Erdős–Rényi random graph

위와 같은 특성으로 인해 ER graph 는 Poisson Random Graph 라고도 불린다. ER graph 에서 분석할 여러가지 특성이 있지만 가장 먼저 Giant Component의 존재성에 대한 분석을 해보려고 한다. 특히 로 설정하고 일때 의 범위에 따른 존재성을 파악하려고 한다. 위의 과정에 앞서 GW brancing process에 대해 알아볼 것이다.
Galton-Watson branching process
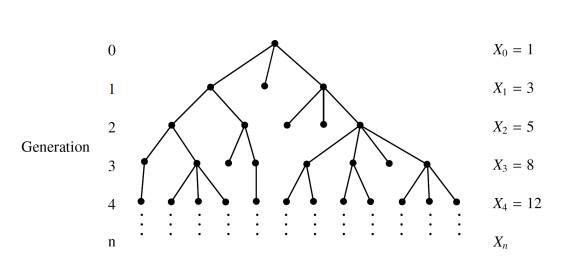
: the number of individual at genration n
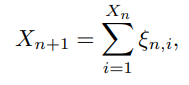
: the number of child of i-th individual at generation n
가 n과 i에 대해 i.i.d. 하다고 하면 로 표현 할 수 있다.
, for non-negative integer k
{} 는 offspring distribution이라고 불린다.
정리하자면 각 노드는 {} 분포로 자식을 가지며 각 노드에 대한 이 분포는 독립적으로 동일하게 적용된다. 이 graph에서 우리가 관심이 있는 것은
(1) {} 분포가 어떤 조건일때 이 그래프가 extinction 하는지
(2) 만약 extinction 한다면 total population이 어떻게 되는지
를 extinction probability 라고 하자.
Depth-first Exploration
(1) {} 분포가 어떤 조건일때 이 그래프가 extinction 하는지
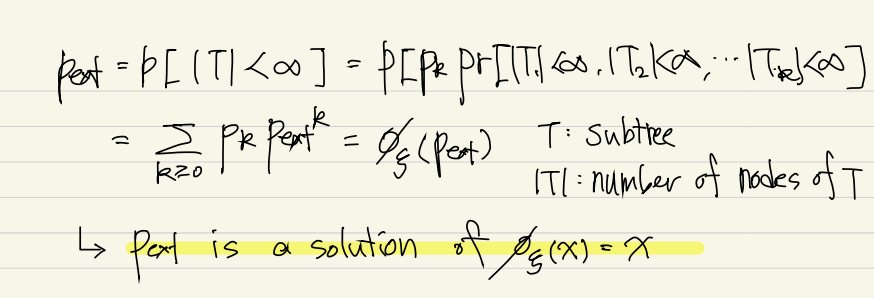
