서론💡
우테코 선발과정이 끝나고 오랜만에 다시 알고리즘을 시작하였다. 알고리즘 스터디를 만들었고, 하루에 최소 한문제씩 문제를 해결하는 것이 목표이다.
DFS와 BFS를 공부하다가 알고리즘을 중단하였기에 블로그에 정리해둔 글과 강의를 통하여 잃어버린 감을 다시 찾으려고 노력하였다.
하지만 백준 2667 번 문제는 내가 처음 겪은 형식이였고, 많은 고민 끝에 문제를 해결하지 못하고 강의를 통해 해결하였다.
유튜브 강의 : 단지 번호 붙이기_자바 (백준 2667)
다른 사람들의 해설과 강의를 통해 약간의 힌트를 얻고 나머지는 스스로 해결하고자 했지만 생각보다 쉽지 않았다.😅
총 두가지 방식의 코드로 해결하였고, 처음 코드는 내가 힌트를 얻고 최초로 해결한 코드이며, 두번쨰 코드는 복습을 위해 다른 방식으로 해결하였다.
문제
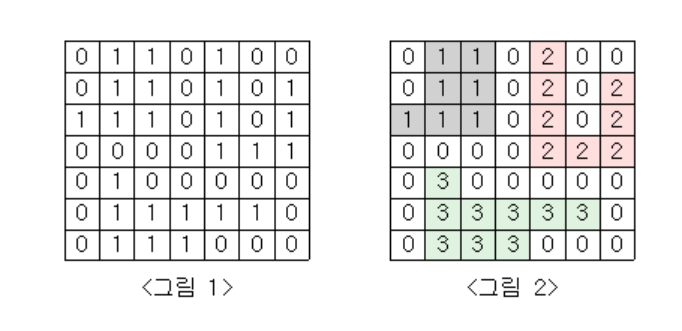
<그림 1>과 같이 정사각형 모양의 지도가 있다. 1은 집이 있는 곳을, 0은 집이 없는 곳을 나타낸다. 철수는 이 지도를 가지고 연결된 집의 모임인 단지를 정의하고, 단지에 번호를 붙이려 한다. 여기서 연결되었다는 것은 어떤 집이 좌우, 혹은 아래위로 다른 집이 있는 경우를 말한다. 대각선상에 집이 있는 경우는 연결된 것이 아니다. <그림 2>는 <그림 1>을 단지별로 번호를 붙인 것이다. 지도를 입력하여 단지수를 출력하고, 각 단지에 속하는 집의 수를 오름차순으로 정렬하여 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
입력
첫 번째 줄에는 지도의 크기 N(정사각형이므로 가로와 세로의 크기는 같으며 5≤N≤25)이 입력되고, 그 다음 N줄에는 각각 N개의 자료(0혹은 1)가 입력된다.
출력
첫 번째 줄에는 총 단지수를 출력하시오. 그리고 각 단지내 집의 수를 오름차순으로 정렬하여 한 줄에 하나씩 출력하시오.
예제 입력
7
0110100
0110101
1110101
0000111
0100000
0111110
0111000
예제 출력
3
7
8
9
풀이🔻
문제에서 가장 중요한 포인트를 생각해보자
- 1은 집이 있는 곳을, 0은 집이 없는 곳을 나타낸다.
- 연결되었다는 것은 어떤 집이 좌우, 혹은 아래위로 다른 집이 있는 경우를 말한다. 대각선상에 집이 있는 경우는 연결된 것이 아니다.
처음 문제를 보았을 때 2차원 배열을 활용해서 각 배열의 값이 1이냐 0이냐를 판단하고자 했다.
static int[][] complex; //1과 0을 저장할 이차원배열
complex = new int[N][N]; //지도 초기화
//단지 입력
String[] line = new String[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
String str = br.readLine();
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
//한줄씩 입력받아 1 혹은 0을 넣는다
complex[i][j] = Character.getNumericValue(str.charAt(j));
}
}그리고 만약 값이 1 이라면 주변의(상하좌우) 값이 1인지, 0인지 확인해야 함을 인지했다.
좌우, 혹은 아래위를 이동하기 위해 X좌표 배열과 Y좌표 배열을 사용하였다.
static int[] x = {0, 0, 1, -1};
static int[] y = {1, -1, 0, 0};만약 0이라면 다음 배열 위치로 넘어가고, 주변에 1이 있다면 그 위치에 DFS를 통하여 진입하고, 또 그 위치에서 주변에 1이 있는지 판단하여 재귀적으로 DFS를 호출한다.
