문제
스프링부트가 띄워질때 뜨는 로그들 중에 살짝 거슬리는 로그를 발견했습니다.
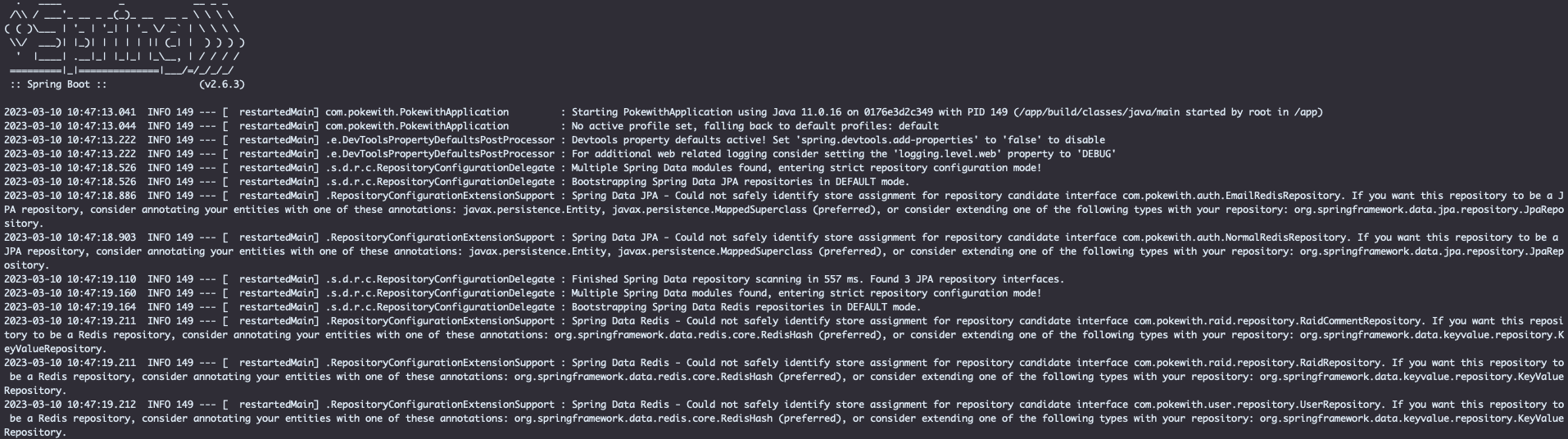
2023-03-10 10:47:18.526 INFO 149 --- [ restartedMain] .s.d.r.c.RepositoryConfigurationDelegate : Bootstrapping Spring Data JPA repositories in DEFAULT mode.
2023-03-10 10:47:18.886 INFO 149 --- [ restartedMain] .RepositoryConfigurationExtensionSupport : Spring Data JPA - Could not safely identify store assignment for repository candidate interface com.pokewith.auth.EmailRedisRepository. If you want this repository to be a JPA repository, consider annotating your entities with one of these annotations: javax.persistence.Entity, javax.persistence.MappedSuperclass (preferred), or consider extending one of the following types with your repository: org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository.
2023-03-10 10:47:18.903 INFO 149 --- [ restartedMain] .RepositoryConfigurationExtensionSupport : Spring Data JPA - Could not safely identify store assignment for repository candidate interface com.pokewith.auth.NormalRedisRepository. If you want this repository to be a JPA repository, consider annotating your entities with one of these annotations: javax.persistence.Entity, javax.persistence.MappedSuperclass (preferred), or consider extending one of the following types with your repository: org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository.
2023-03-10 10:47:19.110 INFO 149 --- [ restartedMain] .s.d.r.c.RepositoryConfigurationDelegate : Finished Spring Data repository scanning in 557 ms. Found 3 JPA repository interfaces.2023-03-10 10:47:19.164 INFO 149 --- [ restartedMain] .s.d.r.c.RepositoryConfigurationDelegate : Bootstrapping Spring Data Redis repositories in DEFAULT mode.
2023-03-10 10:47:19.211 INFO 149 --- [ restartedMain] .RepositoryConfigurationExtensionSupport : Spring Data Redis - Could not safely identify store assignment for repository candidate interface com.pokewith.raid.repository.RaidCommentRepository. If you want this repository to be a Redis repository, consider annotating your entities with one of these annotations: org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisHash (preferred), or consider extending one of the following types with your repository: org.springframework.data.keyvalue.repository.KeyValueRepository.
