동적 프록시의 문제점
- 인터페이스가 있는 경우 JDK 동적 프록시를 적용하고, 그렇지 않은 경우 CGLIB를 적용하려면 어떻게 해야할까?
스프링은 유사한 구체적인 기술들이 있을 때, 그것들을 통합해서 일관성 있게 접근할 수 있고, 더욱 편리하게 사용할 수 있는 추상화된 기술을 제공한다.
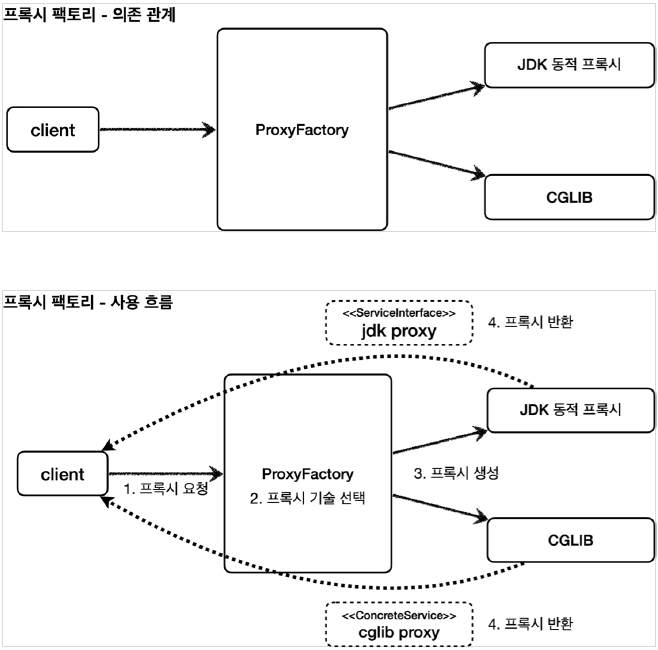
스프링은 동적 프록시를 통합해서 편리하게 만들어주는 프록시 팩토리(ProxyFactory)라는 기능을 제공한다. 이전에는 상황에 따라서 JDK 동적 프록시나 CGLIB를 사용해야 했다면, 이제는 이 프록시 팩토리 하나로 편리하게 동적 프록시를 생성할 수 있다.
프록시 팩토리는 인터페이스가 있으면 JDK 동적 프록시를 사용하고, 구체 클래스만 있다면 CGLIB를 사용한다. 그리고 이 설정을 변경할 수도 있다.
- 두 기술을 함께 사용할 때 부가 기능을 적용하기 위해 JDK 동적 프록시가 제공하는
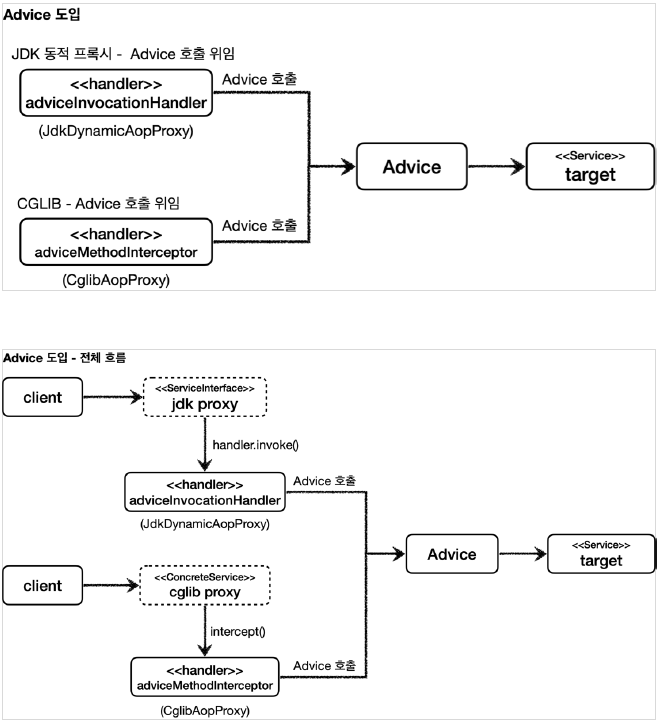
InvocationHandler와 CGLIB가 제공하는MethodInterceptor를 각각 중복으로 따로 만들어야 할까?스프링은 이 문제를 해결하기 위해 부가 기능을 적용할 때
Advice라는 새로운 개념을 도입했다. 개발자는InvocationHandler나MethodInterceptor를 신경쓰지 않고,Advice만 만들면 된다.
결과적으로InvocationHandler나MethodInterceptor는Advice를 호출하게 된다.
프록시 팩토리를 사용하면Advice를 호출하는 전용InvocationHandler나MethodInterceptor를 내부에서 사용한다.
- 특정 조건에 맞을 때 프록시 로직을 적용하는 기능도 공통으로 제공되었으면?
