스프링 시큐리티란?
스프링 기반의 애플리케이션의 보안(인증과 권한, 인가 등)을 담당하는 스프링 하위 프레임워크
보안 관련 많은 기능을 제공, 개발자가 직접 보안 관련 로직을 작정하지 않아도 되는 장점 있음
- 인증(Authenticate) : 접근하려는 유저가 누구인지 확인하는 절차
ex) 로그인을 함 - 인가(Authorization) : 인증된 유저가 요청한 자원에 접근 가능한지를 결정하는 절차
ex) 로그인 한 후 다른 사람의 글을 수정하려 했으나 실패
*인증 절차 후 인가 절차를 거친다.
스프링 시큐리티는 이런 인증, 인가를 위해 아이디로 Principal, 비밀번호로 Credential을 사용하는 Credential 기반의 인증 방식을 사용함
- 접근 주체(Principal) : 보호된 자원에 접근하는 유저
- 비밀번호(Credential) : 자원에 접근하는 유저의 비밀번호
스프링 시큐리티의 동작 원리
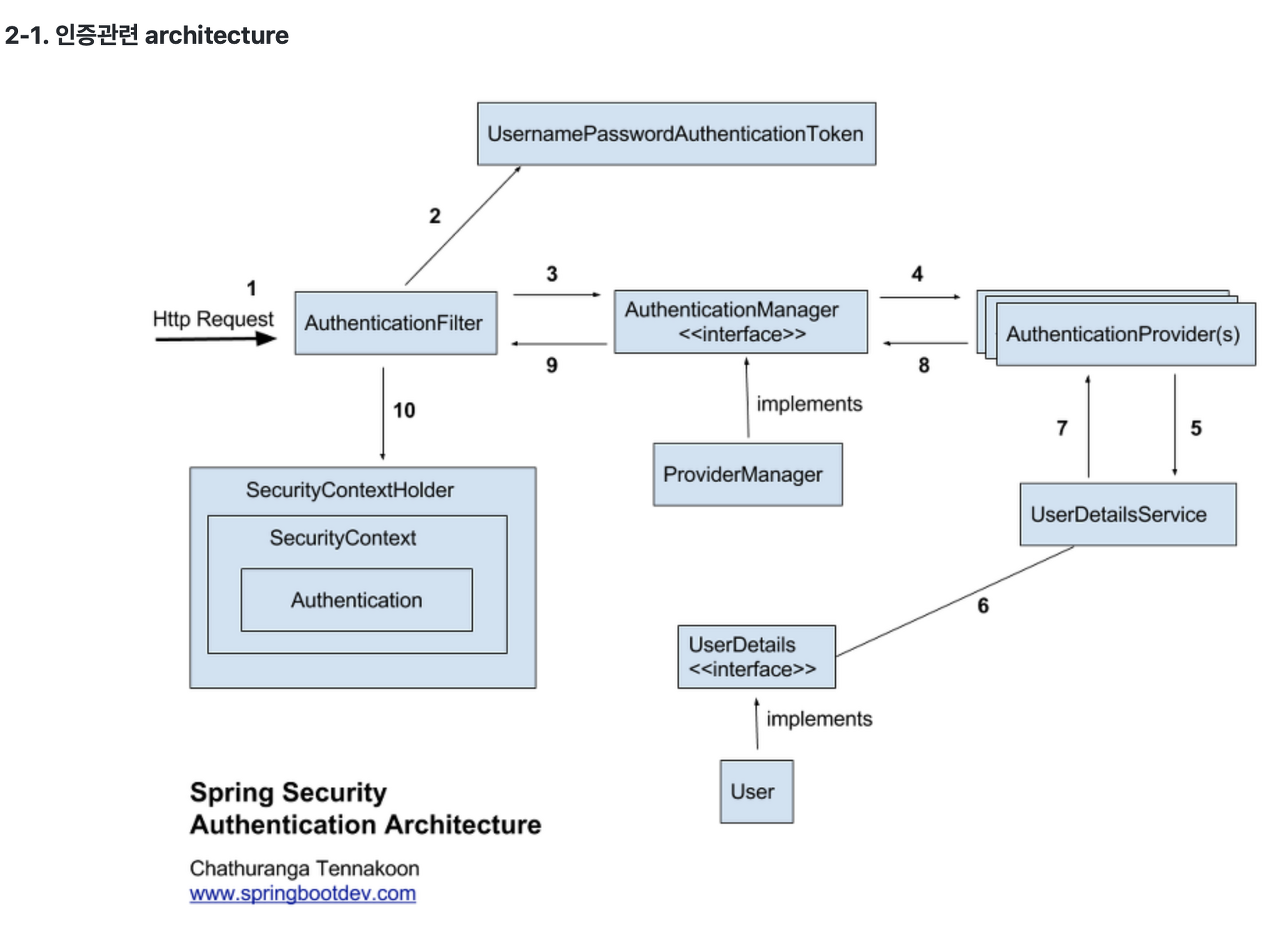
위 그림은 스프링 시큐리티의 아키텍쳐이다. 참고하여 동작하는 과정에 대해 알아보자.
-
유저가 로그인을 요청하면 id, password가 Request에 담겨 보내진다.
-
AuthenticationFilter에서 Request를 가로채 인증용 객체인UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken을 생성한다. -
인증을 담당하는
AuthenticationManager에게 인증용 객체를 준다.