2023-03-10 10:47:19.211 INFO 149 --- [ restartedMain] .RepositoryConfigurationExtensionSupport : Spring Data Redis - Could not safely identify store assignment for repository candidate interface com.pokewith.raid.repository.RaidRepository. If you want this repository to be a Redis repository, consider annotating your entities with one of these annotations: org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisHash (preferred), or consider extending one of the following types with your repository: org.springframework.data.keyvalue.repository.KeyValueRepository.
2023-03-10 10:47:19.212 INFO 149 --- [ restartedMain] .RepositoryConfigurationExtensionSupport : Spring Data Redis - Could not safely identify store assignment for repository candidate interface com.pokewith.user.repository.UserRepository. If you want this repository to be a Redis repository, consider annotating your entities with one of these annotations: org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisHash (preferred), or consider extending one of the following types with your repository: org.springframework.data.keyvalue.repository.KeyValueRepository.
2023-03-10 10:47:19.224 INFO 149 --- [ restartedMain] .s.d.r.c.RepositoryConfigurationDelegate : Finished Spring Data repository scanning in 30 ms. Found 2 Redis repository interfaces.Spring Data JPA와 Spring Data Redis가 Repository를 스캔하면서 발생하는 로그였습니다.
JPA는 Redis Repository를 발견하고 로그를 띄워주고,
Redis는 JPA Repository를 발견하고 로그를 띄워주는 서로 돌고도는 문제였습니다.
Repository
제가 사용하는 Repository들을 먼저 살펴보겠습니다.
먼저 Redis Repository 입니다.
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;
public interface EmailRedisRepository extends CrudRepository<EmailToken, String> {
}import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Getter;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisHash;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.TimeToLive;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Getter
@Builder
@RedisHash
public class EmailToken {
@Id
private String id;
private String random;
@TimeToLive(unit = TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
private Long timeToLive;
}Redis Repository는 공식문서를 참고하여 CrudRepository를 extends해서 interface로 구현했습니다.
https://docs.spring.io/spring-data/redis/docs/2.6.3/reference/html/#redis.repositories
@RedisHash로 Redis Entity를 만들어서 CrudRepository에 넣어주기만 하면 됩니다.
CrudRepository<{entity}, {id type}>
interface를 구현만 해두면 기본적인 crud를 사용할 수 있어서 개발시간을 단축시킬 수 있습니다.
/**
* Interface for generic CRUD operations on a repository for a specific type.
*
* @author Oliver Gierke
* @author Eberhard Wolff
* @author Jens Schauder
*/
@NoRepositoryBean
public interface CrudRepository<T, ID> extends Repository<T, ID> {
<S extends T> S save(S entity);
<S extends T> Iterable<S> saveAll(Iterable<S> entities);
Optional<T> findById(ID id);
boolean existsById(ID id);
Iterable<T> findAll();
Iterable<T> findAllById(Iterable<ID> ids);
long count();
void deleteById(ID id);
void delete(T entity);
void deleteAllById(Iterable<? extends ID> ids);
void deleteAll(Iterable<? extends T> entities);
void deleteAll();CrudRepository에서 제공해주는 기본적인 crud 메소드들 입니다.
다음은 JPA
import com.pokewith.user.User;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import java.util.Optional;
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
Optional<User> findByEmail(String email);
}JPA Repository는 JpaRepository를 사용했습니다.
https://docs.spring.io/spring-data/jpa/docs/current/reference/html/#jpa.repositories
JpaRepository는 CrudRepository에 PagingAndSortingRepository와 JpaRepository 두단계 인터페이스가 추가되어있습니다.
@NoRepositoryBean
public interface JpaRepository<T, ID> extends PagingAndSortingRepository<T, ID>, QueryByExampleExecutor<T> {
...
}@NoRepositoryBean
public interface PagingAndSortingRepository<T, ID> extends CrudRepository<T, ID> {
...
}결론적으로 제가 사용하는 Redis Repository와 JPA Repository는 근본적으로 동일하다고 볼 수 있습니다.
@EnableJpaRepositories
그렇다면 Repository 스캔은 어떻게 설정하는지 찾아보다보니 @EnableJpaRepositories 어노테이션을 발견했습니다.
/**
* Annotation to enable JPA repositories. Will scan the package of the annotated configuration class for Spring Data
* repositories by default.
*
* @author Oliver Gierke
* @author Thomas Darimont
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@Import(JpaRepositoriesRegistrar.class)
public @interface EnableJpaRepositories {
/**
* Alias for the {@link #basePackages()} attribute. Allows for more concise annotation declarations e.g.:
* {@code @EnableJpaRepositories("org.my.pkg")} instead of {@code @EnableJpaRepositories(basePackages="org.my.pkg")}.