앞서 특정 메서드 이름의 조건에 맞을 때만 프록시 부가 기능이 적용되는 코드를 직접 만들었다. 스프링은
PointCut이라는 개념을 도입해서 이 문제를 일관성 있게 해결한다.
프록시 팩토리
Advice 예제
InvocationHandler나 MethodInterceptor를 개념적으로 추상화 한 것이 Advice이다. 프록시 팩토리를 사용하면 둘 대신 Advice를 사용하면 된다. Advice를 만드는 방법 중 기본적인 방법은 다음 인터페이스를 구현하면 된다.
package org.aopalliance.intercept;
public interface MethodInterceptor extends Interceptor {
Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable;
}MethodInvocation invocation: 내부에는 다음 메서드를 호출하는 방법, 현재 프록시 객체 인스턴스, args, 메서드 정보 등이 포함되어 있다. 기존에 파라미터로 제공되는 부분들이 이 안으로 모두 들어갔다고 생각하면 된다.MethodInterceptor는Interceptor를 상속하고Interceptor는Advice인터페이스를 상속한다.
실제 Advice를 만드는 예시는 다음과 같다.
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation;
@Slf4j
public class TimeAdvice implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
log.info("TimeProxy 실행");
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Object result = invocation.proceed();
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long resultTime = endTime - startTime;
log.info("TimeProxy 종료 resultTime={}ms", resultTime);
return result;
}
}Object result = invocation.proceed()를 살펴보자.
invocation.proceed()를 호출하면target클래스를 호출하고 그 결과를 받는다.- 기존 코드와는 다르게
target클래스의 정보가 보이지 않는다.target클래스의 정보는MethodInvocation invocation안에 모두 포함되어 있다. - 그 이유는 프록시 팩토리로 프록시를 생성하는 단계에서 이미
target정보를 파라미터로 전달받기 때문이다.
테스트 코드는 다음과 같다.
@Slf4j
public class ProxyFactoryTest {
@Test
@DisplayName("인터페이스가 있으면 JDK 동적 프록시 사용")
void interfaceProxy() {
ServiceInterface target = new ServiceImpl();
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory(target);
proxyFactory.addAdvice(new TimeAdvice());
ServiceInterface proxy = (ServiceInterface) proxyFactory.getProxy();
log.info("targetClass={}", target.getClass());
log.info("proxyClass={}", proxy.getClass());
proxy.save();
assertThat(AopUtils.isAopProxy(proxy)).isTrue();
assertThat(AopUtils.isJdkDynamicProxy(proxy)).isTrue();
assertThat(AopUtils.isCglibProxy(proxy)).isFalse();
}
@Test
@DisplayName("구체 클래스만 있으면 CGLIB 사용")
void concreteProxy() {
ConcreteService target = new ConcreteService();
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory(target);
proxyFactory.addAdvice(new TimeAdvice());
ConcreteService proxy = (ConcreteService) proxyFactory.getProxy();
log.info("targetClass={}", target.getClass());
log.info("proxyClass={}", proxy.getClass());
proxy.call();
assertThat(AopUtils.isAopProxy(proxy)).isTrue();
assertThat(AopUtils.isJdkDynamicProxy(proxy)).isFalse();
assertThat(AopUtils.isCglibProxy(proxy)).isTrue();
}
@Test
@DisplayName("ProxyTargetClass 옵션을 사용하면 인터페이스가 있어도 CGLIB를 사용하고, 클래스 기반 프록시 사용")
void proxyTargetClass() {
ServiceInterface target = new ServiceImpl();
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory(target);
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true); // 중요: 인터페이스와 상관없이 강제로 CGLIB 사용
proxyFactory.addAdvice(new TimeAdvice());
ServiceInterface proxy = (ServiceInterface) proxyFactory.getProxy();
log.info("targetClass={}", target.getClass());
log.info("proxyClass={}", proxy.getClass());
proxy.save();
assertThat(AopUtils.isAopProxy(proxy)).isTrue();
assertThat(AopUtils.isJdkDynamicProxy(proxy)).isFalse();
assertThat(AopUtils.isCglibProxy(proxy)).isTrue();
}
}정리
- 대상에 인터페이스가 있으면: JDK 동적 프록시, 인터페이스 기반 프록시
- 대상에 인터페이스가 없으면: CGLIB, 구체 클래스 기반 프록시
proxyTargetClass=true: CGLIB, 구체 클래스 기반 프록시, 인터페이스 여부와 상관 없음- 프록시 팩토리의 서비스 추상화 덕분에 구체적인 CGLIB, JDK 동적 프록시 기술에 의존하지 않고, 매우 편리하게 동적 프록시를 생성할 수 있다.
- 프록시의 부가 기능 로직도 특정 기술에 종속적이지 않게
Advice하나로 편리하게 사용할 수 있다. 이는 프록시 팩토리가 내부에서 상황에 따라Advice를 호출하도록 기능을 개발해두었기 때문이다.
