학습 내용
1. 첫 번째 학습 내용: 인스턴스 메소드, 내부함수 호출
- 인스턴스 메소드
class Weekday {
func notifyLunch() -> String {
return "밥을 먹자!"
}
}
var day = Weekday()
print(day.notifyLunch())
// print 밥을 먹자!'day'란 인스턴스를 만들어주고, Weekday의 내부함수인 notifyLunch()를 호출하여 값을 받아냄.
→ 인스턴스를 만들고 내부함수 호출
참고자료
(Swift) 타입 메소드 & 인스턴스 메소드 by Jiseob Kim
yagom's Swift Basic 인스턴스의 생성과 소멸
2. 두 번째 학습 내용: CaseIterable 프로토콜로 배열 만들기
enum Fruit: CaseIterable {
case strawberry, banana, pineapple, kiwi, mango
}
print(Fruit.allCases)
// print [JuiceMaker.Fruit.strawberry, JuiceMaker.Fruit.banana, JuiceMaker.Fruit.pineapple, JuiceMaker.Fruit.kiwi, JuiceMaker.Fruit.mango]CaseIterable 프로토콜을 이용해서 배열을 만들어줬기 때문에 → allCases를 써줄 수 있었던 거임.
import Foundation
enum Exercise: CaseIterable {
case yoga, running, walking
}