AuthenticationManager는 등록된AuthenticationProvider들을 조회하여 인증 요구.
*인터페이스AuthenticationManager의 구현체 :ProviderManager -
Token 처리를 할 수 있고, 실제로 인증을 하는
AuthenticationProvider에게 다시 인증용 객체를 전달한다. -
AuthenticationProvider인터페이스가 실행되며 DB에 있는 유저 정보와 입력한 로그인 정보를 비교한다. -
AuthenticationProvider에서 DB에 있는 유저 정보를 가져오기 위해선UserDetailsService인터페이스를 사용한다. -
User에 일치하는 유저가 있으면 그 정보를
UserDetails형으로 가져온다.
*이용자가 존재하지 않으면 예외 던짐 -
5, 6, 7 과정을 통해 가져온 유저 정보를 비교하여, DB의 정보와 입력한 정보가 일치하면
Authentication참조를 반환한다.
*일치하지 않으면 예외던짐 -
인증 완료 시
Authentication객체를SecurityContextHolder에 담아AuthenticationSuccessHandler를 실행 한다.
AuthenticationFilter
- 모든 Request는 인증과 인가를 위해 이 필터를 통과
- 인증 성공 시 얻은 Authentication 객체를 SecurityContext 에 저장 후 AuthenticationSuccessHandler 실행
- 인증 실패 시 AuthenticationFailureHandler 실행
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken
- Authentication을 구현한 AbstractAuthenticationToken의 하위 클래스임
public class UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken extends AbstractAuthenticationToken {
// ID
private final Object principal;
// PW
private Object credentials;
// 인증 전 객체 생성
public UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(Object principal, Object credentials) {
super(null);
this.principal = principal;
this.credentials = credentials;
setAuthenticated(false);
}
// 인증 완료 객체 생성
public UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(Object principal, Object credentials,
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities) {
super(authorities);
this.principal = principal;
this.credentials = credentials;
super.setAuthenticated(true); // must use super, as we override }
}
}
public abstract class AbstractAuthenticationToken implements Authentication, CredentialsContainer {
}AuthenticationManager
- 인증을 처리하는 인터페이스.
*실질적으론 AuthenticationManager에 등록된 AuthenticationProvider에 의해 처리 됨 - Authentication 객체를 리턴
public interface AuthenticationManager {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException; }ProviderManager
- AuthenticationManager의 구현체
- 사용자 인증 시도
- 아래 코드에서 볼 수 있듯, 실제 인증 과정에 대한 로직이 있는 AuthenticationProvider을 List로 가지고 있다.
- 모든 provider 조회하며 인증(Authenticate) 처리
public class ProviderManager implements AuthenticationManager, MessageSourceAware,
InitializingBean {
public List<AuthenticationProvider> getProviders() {
return providers;
}
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
Class<? extends Authentication> toTest = authentication.getClass();
AuthenticationException lastException = null;
Authentication result = null;
boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
// result가 나올 때 까지 반복
for (AuthenticationProvider provider : getProviders()) {
....
try {
// 모든 provider 조회하며 인증(Authenticate) 처리
result = provider.authenticate(authentication);
if (result != null) {
copyDetails(authentication, result);
break;
}
} catch (AccountStatusException e) {
prepareException(e, authentication);
// SEC-546: Avoid polling additional providers if auth failure is due to
// invalid account status
throw e;
}
....
}
throw lastException;
}
}AuthenticationProvider
- 실제 인증을 담당하는 인터페이스
- 인증 전 Authentication 객체를 받아 DB의 유저 정보와 입력한 유저 정보를 비교하여, 인증된 객체인 Authentication를 반환한다.
public interface AuthenticationProvider {
// 인증 전의 Authenticaion 객체를 받아서 인증된 Authentication 객체를 반환
Authentication authenticate(Authentication var1) throws AuthenticationException;
boolean supports(Class<?> var1);
}Authentication
- 현재 접근하는 주체의 정보와 권한을 담는 인터페이스
- Authentication 객체는 SecurityContext에 저장되며 SecurityContextHolder를 통해 SecurityContext에 접근하고 SecurityContext를 통해 Authentication에 접근 할 수 있다.
public interface Authentication extends Principal, Serializable {
// 현재 사용자 권한 목록
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();
// 비밀번호
Object getCredentials();
Object getDetails();
// Principal 객체
Object getPrincipal();
// 인증 여부
boolean isAuthenticated();
// 인증 여부 설정
void setAuthenticated(boolean isAuthenticated) throws IllegalArgumentException;
}UserDetailsService
- DB의 유저 정보를 가져오는 인터페이스
public interface UserDetailsService {
UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String var1) throws UsernameNotFoundException;
}UserDetails
- 사용자 정보를 담는 인터페이스, 구현해서 사용
public interface UserDetails extends Serializable {
// 권한 목록
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();
// 비밀번호
String getPassword();
// 계정 고유 값
String getUsername();
// 만료 여부
boolean isAccountNonExpired();
// 잠김 여부
boolean isAccountNonLocked();
// 비밀번호 만료 여부
boolean isCredentialsNonExpired();
// 활성화 여부
boolean isEnabled();
}참고
https://velog.io/@soyeon207/SpringBoot-스프링-시큐리티란
https://parkmuhyeun.github.io/study/spring security/2022-01-29-Spring-Security(1)/
https://mangkyu.tistory.com/76