(2) 만약 extinction 한다면 total population이 어떻게 되는지
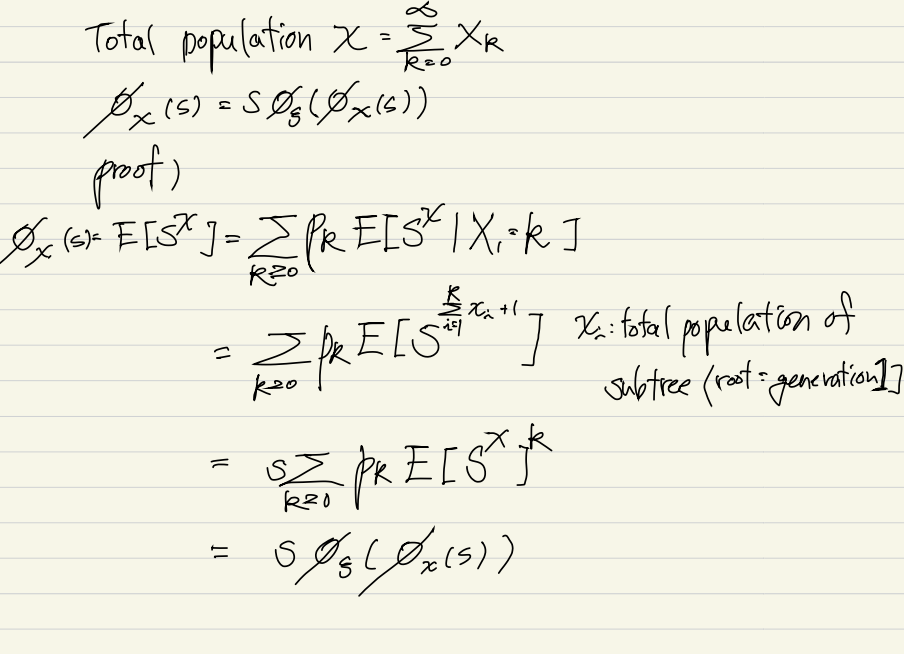
Breadth-first Exploration
(1) is the smallest solution of
(2) 일때 아래의 특성을 보임
(2-1) Subcritical regime : If , then
(2-2) Critical regime : If and , then
(2-3) Supercritical regime : If , then
(1)'s proof
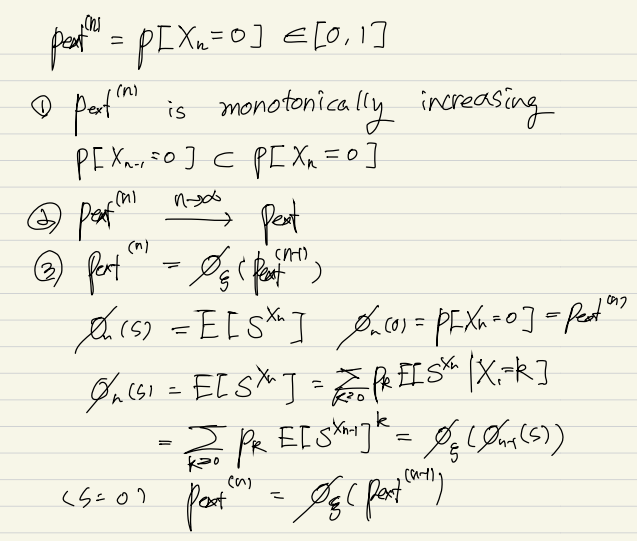
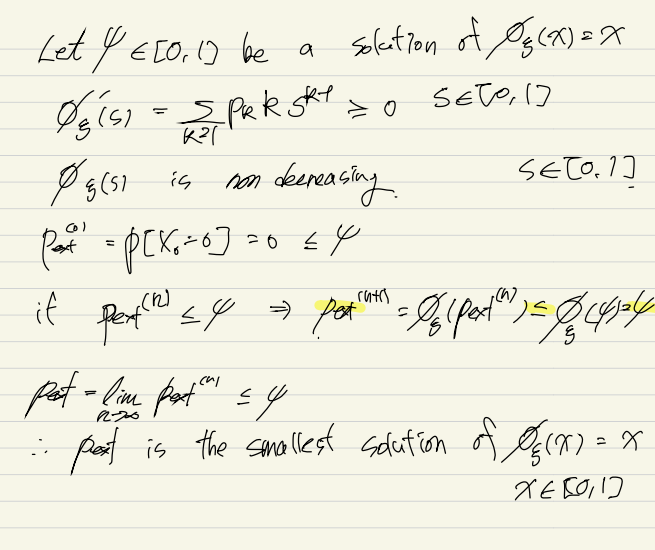
(2)'s proof
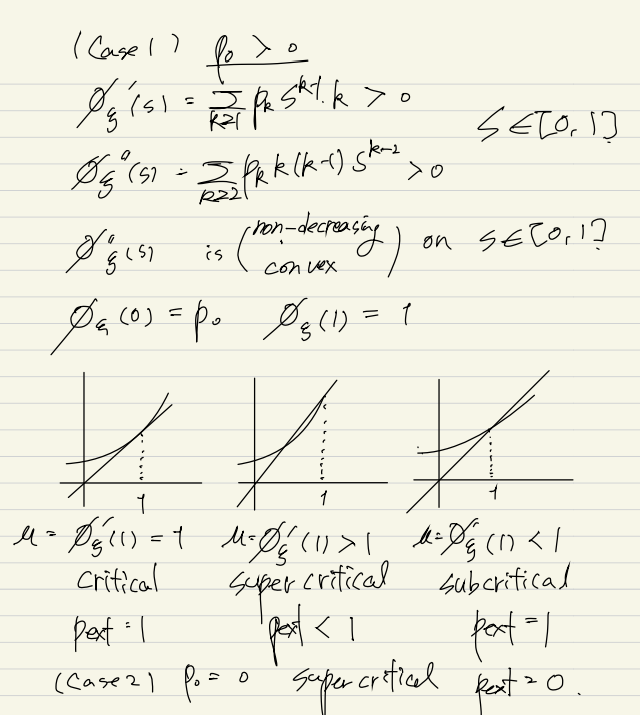
One-by-one Exploration
Exploration model
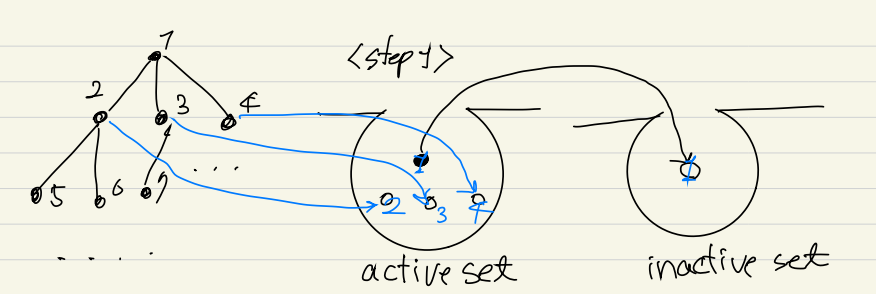
초기 조건은 active set에 root node만 존재
1. active set에서 무작위로 하나의 node 선택
2. 선택된 node의 child node를 모두 active set에 넣고 선택된 node를 inactive set에 넣는다
3. active set에 node가 존재하면 1 로 돌아가고 그렇지 않으면 종료
이런 모델을 통해 total population 의 추정을 하고자 한다.
: the number of active nodes at step n
: the number of children of the node chosen at step n