*/
String[] value() default {};
/**
* Base packages to scan for annotated components. {@link #value()} is an alias for (and mutually exclusive with) this
* attribute. Use {@link #basePackageClasses()} for a type-safe alternative to String-based package names.
*/
String[] basePackages() default {};
/**
* Type-safe alternative to {@link #basePackages()} for specifying the packages to scan for annotated components. The
* package of each class specified will be scanned. Consider creating a special no-op marker class or interface in
* each package that serves no purpose other than being referenced by this attribute.
*/
Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {};
/**
* Specifies which types are eligible for component scanning. Further narrows the set of candidate components from
* everything in {@link #basePackages()} to everything in the base packages that matches the given filter or filters.
*/
Filter[] includeFilters() default {};
/**
* Specifies which types are not eligible for component scanning.
*/
Filter[] excludeFilters() default {};
/**
* Returns the postfix to be used when looking up custom repository implementations. Defaults to {@literal Impl}. So
* for a repository named {@code PersonRepository} the corresponding implementation class will be looked up scanning
* for {@code PersonRepositoryImpl}.
*
* @return
*/
String repositoryImplementationPostfix() default "Impl";
/**
* Configures the location of where to find the Spring Data named queries properties file. Will default to
* {@code META-INF/jpa-named-queries.properties}.
*
* @return
*/
String namedQueriesLocation() default "";
/**
* Returns the key of the {@link QueryLookupStrategy} to be used for lookup queries for query methods. Defaults to
* {@link Key#CREATE_IF_NOT_FOUND}.
*
* @return
*/
Key queryLookupStrategy() default Key.CREATE_IF_NOT_FOUND;
/**
* Returns the {@link FactoryBean} class to be used for each repository instance. Defaults to
* {@link JpaRepositoryFactoryBean}.
*
* @return
*/
Class<?> repositoryFactoryBeanClass() default JpaRepositoryFactoryBean.class;
/**
* Configure the repository base class to be used to create repository proxies for this particular configuration.
*
* @return
* @since 1.9
*/
Class<?> repositoryBaseClass() default DefaultRepositoryBaseClass.class;
// JPA specific configuration
/**
* Configures the name of the {@link EntityManagerFactory} bean definition to be used to create repositories
* discovered through this annotation. Defaults to {@code entityManagerFactory}.
*
* @return
*/
String entityManagerFactoryRef() default "entityManagerFactory";
/**
* Configures the name of the {@link PlatformTransactionManager} bean definition to be used to create repositories
* discovered through this annotation. Defaults to {@code transactionManager}.
*
* @return
*/
String transactionManagerRef() default "transactionManager";
/**
* Configures whether nested repository-interfaces (e.g. defined as inner classes) should be discovered by the
* repositories infrastructure.
*/
boolean considerNestedRepositories() default false;
/**
* Configures whether to enable default transactions for Spring Data JPA repositories. Defaults to {@literal true}. If
* disabled, repositories must be used behind a facade that's configuring transactions (e.g. using Spring's annotation
* driven transaction facilities) or repository methods have to be used to demarcate transactions.
*
* @return whether to enable default transactions, defaults to {@literal true}.
*/
boolean enableDefaultTransactions() default true;
/**
* Configures when the repositories are initialized in the bootstrap lifecycle. {@link BootstrapMode#DEFAULT}
* (default) means eager initialization except all repository interfaces annotated with {@link Lazy},
* {@link BootstrapMode#LAZY} means lazy by default including injection of lazy-initialization proxies into client
* beans so that those can be instantiated but will only trigger the initialization upon first repository usage (i.e a
* method invocation on it). This means repositories can still be uninitialized when the application context has
* completed its bootstrap. {@link BootstrapMode#DEFERRED} is fundamentally the same as {@link BootstrapMode#LAZY},
* but triggers repository initialization when the application context finishes its bootstrap.
*
* @return
* @since 2.1
*/
BootstrapMode bootstrapMode() default BootstrapMode.DEFAULT;
/**
* Configures what character is used to escape the wildcards {@literal _} and {@literal %} in derived queries with
* {@literal contains}, {@literal startsWith} or {@literal endsWith} clauses.
*
* @return a single character used for escaping.
*/
char escapeCharacter() default '\\';
}제일 상단 설명을 보면
Will scan the package of the annotated configuration class for Spring Data repositories by default.
