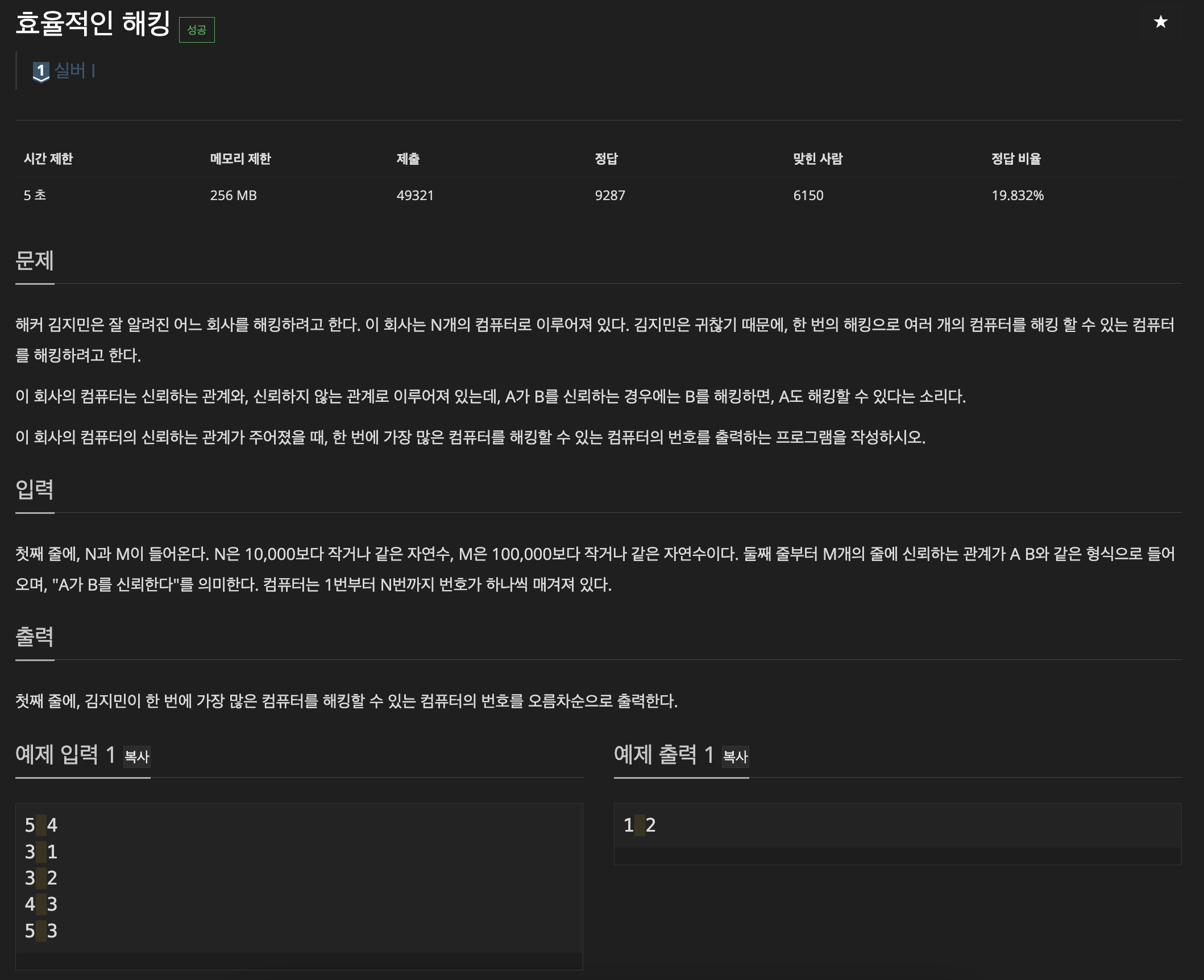
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1325
풀이 ① - DFS
1. 아이디어
-
"A가 B를 신뢰" 하는 경우, B를 해킹하면 A도 해킹 가능
=> 신뢰 관계 (방향이 있는 간선)을 따라 그래프 탐색
=> 인접 리스트List<Integer>[] lists에 간선 정보 저장 -
각
[i]번 컴퓨터를 시작 노드로 하여, 전체 DFS n번 수행
ex) 예제 입력 1
인접 리스트:List<Integer>[] lists
lists[1] = []
lists[2] = []
lists[3] = [1, 2]
lists[4] = [3]
lists[5] = [3]
[1]번 ~[5]번 컴퓨터를 시작 노드로 하여, 각각 DFS 수행
[1]번 컴퓨터에서 해킹 (탐색 시작)[2]번 컴퓨터에서 해킹[3]번 컴퓨터에서 해킹 ->[1],[2]번 컴퓨터 해킹[4]번 컴퓨터에서 해킹 ->[3]번 컴퓨터 해킹 ->[1],[2]번 컴퓨터 해킹[5]번 컴퓨터에서 해킹 ->[3]번 컴퓨터 해킹 ->[1],[2]번 컴퓨터 해킹
2. 자료구조
-
List<Integer>[] lists: 신뢰 관계 간선 정보 (인접 리스트) -
int[] hackCounts: 각 컴퓨터를 해킹 했을 때, 해킹 가능한 컴퓨터 수 배열
ex)hackCounts[i]:[i]번 컴퓨터를 해킹 했을 때, 해킹 가능한 컴퓨터 수 -
boolean[] visited
3. 시간 복잡도
-
인접 리스트로 구현한 DFS / BFS의 시간 복잡도: O(V + E)
-
각
[i]번 컴퓨터를 시작 노드로 하여 DFS n번 수행: O(V (V + E))
여기서 V = 입력
n, E = 입력m이 아닐 수 있음
- 각
[i]번 컴퓨터를 시작 노드로 하여 DFS 탐색할 때,
방문하는 노드 개수 V, 연결된 간선 개수 E
코드
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main_DFS {
static int n, m; // n개 컴퓨터, m개 컴퓨타 신뢰 관계
static List<Integer>[] lists; // 컴퓨터 신뢰 관계 (인접 리스트)
static int[] hackCounts; // [i]번 컴퓨터를 해킹 했을때, 해킹 가능한 컴퓨터 수
static boolean[] visited;
static void dfs(int currentIdx) {
for (int nextIdx : lists[currentIdx]) {
if (!visited[nextIdx]) {
visited[nextIdx] = true;
hackCounts[nextIdx]++;
dfs(nextIdx);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(System.in)
);
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
n = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
m = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
lists = new List[n + 1]; // 컴퓨터(정점) 번호 [1] ~ [n] 사용
hackCounts = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
lists[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int start = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int end = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
lists[start].add(end);
}
// 각 [i]번 컴퓨터를 시작 노드로 하여 DFS 탐색 수행
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
visited = new boolean[n + 1]; // 방문 처리 배열 초기화
visited[i] = true;
hackCounts[i]++;
dfs(i);
}
int maxHackCount = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
maxHackCount = Math.max(maxHackCount, hackCounts[i]);
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (hackCounts[i] == maxHackCount) {
sb.append(i).append(" ");
}
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
}풀이 ② - BFS
1. 아이디어
-
"A가 B를 신뢰" 하는 경우, B를 해킹하면 A도 해킹 가능
