<월요일 복습문제>
-
- lambda는 어떤 함수인가?
: 이름없는 함수, anonymous, 익명함수
- lambda는 어떤 함수인가?
-
- add(a,b)
: 매개변수, parameter, argument
- add(a,b)
-
- 1부터 100까지 숫자 합 while문.
i=0
sum=0
while i < 100 :
i += 1
sum += i
print(sum) count = 0
sum = 0
while(True):
sum += count
count += 1
if count == 101:
break
print(sum) - 1~45 중에서 임으의 6개의 수 오름차순으로 정리하시오.
import random
random.randint(1,45)
☆
import random as r
num = [0,0,0,0,0,0]
for i in range(6):
num[i] = r.randint(1,45)
num.sort()
num
★
num = [r.randint(1,45) for i in range(6)]
num.sort()
num
☆
import random
l = []
while True:
if len(l) >= 6:
break
else:
i =random.randint(1, 45)
l.append(i)
l.sort()
print(l) - 함수를 만드시오. 리턴값이 딕셔너리로 나오게
diction(a=1,b=3,c="hello")
{a:1}
def diction(*kwargs):
print(kwargs)-
6.print 와 return의 차이점
:return은 결과값을 돌려주지만 print는 결과를 보여주기만 하고 없어짐 -
- while 문으로 1부터 30까지 숫자 나열 하고, 3의 배수 는 짝으로 표기하시오.
li=[]
i=0
while i < 30 :
i += 1
li.append(i)
print(li)
i = 0
while i < 30:
i += 1
if i % 3 == 0:
print("짝")
else:
print(i)
i = 0
while i < 30:
i += 1
if i % 3 != 0:
print(i)
continue
print("짝")- 세 개의 숫자를 입력 받고 최댓값과 최솟값의 차이를 구해주는 함수를 만들어주세요.
☆
def maxmin(a, b, c):
x = max(a,b,c)
y = min(a,b,c)
return(x-y)
★
def f(a, b, c):
li = [a, b, c]
return max(li) - min(li)- 8.아래 식을 한줄로 표현하시오.
a= [1,2,3,4 ]
b= []
for i in a:
if i % 2 == 0:
b.append(i*3)
b = [i * 3 for i in a if i % 2 == 0] - 입력한 두 수 사이에 있는 값들의 합을 구해주는 함수를 만들기
add(a,b)
(a<b)
def add(a, b):
sum = 0
for i in range(a, b + 1): # --> +1 하는 이유는?
sum += i
return sum
add(1,3)- 입력한 두 수 사이에 있는 값들의 합을 구해주는 함수를 만들기
☆
def add(a, b):
sum = 0
if b > a:
for i in range(a, b + 1):
sum += i
elif a > b:
for i in range(b, a + 1):
sum += i
return sum
★
def add(a,b):
M=max(a,b)
m=min(a,b)
sum=0
for i in range(m,M+1):
sum += i
return sum
def add(a,b):
if a > b:
a, b = b, a
sum = 0
for i in range(a, b+1):
sum += i
return sum
add(2,5) [ 오전 수업 시작 p171 ]
< 파일 만들기 >
- 파일 열기 모드
r: read
w: write
a: appended
b: binary : 택스트가 아닌거. 음악, 사진, 동영상,
wb:
파이썬은 모든것이 객체이다.
f= lambda a,b : a+b -> f: 객체이다.
<파일 생성하기>
파일객체 = open(파일이름, 파일 열기 모드)
- f = open("new.txt", 'w') : 객체를만들고
- f.write("hello") : 메소드르 만들어 내용 쓰고
- f.close() : 닫아준다.
"hello 10번 기록되게"
f = open("new.txt", 'w')
for i in range(10):
f.write(f"hello")
f.close() 
"hello 10번 기록되게", "good moring "도 추가해주세요.
f = open("new.txt", 'a')
for _ in range(10):
f.write(f"\ngood moring")
f.close() 
< 파일 읽기 >
- f . readline
- f. readlines()★
- f.read()
< f . readline() p173 >
f= open ('new.txt', 'r')
data =f.readline()
print(data)
f.close()f= open ('new.txt', 'r')
while True:
data = f.readline()
if not data: break
print(data)
f.close():결과 값이 똑같다.
