Data Structures & Algorithms Review
Adopted and summarized from Columbia University COMS W3251 Professor Bauer's class
Graph Traversals
Depth First Search (uses Stack)
Single-source shortest paths
protected Set<Node> marked;
protected Graph graph;
public DepthFirstSearch(Graph graphToSearch) {
marked = new HashSet<Node>();
graph = graphToSearch;
}
public boolean dfs(Node start, String elementToFind) {
if (start.getElement().equals(elementToFind)) {
return true;
} else {
marked.add(start);
for (Node neighbor : graph.getNodeNeighbors(start)) {
if (!marked.contains(neighbor) &&
dfs(neighbor, elementToFind)
return true;
}
return false;
}
}Breadth First Search (uses Queue)
Basic pseudocode for graph traversal
Queue q
q.enqueue(start)
Set visited
while (q is not empty):
u = q.dequeue()
for each v adjacent to u:
if (v is not in visited):
q.enqueue(v)Single-source unweighted shortest paths
Using "cost" attribute of each vertex to store distances
public void unweighted_shortest_paths(V start) {
LinkedList<Vertex> queue = new LinkedList<>();
Vertex startv = vertices.get(start);
startv.cost = 0 ;
startv.discovered = true;
queue.addLast(startv); // add start vertex
while (queue.size() > 0 ) { // as long as the queue is not empty
Vertex u = queue.pollFirst(); // Visit u
System.out.println(u);
for (Edge uv : u.adjacent ){ // Discover v
Vertex v = uv.target;
if (!v.discovered) { // if v has not been seen before
v.cost = u.cost + 1; // set cost
v.prev = u; // set reference to previous vertex on shortest path
v.discovered = true;
queue.addLast(v); // add v to the queue.
}
}
}
}Using HashMap to store distances
public int bfsDistance(Node start, string elementToFind) {
HashMap<Node, Integer> distances = new HashMap<Node, Integer>();
Queue<Node> toExplore = new LinkedList<Node>();
Set<Node> marked = new HashSet<Node>();
marked.add(start);
toExplore.add(start);
distances.put(start, 0);
while (!toExplore.isEmpty()) {
Node current = toExplore.remove();
for (Node neighbor : graph.getNodeNeighbors(current)) {
if (!marked.contains(neighbor)) {
distances.put(neighbor, distances.get(current) + 1);
if (neighbor.getElement().equals(elementToFind)) {
return distances.get(neighbor);
}
marked.add(neighbor);
toExplore.add(neighbor);
}
}
}
return -1;
}Topological Sort for Directed Acyclic Graphs (using LinkedList, BFS approach)

protected Map<V, Vertex> vertices;
private void compute_indegrees() {
for (Vertex u : vertices.values()) {
for (Edge uv : u.adjacent) {
Vertex v = uv.target;
v.indegree += 1;
}
}
}
public List<V> topo_sort() {
ArrayList<V> sort = new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList<Vertex> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// compute indegrees
compute_indegrees();
// Add all vertices with indegree 0 to queue.