=> 신뢰 관계 (방향이 있는 간선)을 따라 그래프 탐색
=> 인접 리스트List<Integer>[] lists에 간선 정보 저장 -
각
[i]번 컴퓨터를 시작 노드로 하여, 전체 BFS n번 수행
ex) 예제 입력 1
인접 리스트:List<Integer>[] lists
lists[1] = []
lists[2] = []
lists[3] = [1, 2]
lists[4] = [3]
lists[5] = [3]
[1]번 ~[5]번 컴퓨터를 시작 노드로 하여, 각각 BFS 수행
[1]번 컴퓨터에서 해킹 (탐색 시작)[2]번 컴퓨터에서 해킹[3]번 컴퓨터에서 해킹 ->[1],[2]번 컴퓨터 해킹[4]번 컴퓨터에서 해킹 ->[3]번 컴퓨터 해킹 ->[1],[2]번 컴퓨터 해킹[5]번 컴퓨터에서 해킹 ->[3]번 컴퓨터 해킹 ->[1],[2]번 컴퓨터 해킹
2. 자료구조
-
List<Integer>[] lists: 신뢰 관계 간선 정보 (인접 리스트) -
int[] hackCounts: 각 컴퓨터를 해킹 했을 때, 해킹 가능한 컴퓨터 수 배열
ex)hackCounts[i]:[i]번 컴퓨터를 해킹 했을 때, 해킹 가능한 컴퓨터 수 -
Queue<Integer>,LinkedList<Integer>: BFS 수행 -
boolean[] visited
3. 시간 복잡도
-
인접 리스트로 구현한 DFS / BFS의 시간 복잡도: O(V + E)
-
각
[i]번 컴퓨터를 시작 노드로 하여 BFS n번 수행: O(V (V + E))
여기서 V = 입력
n, E = 입력m이 아닐 수 있음
- 각
[i]번 컴퓨터를 시작 노드로 하여 BFS 탐색할 때,
방문하는 노드 개수 V, 연결된 간선 개수 E
코드
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main_BFS {
static int n, m; // n개 컴퓨터, m개 컴퓨타 신뢰 관계
static List<Integer>[] lists; // 컴퓨터 신뢰 관계 (인접 리스트)
static int[] hackCounts; // [i]번 컴퓨터를 해킹 했을때, 해킹 가능한 컴퓨터 수
static boolean[] visited;
static Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
static void bfs() {
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int currentIdx = queue.remove();
for (int nextIdx : lists[currentIdx]) {
if (!visited[nextIdx]) {
visited[nextIdx] = true;
hackCounts[nextIdx]++;
queue.add(nextIdx);
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(System.in)
);
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
n = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
m = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
lists = new List[n + 1]; // 컴퓨터(정점) 번호 [1] ~ [n] 사용
hackCounts = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
lists[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int start = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int end = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
lists[start].add(end);
}
// 각 [i]번 컴퓨터를 시작 노드로 하여 BFS 탐색 수행
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
visited = new boolean[n + 1]; // 방문 처리 배열 초기화
visited[i] = true;
hackCounts[i]++;
queue.add(i);
bfs();
}
int maxHackCount = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
maxHackCount = Math.max(maxHackCount, hackCounts[i]);
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (hackCounts[i] == maxHackCount) {
sb.append(i).append(" ");
}
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
}