//각 단지의 개수를 저장하기 위한 ArrayList를 하나 생성
ArrayList<Integer> countList = new ArrayList<> ();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (complex[i][j] == 1) { //만약 현재 위치의 값이 1이라면
countDanji = 0;
dfs(i, j); //dfs시작
countList.add(countDanji); //dfs종료후 리스트에 추가
}
}
}
가장 핵심 로직인 DFS메서드 이다.
1. 현재위치를 방문했다는 것을 기록하기 위해 현재 배열값을 1 -> 0으로 바꾸어준다
2. 단지의 개수를 1증가 시킨다.
3. 상하좌우가 1인지 0인지 판단하기 위해 현재 배열위치에서
(-1,0),(1,0),(0,-1),(0,1) 해주며 만약 조건에 맞는다면 DFS 메서드를 재귀호출한다.
java
static void dfs(int i, int j) {
complex[i][j] = 0;
countDanji++;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int newX = i + x[k];
int newY = j + y[k];
// 유효성 검사: 범위를 벗어나지 않고 값이 1인지 확인
if (newX >= 0 && newX < complex.length && newY >= 0 && newY < complex[0].length && complex[newX][newY] == 1) {
dfs(newX, newY);
}
}
}전체코드
1번 코드
- 단지 배열을 1과 0으로 채움
- 방문 기록을 단지 배열의 값을 1 -> 0로 바꾸는 것으로 판단
- BufferedWriter를 사용
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class B_2667 {
static int[][] complex;
static int countDanji;
static int[] x = {0, 0, 1, -1};
static int[] y = {1, -1, 0, 0};
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
//지도 크기 입력
int N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
//지도 초기화
complex = new int[N][N];
//visit 초기화
//지도 입력
String[] line = new String[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
String str = br.readLine();
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
complex[i][j] = Character.getNumericValue(str.charAt(j));
}
}
//돌면서 dfs;
ArrayList<Integer> countList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (complex[i][j] == 1) {
countDanji = 0;
dfs(i, j);
countList.add(countDanji);
}
}
}
//출력
bw.write(countList.size()+"\n");
Collections.sort(countList);
for (int i = 0; i < countList.size(); i++) {
bw.write(countList.get(i) +"\n");
}
//bw,br 종료
br.close();
bw.flush();
bw.close();
}
static void dfs(int i, int j) {
complex[i][j] = 0;
countDanji++;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int newX = i + x[k];
int newY = j + y[k];
// 유효성 검사: 범위를 벗어나지 않고 값이 1인지 확인
if (newX >= 0 && newX < complex.length && newY >= 0 && newY < complex[0].length && complex[newX][newY] == 1) {
dfs(newX, newY);
}
}
}
}2번 코드
- 단지 배열을 boolean형으로 true와 false로 채움
- 방문 기록을 boolean형 visited배열을 통해 true와 false로 구분함
- 단지 배열과 visited배열을 초기화 할 때 공간을 크게 할당하여
Index out of bounds for length에러를 예방함 - System.out 사용
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class B_2667_v2 {
static boolean[][] visited;
static boolean[][] complex;
static int countPerDanji;
static int[] dirX = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
static int[] dirY = {0, 0, -1, 1};
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
//지도 크기 입력
int N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
//초기화
visited = new boolean[N + 10][N + 10];
complex = new boolean[N + 10][N + 10];
//지도(complex) 초기값 설정
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
//한줄씩 입력
String str = br.readLine();
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++) {
if (str.charAt(j-1) == '1') {
complex[i][j] = true;
}
}
}
br.close();
ArrayList<Integer> danji = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++) {
if (complex[i][j] && !visited[i][j]) {
countPerDanji = 0;
dfs(i, j);
danji.add(countPerDanji);
}
}
}
System.out.println(danji.size());
Collections.sort(danji);
for (int i = 0; i < danji.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(danji.get(i));
}
}
//dfs 구현
static void dfs(int x, int y) {
visited[x][y] = true;
countPerDanji++;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int positionX = dirX[i] + x;
int positionY = dirY[i] + y;
if (!visited[positionX][positionY] && complex[positionX][positionY]) {
dfs(positionX, positionY);
}
}
}
}