k];
if (nowX >= 0 && nowY >= 0 && nowX < n && nowY < n) {
if (!visited[nowX][nowY] && A[nowX][nowY] == 1) {
visited[nowX][nowY] = true;
count[danji]++;
queue.add(new int[] {nowX, nowY});
}
}
}
}
}
}