Exponentially tilted distribution
특정 Distribution을 분석하기 어려울때 이 Distribution을 tilt 해서 분석하기 쉬운 약간 다른 Distribution을 생성하여 두 Distribution의 mapping 관계를 이용하는 경우가 많다. 여기서는 offspring distribution 의 Critical regime, 즉 and 일때 를 Exponentially tilted distribution으로 변환하여 사용하려고 한다.

(1) (resp. ) the offspring distribution leads to supercritical(resp. subcritical) process
proof)

Daul Parameter
다음 조건을 만족하는 는 의 dual parameter 이다.
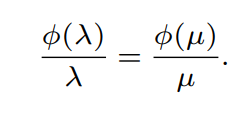
(1) Dual Paramter 는 unique 한 쌍을 가지며 이면 이다.
(2) 와 는 를 만족한다. 이 때 는 offspring distribution {} 의 extinction probability 이다.
(1)'s proof
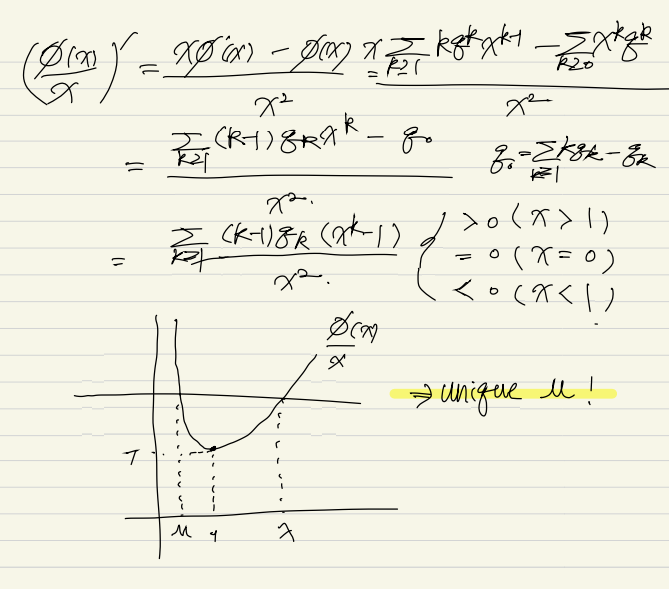
(2)'s proof

Duality of Branching Process
일때 offspring distribution { } 의 distribution of history conditioned on extinction은 { } 의 distribution of history 와 일치한다. ( is dual parameter of )
proof

Meaning : Supercritical branching process 는 분석하기 매우 까다롭다.(extinction 이 확정적으로 일어나지 않기 떄문) subcritical brancing process인 dual parameter를 이용하면 비교적 쉽게 분석할 수 있다.
