문제
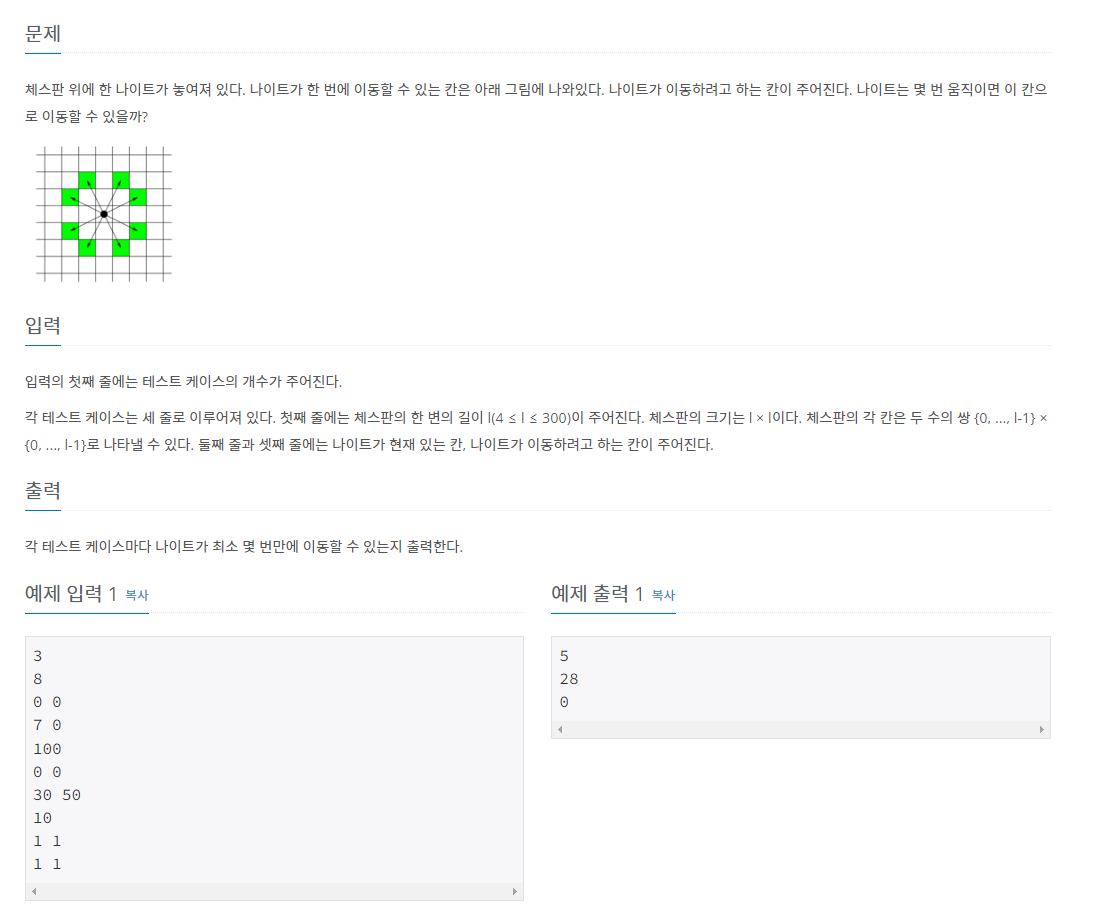
풀이
// 나이트의 이동 - S1 - BFS
import java.util.*;
class Point{
int x;
int y;
Point(int x, int y){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
public class ex7562 {
static int[] dx = { -1, -2, -2, -1, 1, 2, 2, 1 };
static int[] dy = { -2, -1, 1, 2, 2, 1, -1, -2 };
static int[][] dis;
static boolean[][] ch;
static int T;
public static void BFS(ArrayList<Point> arr , int n, int[][] dis, boolean[][] ch){
Queue<Point> Q = new LinkedList<>();
Q.offer(arr.get(0));
ch[arr.get(0).x][arr.get(0).y] = true;
while(!Q.isEmpty()){
Point poll = Q.poll();
for(int i=0; i<8; i++){
int nx = poll.x + dx[i];
int ny = poll.y + dy[i];
if(nx>=0 && nx<n && ny>=0 && ny<n && !ch[nx][ny]){
ch[nx][ny] = true;
Q.offer(new Point(nx,ny));
dis[nx][ny] = dis[poll.x][poll.y]+1;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
T = sc.nextInt();
while(T-- >0){
int n = sc.nextInt();
dis = new int[n][n];
ch = new boolean[n][n];
ArrayList<Point> arr = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0; i<2; i++){
int st = sc.nextInt();
int et = sc.nextInt();
arr.add(new Point(st,et));
// arr.get(0) -> 시작점
// arr.get(1) -> 끝점
}
BFS(arr,n,dis,ch);
System.out.println(dis[arr.get(1).x][arr.get(1).y]);
}
}
}
BFS 필수 선언
- 커스텀 클래스 -> 좌표 저장용
- 거리 저장용 dis[][] 배열
- board[][] 에다가 체크할수있으면 숫자바꿔가면서 체크하면서, 만약에 board[][] 배열 없으면 따로 boolean[][] ch 배열 만들어서 방문체크 배열
오랜만에 BFS 풀었다. 나는 극 DFS 주의이긴 한데, 혹시나 풀어야할 상황이 나올 수 있어서 연습해봤다.