라고 되어있습니다.
Spring Data repositories 라는 단어가 들어있습니다. 이게 어떤걸까 하고 찾아보니
https://www.baeldung.com/spring-data-repositories
- CrudRepository
- PagingAndSortingRepository
- JpaRepository
짠 우리가 사용하던 친구들이었습니다.
Redis Repository에서도 CrudRepository를 사용하고 있으니 함께 스캔 대상으로 잡히는 것이었네요.
해결방법
그렇다면 스캔 대상으로 잡히지 않게 하려면 어떻게 해야할까요?
제가 찾은 방법은 스캔할 패키지를 지정해주는 방법이었습니다.
@EnableJpaRepositories 어노테이션 설명을 보면 basePackages() 메소드가 있습니다.
이 기능을 사용하면 스캔할 패키지를 직접 지정할 수 있습니다.
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.config.EnableJpaRepositories;
@EnableJpaRepositories(basePackages = {"com.pokewith.user.repository", "com.pokewith.raid.repository"})
@SpringBootApplication
public class PokewithApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(PokewithApplication.class, args);
}
}이 기능을 사용해서 JPA Repository가 들어있는 패키지만 스캔하도록 설정해줬습니다.
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.lettuce.LettuceConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.repository.configuration.EnableRedisRepositories;
@Configuration
@EnableRedisRepositories(basePackages = {"com.pokewith.auth"})
public class RedisConfig {
@Value("${spring.redis.host}")
private String redisHost;
@Value("${spring.redis.port}")
private int redisPort;
@Bean
public RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory() {
return new LettuceConnectionFactory(redisHost, redisPort);
}
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<?, ?> redisTemplate() {
RedisTemplate<byte[], byte[]> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory());
return redisTemplate;
}
}Redis도 마찬가지로 @EnableRedisRepositories 어노테이션이 있고 basePackages() 메소드가 있습니다.
같은 방식으로 Redis Repository가 있는 패키지만 스캔하도록 지정해줬습니다.
그리고 다시 스프링부트를 띄워보니
2023-03-12 13:36:06.958 INFO 148 --- [ restartedMain] .s.d.r.c.RepositoryConfigurationDelegate : Bootstrapping Spring Data JPA repositories in DEFAULT mode.
2023-03-12 13:36:07.060 INFO 148 --- [ restartedMain] .s.d.r.c.RepositoryConfigurationDelegate : Finished Spring Data repository scanning in 91 ms. Found 3 JPA repository interfaces.2023-03-12 13:36:06.424 INFO 148 --- [ restartedMain] .s.d.r.c.RepositoryConfigurationDelegate : Bootstrapping Spring Data Redis repositories in DEFAULT mode.
2023-03-12 13:36:06.885 INFO 148 --- [ restartedMain] .s.d.r.c.RepositoryConfigurationDelegate : Finished Spring Data repository scanning in 402 ms. Found 2 Redis repository interfaces.짠 거슬리는 로그들이 사라졌습니다.
추가사항
로그 처음항목을 보면
Bootstrapping Spring Data JPA repositories in DEFAULT mode.
라는 내용이 있습니다.
이 내용을 조사해보니,
@EnableJpaRepositories에는 BootstrapMode 설정이 있다고 합니다.
- DEFAULT : 가장 기본으로 모든 Repository를 즉시 인스턴스화 시킵니다. Repository가 많은 경우 스프링 시작 시간이 지연되는 단점이 있습니다.
- LAZY : 모든 Repository를 프록시로 만들어두고, 처음 사용할 때 실제 인스턴스로 만들어 줍니다.
- DEFERRED : 기본적으로 LAZY와 동일하지만 비동기적으로 작업하고, ContextRefreshedEvent에 의해 Repository가 초기화 되어 검증되도록 진행합니다.
DEFAULT는 안전하지만 오래걸린다는 단점이 있고,
LAZY는 빠르지만 처음 Repository 사용시에 약간의 딜레이 발생이 있고, 오류 발생시 초기가 아닌 사용 시점에 발생한다는 문제가 있습니다.
DEFERRED는 LAZY와 비슷하지만 Repository가 초기화가 보장되어 로드가 빠르고 유효성 검증이 보장됩니다.
작은 규모의 프로젝트라면 DEFAULT로 사용해도 문제없을것 같습니다.
보통은 DEFERRED가 권장되고, LAZY는 개발환경 세팅에서 사용하기 좋을 것 같습니다.
상황에 맞게 설정을 잘 사용하면 되겠습니다.