Exercise.allCases
Exercise.allCases.count
Array(Exercise.allCases)
for exercise in Exercise.allCases {
print(exercise)
} // print yoga running walking참고자료
CaseIterable by Apple
Swift 4.2 변경사항 by Zedd
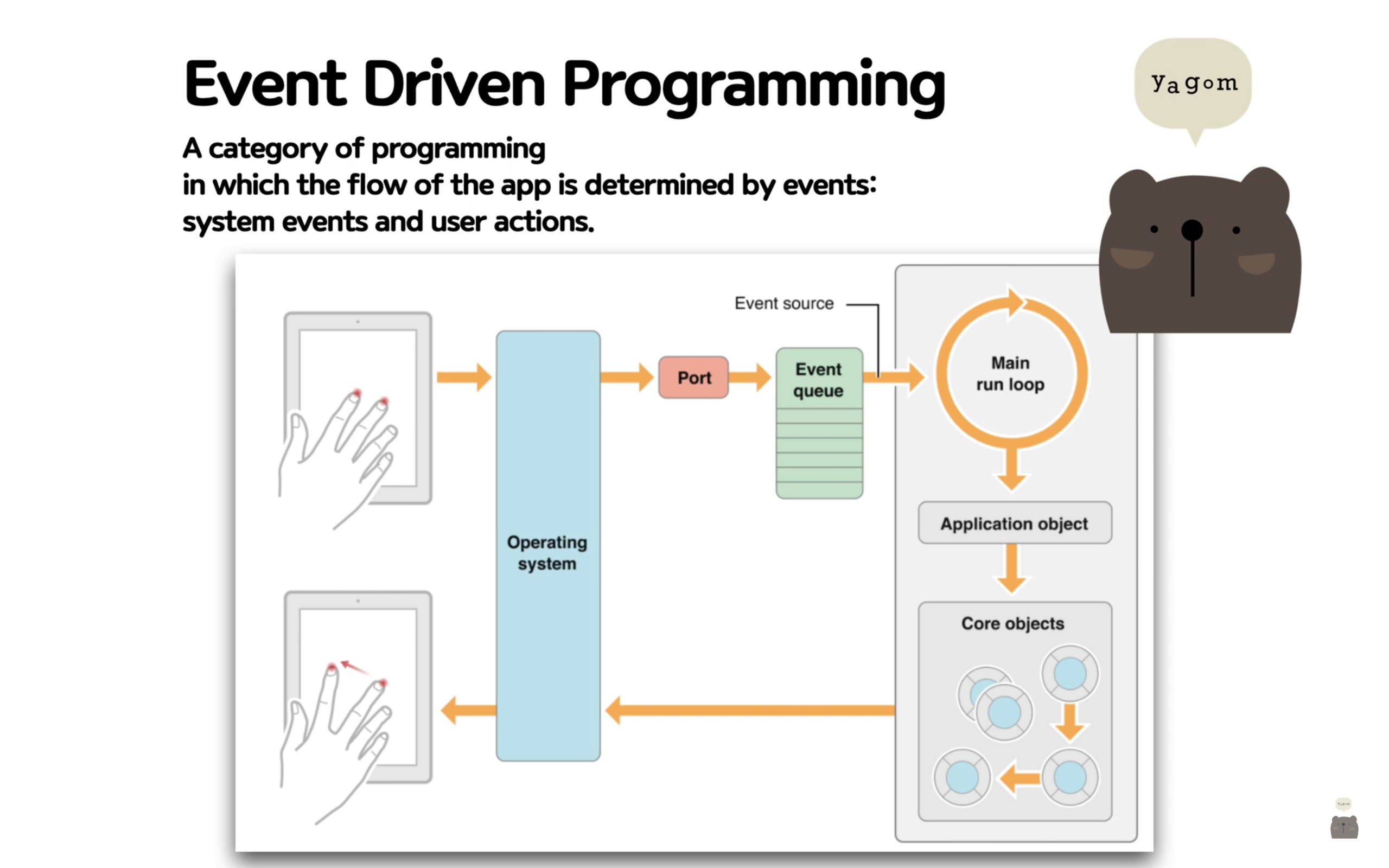
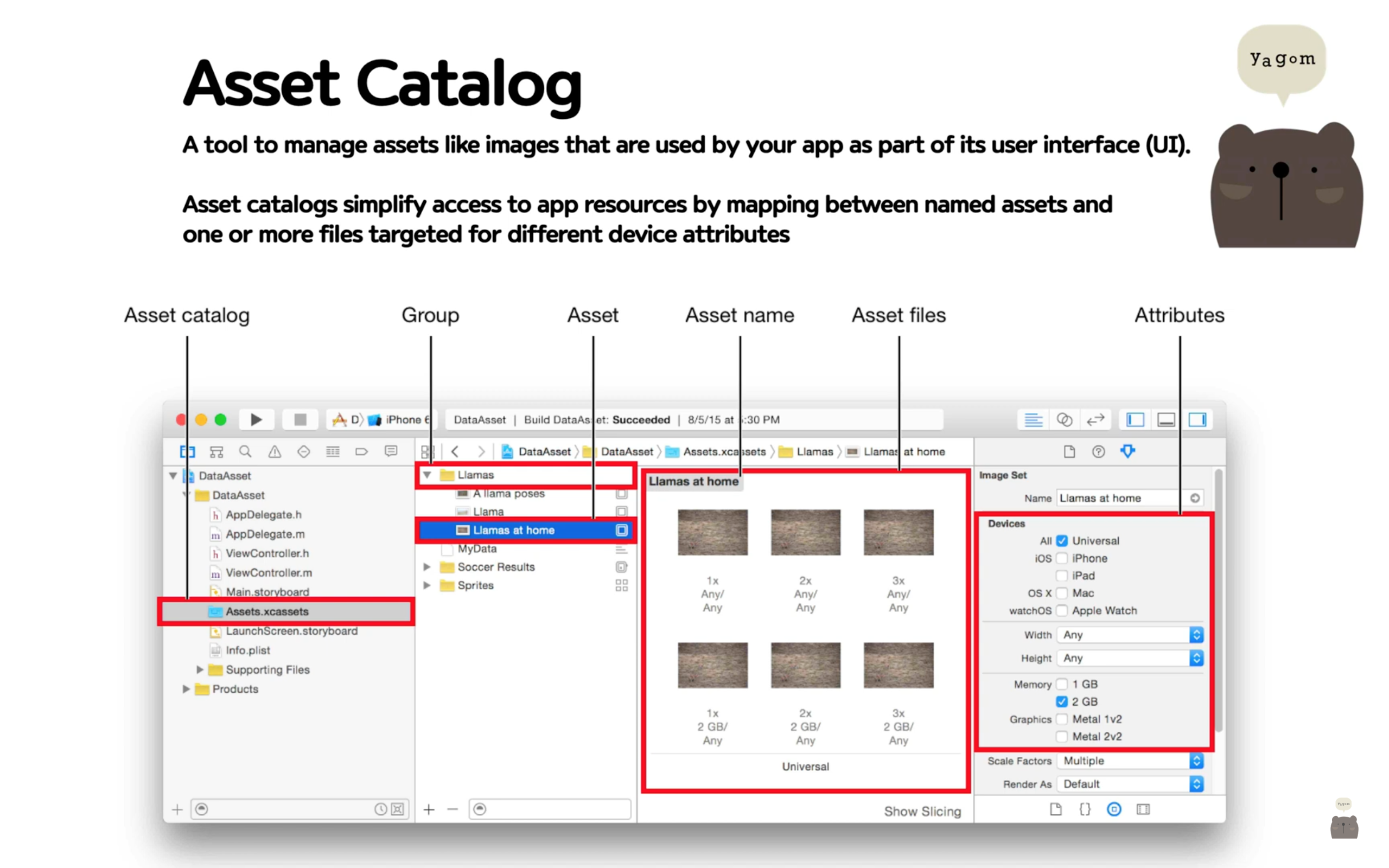
3. 세 번째 학습 내용: 왕초보를 위한 iOS 앱개발 - 코드로 구현하기
- IBAction: 인터페이스 빌더에 어떤 요소들이 이벤트를 받았을 때 반응하기 위한 액션 코드를 작성하기 위해 사용
- IBOutlet: 인터페이스 빌더에 올라와있는 UI 요소의 어떤 값을 가져오고 싶을때, 아니면 그걸 코드에서 활용하고 싶을 때 사용

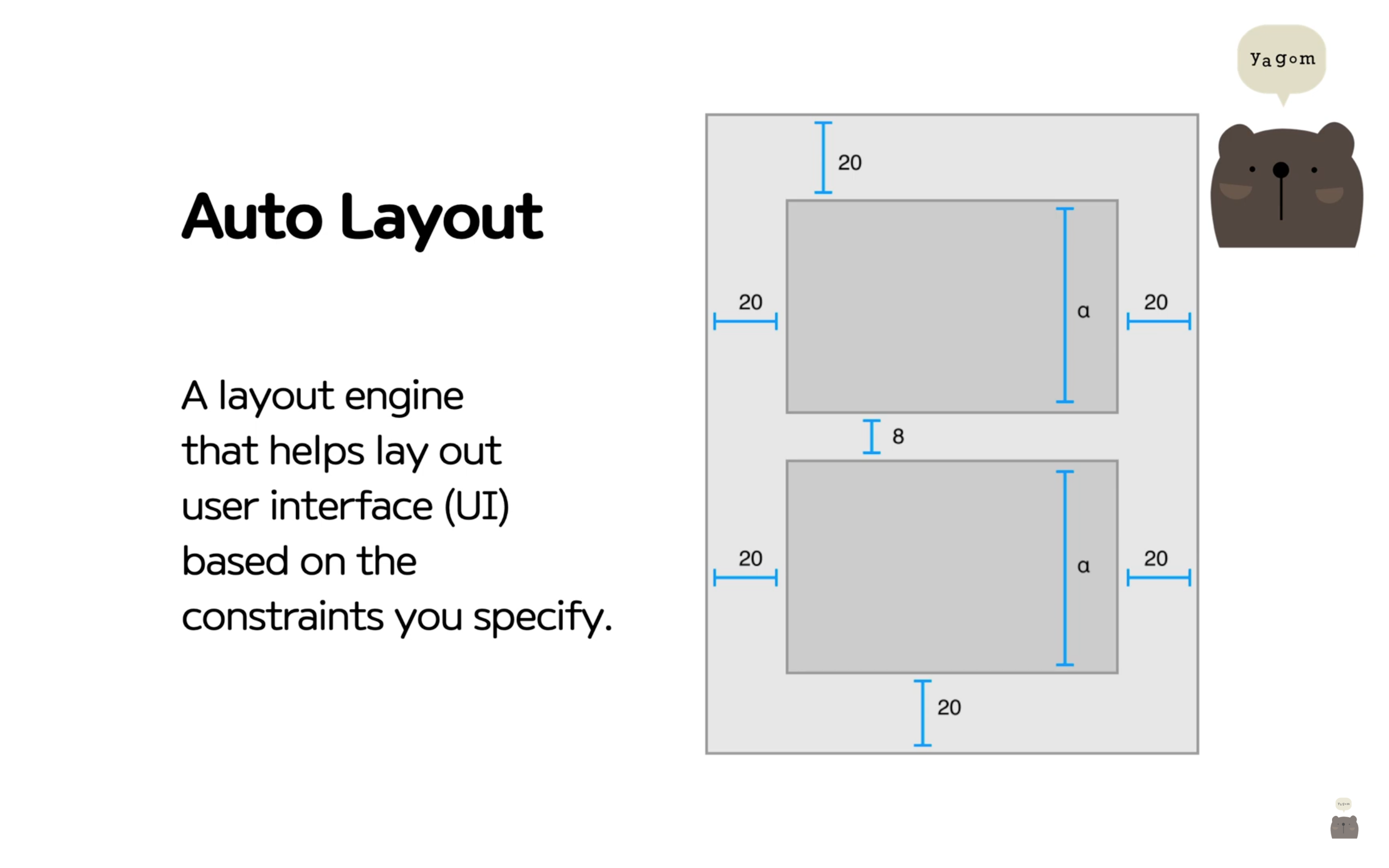
- Refactor 기능: (예를 들어, 함수 이름 잘못 적어줬을때) 바꿔야 하는 동일 이름 모두 바꿔줄 수 있음.
참고자료 : Swift IBOutlet 변수명 Refactor로 간편하게 바꾸기 - MungGu Story
- if 안에서 return이 필요할 때와 vs. 그렇지 않을 때
if randomValue == hitValue {
print("YOU HIT!!")
reset()
return
}
if tryCount >= 5 {
print("You lose...")
reset()
return
}
if randomValue > hitValue {
slider.minimumValue = Float(hitValue)
minimumValueLabel.text = String(hitValue)
} else if randomValue < hitValue {
slider.maximumValue = Float(hitValue)
maximumValueLabel.text = String(hitValue)
}if randomValue == hitValue {
print("YOU HIT!!")
reset()
} else if tryCount >= 5 {
print("You lose...")
reset()
} else if randomValue > hitValue {
slider.minimumValue = Float(hitValue)
minimumValueLabel.text = String(hitValue)
} else {
slider.maximumValue = Float(hitValue)
maximumValueLabel.text = String(hitValue)
}왜 위에서 있던 return이 아래에서는 필요가 없을까?
→ 위의 예시에서는 if 조건이 성립되면 안에 내용을 실행하고 return을 해서 해당 if문을 나가버림.
아래 예시에서는 해당 if 조건이 성립 안하면 어차피 다음 else if문이 성립하는지 확인하러 가기 때문에 굳이 return을 써서 if문을 나가야 할 필요가 없음.