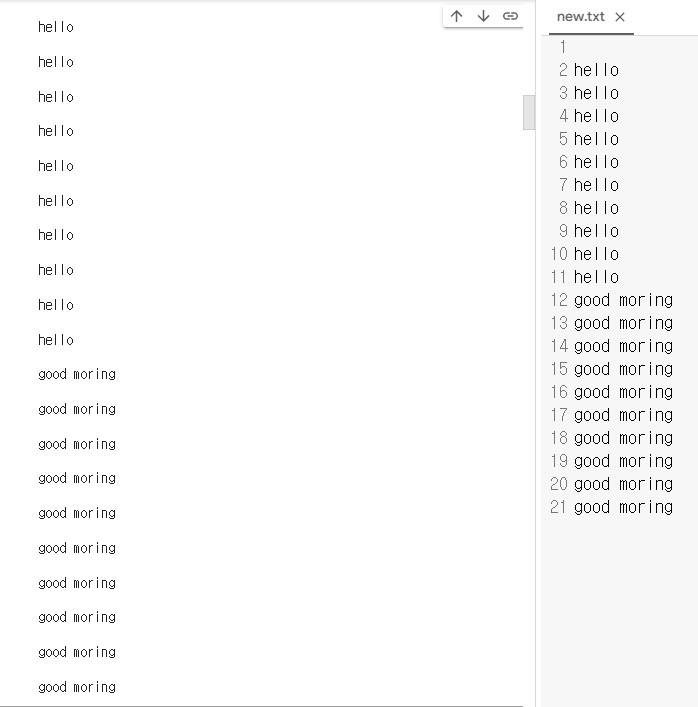
< f. readlines()★ p175>
:리스트에 묶여 나옴
f= open ('new.txt', 'r')
data =f.readlines()
print(data)
f.close()- 위에꺼는 한줄만 나옴
- 밑에꺼는 20 * 20 나옴
f= open ('new.txt', 'r')
data =f.readlines()
for i in data:
print(data)
f.close()< f. read() p175 >
:문자열로 나옴
f= open ('new.txt', 'r')
data =f.read()
print(data)
f.close()
< with open as f p176 >
- (1) 정답:
with open("new.txt", 'w') as f :
f.write("hello \n")- (2) 정답:
with open ('new.txt', 'r') as f:
data =f.readline()
print(data)-둘다 같은 값 나옴. -> 'hello'
문제 (with 사용해서, 10번째 까지 나오게. {i}번째입니다\n", end="")
with open("test.txt", "w") as f:
for i in range(1,11):
print(f"{i}번째입니다\n", end="")with open("test.txt", "w",encoding='utf-8') as f:
for i in range(1,11):
f.write(f"{i}번째입니다. \n")- 둘다 같은 값 나온다.

문제 (이름과 나이를 입력받아 people.txt 만들자. while 문을 써서 엔터 (빈칸)으로 입력되면 while문 종료.)
- (1) 정답:
f = open("people.txt",'w', encoding="UTF-8")
while True:
name = input("이름을 입력하세요: ")
if name=="":
break
age = input("나이를 입력하세요: ")
f.write(f"{name} : {age}\n")
f.close()- (2) 정답:
with open("people.txt", 'w', encoding = 'utf-8') as f:
while True:
name = input("이름을 입력하시오")
age = input("나이를 입력하시오")
f.write(name + ": " + age + '\n')
if name == "":
break <클래스>
:같은 성격끼리 모아 놓은 반. 80% 만들고 20% 데코레이션
< 계산기 만들기 >
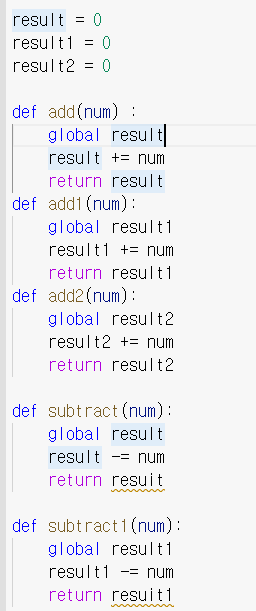
- 함수를 각각 따로 만들어야 한다.
< 클래스 만들기 >
class Calculator:
def _init_(self):
self.result = 0
def add(self, num): #셀프는 항상 들어감.
self.result += num
return self.result클래스 개념 p189
- 객체 : object, instance,
- 동사: 메소드,
- 형용사: 속성, 애트리뷰트
- car: car.go(), car.back(), car, turn() car.color, car.size
- bird : bird.fly() ,bird.sing() bird.color
객체에 숫자 지정할 수있게 만들기 p190
class FourCal:
def setdata(self, a, b):
self.first = a
self.second = b #setdata 먼저 실행해야만 한다.
def add(self):
self.result = self. first + self.second
return self.result
def subtract(self):
self.result = self. first - self.second
return self.resultcal.setdata(1,2) #setdata(cal=self, a=1, b=2)
cal.first 독립적인 객체변수 p195
class Calculator():
def __init__(self,a,b): #(a,b):
self.first = a #self는 객체를 지정해준다.
self.second = b곱하기 더하기 추가하기 p197
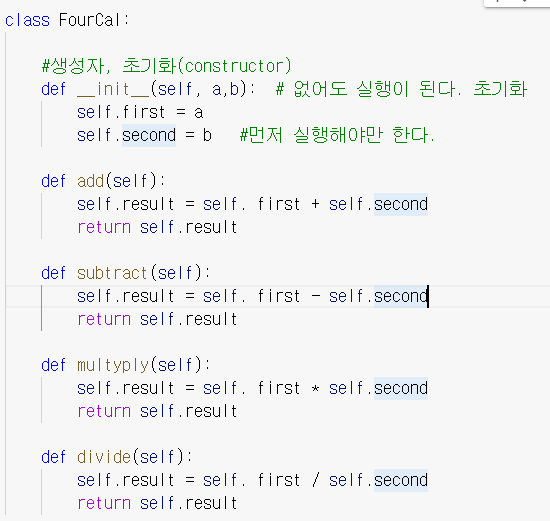
상속(inheritance) p201
class Child(FourCal):
pass
상속 메소드 추가하기

메소드 오버라이딩 p203
: 메소드 재정의
상속 메소드 덮어쓰기