for (Vertex u : vertices.values()) {
if (u.indegree == 0)
queue.addLast(u);
}
// Main loop of topological sort
while (queue.size() > 0) {
Vertex u = queue.pollFirst(); // dequeue first element
sort.add(u.name);
for (Edge uv : u.adjacent) {
Vertex v = uv.target;
if (--v.indegree == 0)
queue.addLast(v);
}
}
return sort;
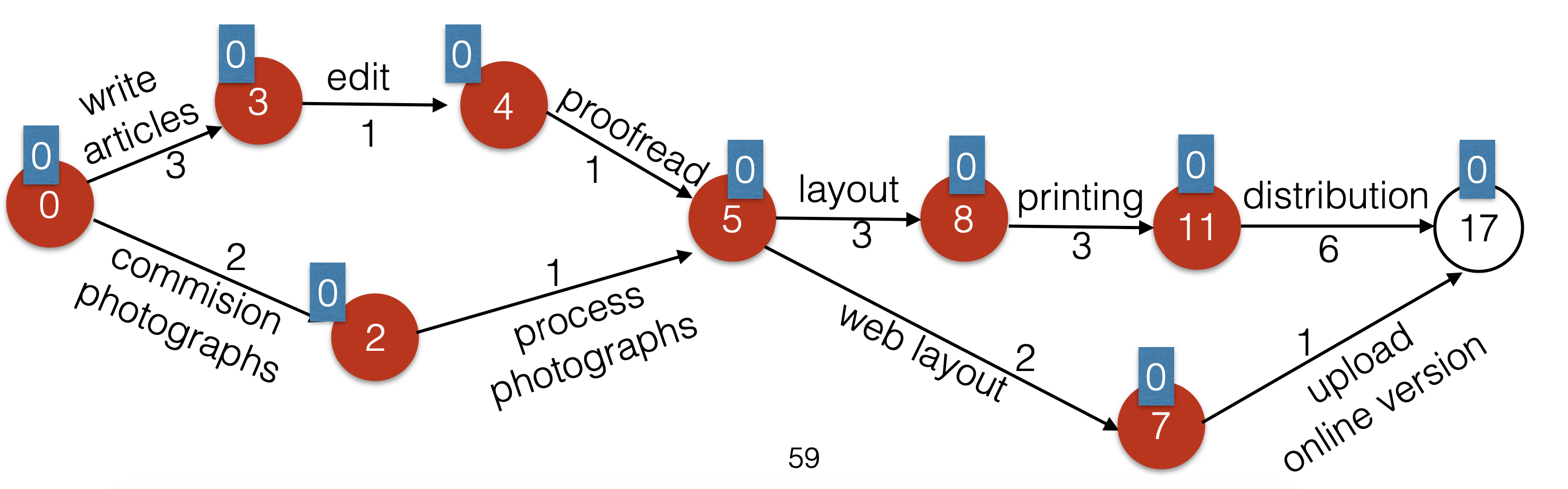
}Earliest Completion Time with Topological Sort
- Earliest completion time for each vertex is the same as the magnitude of the longest distance to reach the vertex (because any of the incoming path has to be completed in order for the work in the target vertex to be completed)
- While the queue is not empty, dequeue a vertex, decrement the indegree of its adjacent nodes. Then update earliest completion time for each adjacent node (possibly using an if statement to compare whether the incoming edge results in maximum path currently recorded for the target vertex)
Dijkstra's Algorithm for Weighted Shortest Path (using heap, BFS approach)
- Keep nodes on a priority queue and always expand the vertex with the lowest cost annotation first (adopting the greedy algorithm approach)
Pseudocode
for all v:
v.cost = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY
v.visited = false
v.prev = null
start.cost = 0
PriorityQueue q
q.insert(start)
while (q is not empty):
u = q.pollMin() // visit vertex u
u.visited = true
// discover and relax vertex v
for each v adjacent to u:
if not v.visted:
c = u.cost + cost(u,v)
if (c < v.cost):
v.cost = c
v.prev = u
q.insert(v)
Minimuim Spanning Tree using Prim's Algorithm
- Another greedy algorithm that is a slight variation of Dijkstra's algorithm.
Pseudocode
for all v:
v.cost = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY
v.visited = false
v.prev = null
start.cost = 0
PriorityQueue q
q.insert(start)
while (q is not empty):
u = q.pollMin() // visit vertex u
u.visited = true
// discover and relax vertex v
for each v adjacent to u:
if not v.visted:
if (cost(u,v) < v.cost):
v.cost = cost(u,v)
v.prev = u
q.insert(v) Runtime Summary
BFS : O( |V|+|E| )
Topological Sort : O( |V|+|E| )
Dijkstra : O( |E| log|E| ) = O( |E| log|V| )
- |E| insert + deleteMin operations
- Each insertion takes O(log|E|)
- |E| <= |V|^2 always
Prim's algorithm : Same as Dijkstra
Heap
- getMin() / getMax() in O(1)
- inserting N items to a heap in O(N)
- Heap sort --> O(N log N)
Heap as an array representation
- leftChild(i) = 2i
- rightChild(i) = 2i + 1
- parent(i) = floor(i/2)
Heap property
- The values of all nodes in the subtree rooted in n are gerater or equal than the value of n (for min-heap)
Insert(x)
- insert at the last array position
- if heap order property is violated, percholate the value up
percholate up
- swap the value in the hole and value in the parent cell
- if heap order is still violated, continue until correct position is found
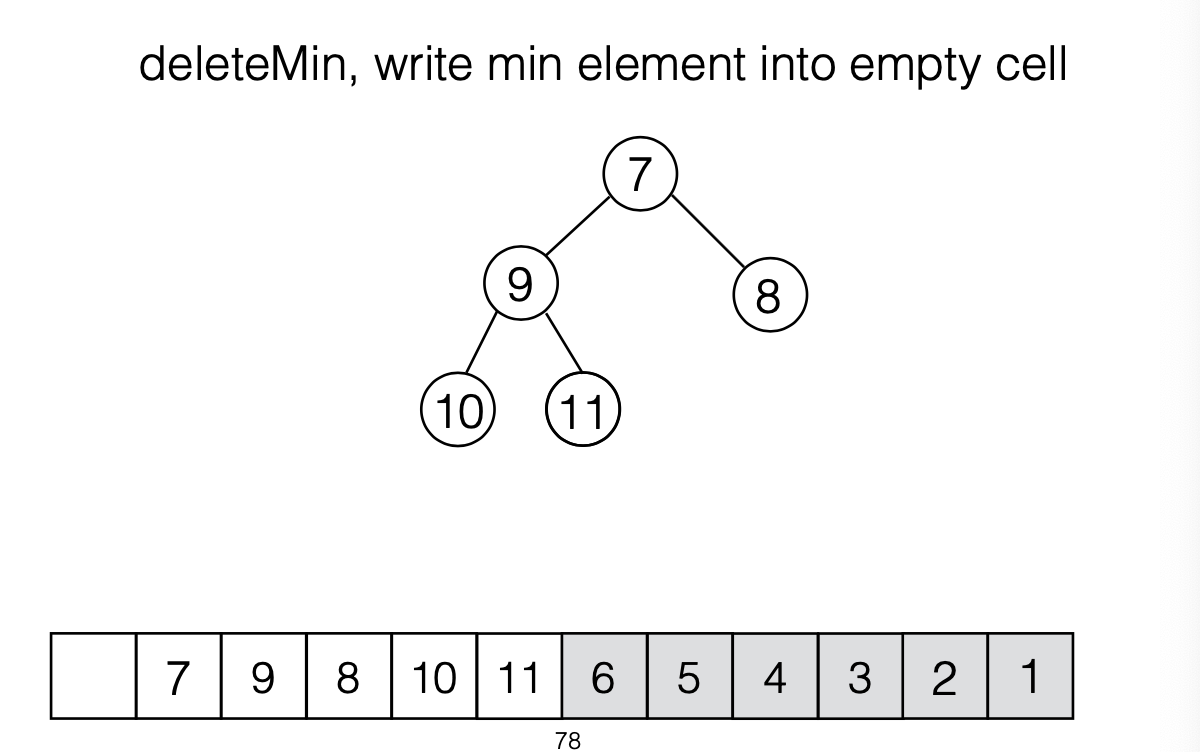
deleteMin()
- remove root
- try placing the last item in the heap into the root
- if heap order is violated, percholate the value down
- swap with smaller child in every level until correct position is found
Heapify()
- O(N)
- start with an unordered array and restore heap property bottom-up
public void buildHeap( ) {
// start evaluating heap property from the lowest level
for( int i = currentSize / 2; i > 0; i-- )
percolateDown( i );
}
private void percolateDown( int hole ) {
int child;
T tmp = array[ hole ];
boolean done = false;
while (!done && hole * 2 <= currentSize) {
// Select the index of the smaller child
child = hole * 2; // left child
if( child != currentSize && // is there a right child?
array[ child + 1 ].compareTo( array[ child ] ) < 0 ) // right child < left child?
child++; // if so, let child point to the right child index
if( array[ child ].compareTo( tmp ) < 0 ) {
array[ hole ] = array[ child ];
hole = child;
}
else
done=true;
}
array[ hole ] = tmp;
}Heap Sort
- Convert an unordered array into a heap in O(N) time (Heapify)
- Perform N deleteMin operations to retrieve the elements in sorted order
- each deleteMin is O(log N)- total : O (N log N)
- To minimize space complexity, instead of using a second array to store the output, re-use the freed space after each deleteMin
Selection Problem
- selecting the k-th largest number from a sequence of N numbers
Option 1 w/ Max-Heap
- build a Max-Heap in O(N), then call deleteMax() k times
- Total: O(N log N)
Option 2 w/ Min-Heap
- build a Min-Heap in O(k) for only the first k unordered elements
- iterate through the rest of the sequence (N-k elements)
- if a number is larger than the root of the heap, remove the root of the heap and insert the new number into the heap, which takes O(log K) - Total : O(N log k)
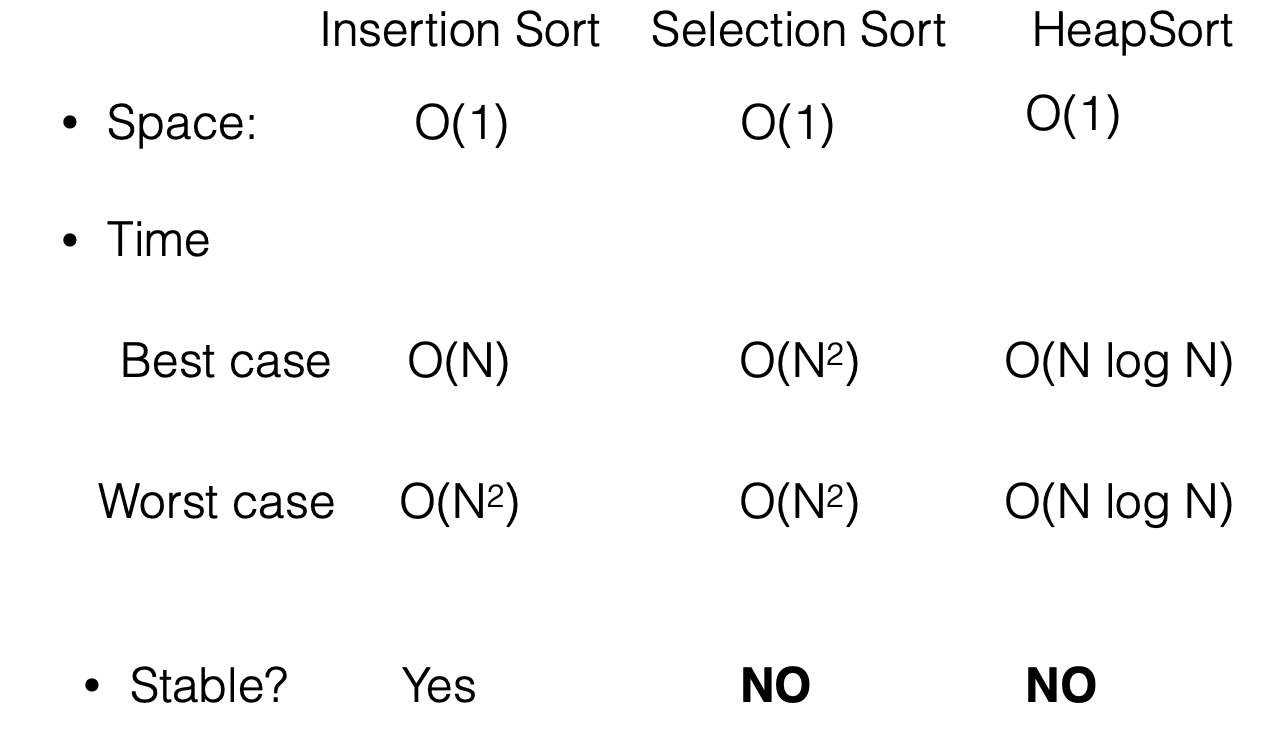
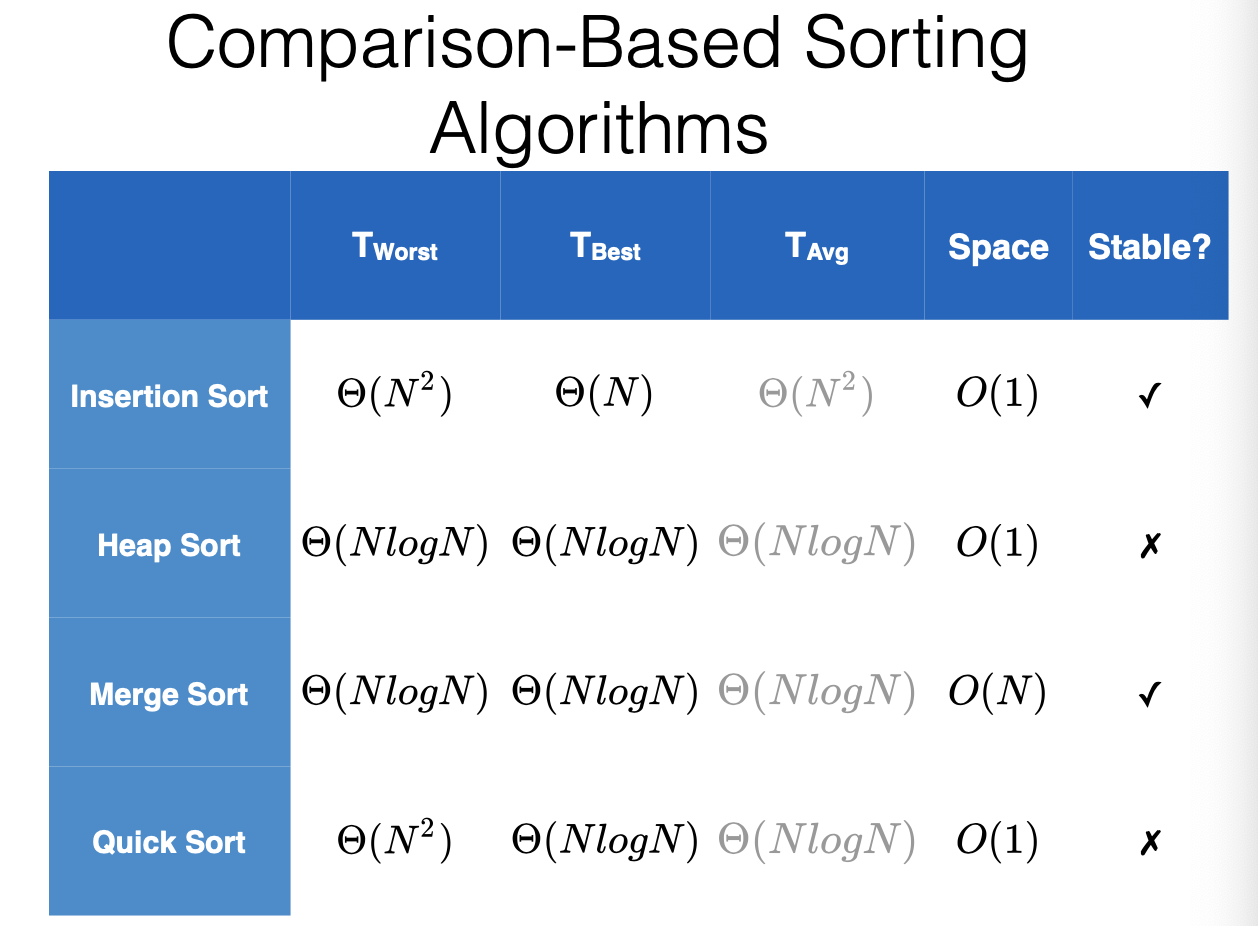
Sorting Algorithms
- A sorting algorithm is stable if the relative order of duplicate items in the input is preserved
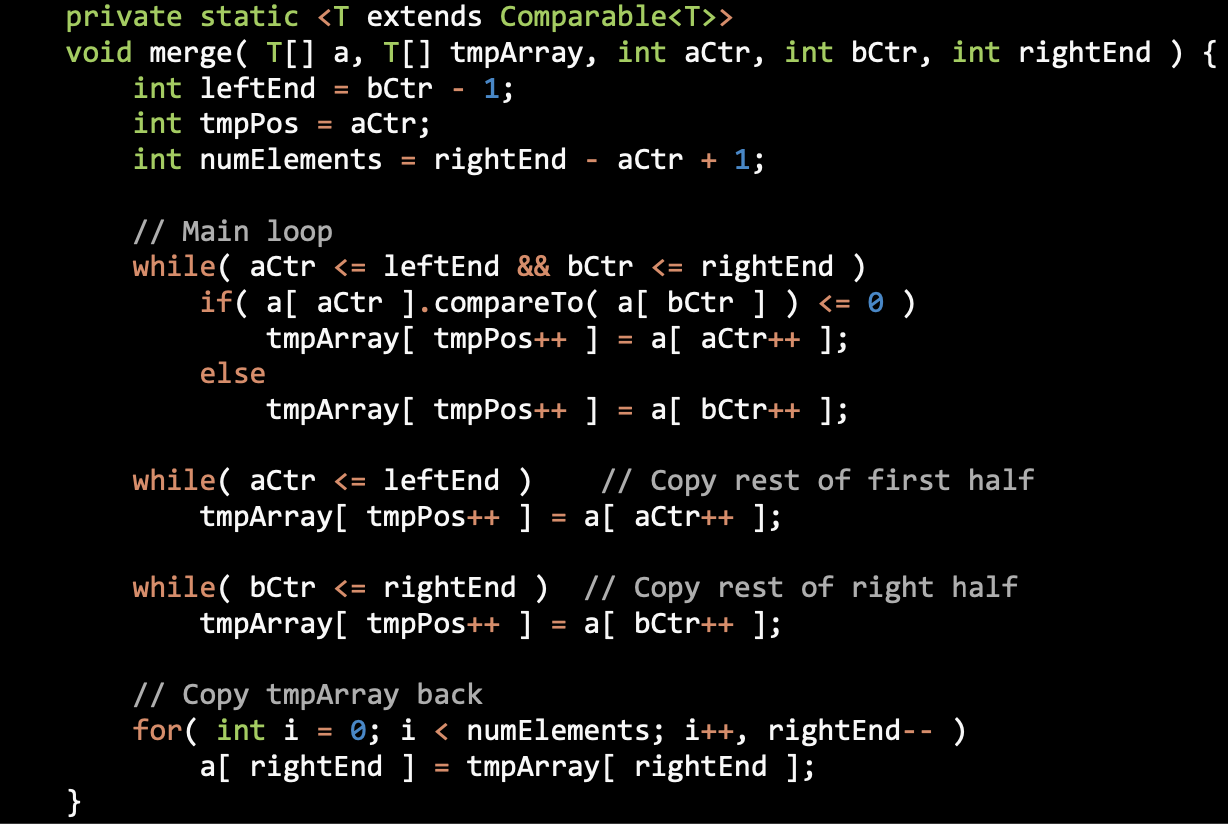
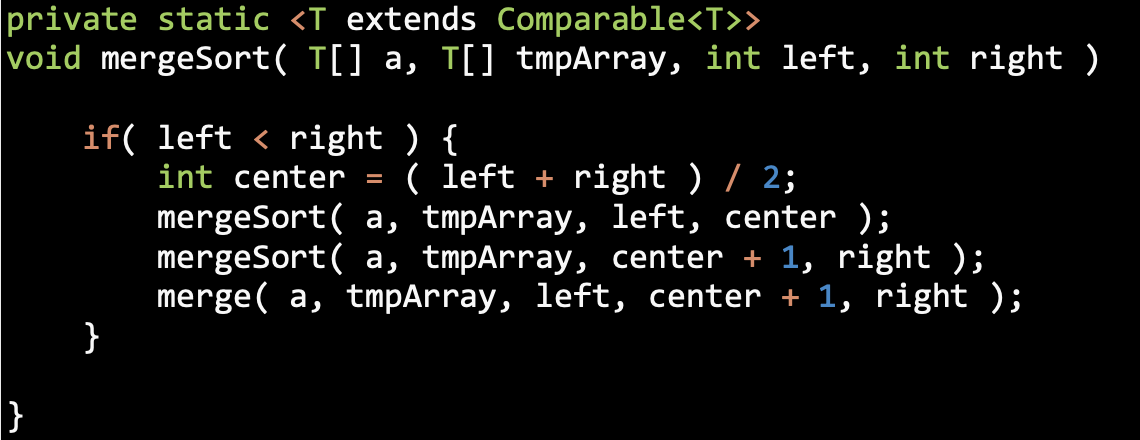
Merge Sort
Merging Sorted Sublists
Merge Sorting
Quick Sort

Partitioning the Subarrays
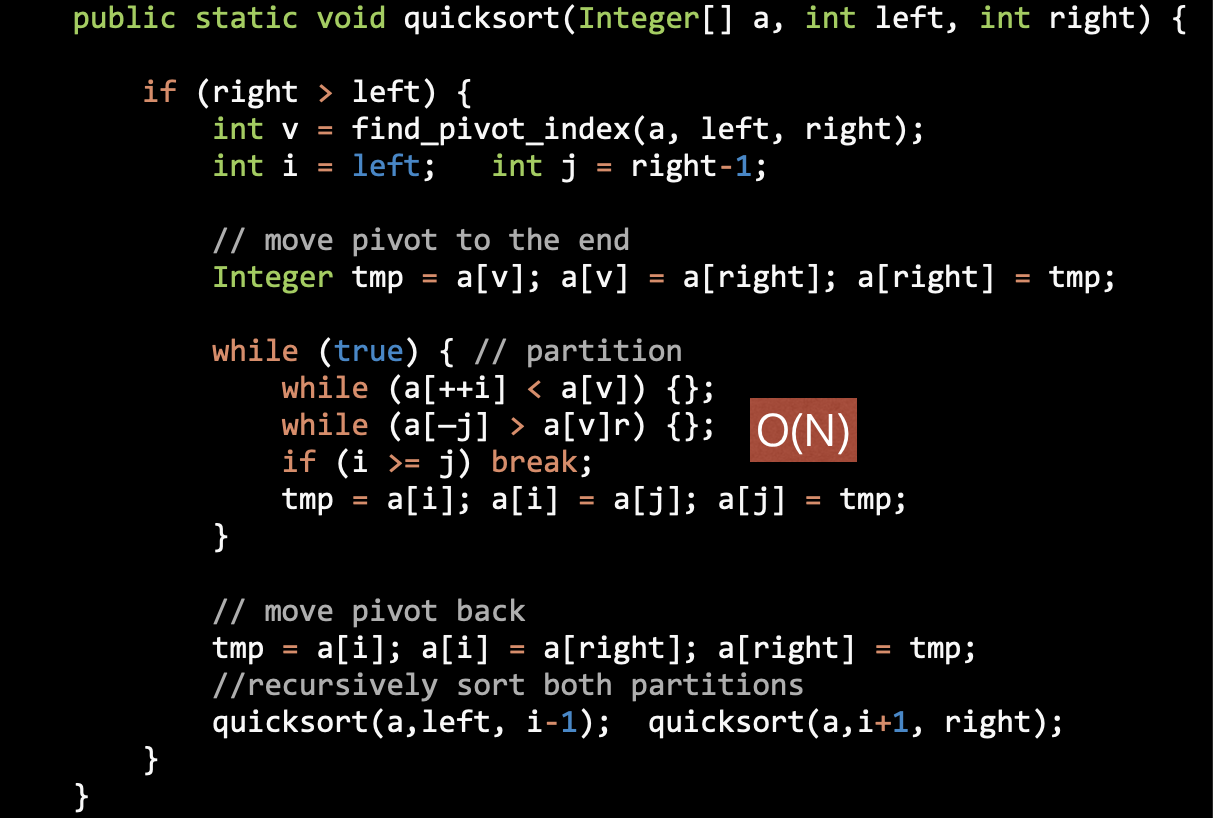
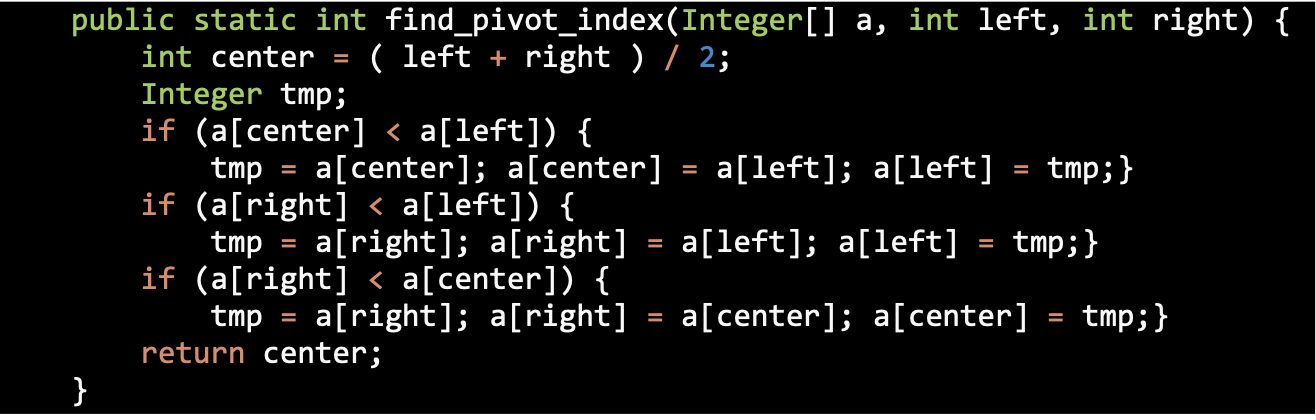
Choosing the Pivot
- computing the pivot should be a constant time
- choose a random element for the pivot, or "median-of-three" (choosing the element at the beginning / end / middle is a terrible idea)
Median of Three
Runtime Analysis
Hash Table
Collision Resolution Strategies
(hash(x) + f(i)) % TableSize
- linear probing : f(i) = i
- quadratic probing : f(i) = i^2
Quadratic Probing Theorem
If
TableSizeis prime, then the firstTableSize/2cells visited by quadratic probing are distinct.
Therefore we can always find an empty cell if the table is at most half full.
Double hashing
f(i) = i * hash2(x)
- Compute a second hash function to determine a linear offset for this key
- A good choice for integers is
hash2(x) = R - (x % R)

Mastering data structures and algorithms is crucial for any aspiring programmer. Whether you're preparing for interviews or aiming to improve coding efficiency, understanding concepts like trees, graphs, and sorting methods is a must. In the detailed guide, Oh It's Reviewed, every topic is broken down with clarity and real-world examples. It’s the perfect roadmap for coding success!