백준 6091 핑크 플로이드
풀이
 주어진 예제를 기반으로 표를 인접 행렬을 표로 그려보면
주어진 예제를 기반으로 표를 인접 행렬을 표로 그려보면
| 입력 | 출력 |
|---|---|
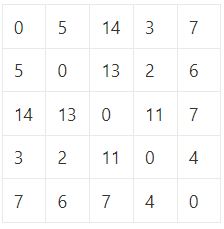 | 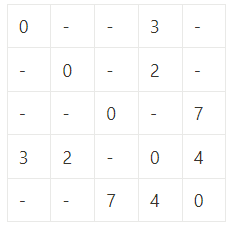 |
이런 형태의 연결 관계를 보입니다.
이 출력 표를 기반으로 그래프를 그려보았습니다.
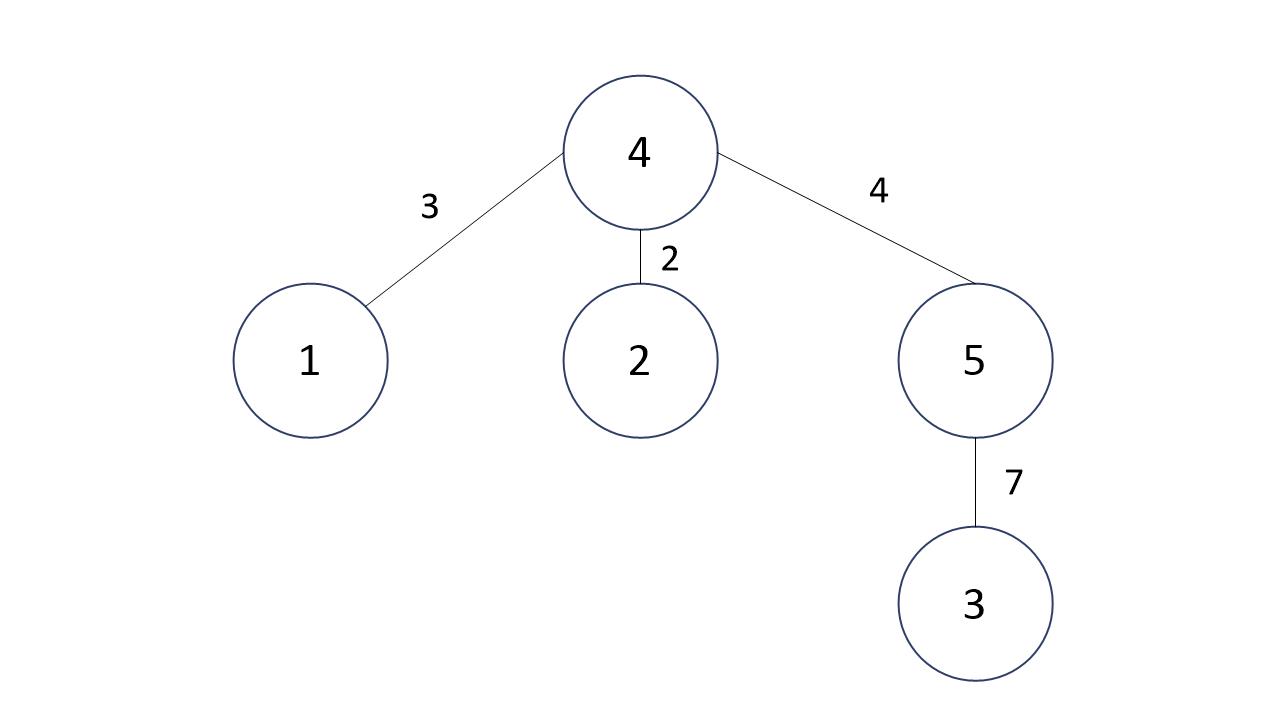
해당 표를 보면 알 수 있듯이 입력으로 주어진 인접 행렬을 기반으로 MST를 만들면 그것이 원본(출력)이 된다는 사실을 알 수 있습니다.
MST (최소 신장 트리)
MST란?
사이클없이 모든 간선을 연결하는 부분 그래프 중 간선 가중치의 합이 최소인 그래프입니다.
모든 정점을 연결하며 사이클이 존재하면 안되기 때문에 MST에는 N개의 정점이 존재한다면 (N - 1)개의 간선만을 포함해야 합니다.
이러한 MST를 구하는 알고리즘으로는 Kruskal 알고리즘과 Prim 알고리즘이이 있습니다.
본 코드에선 Kruskal 알고리즘을 사용하였습니다.
Kruskal 알고리즘
Kruskal 알고리즘은 간선 중심으로 MST를 구하는 알고리즘입니다. 간선을 오름차순으로 정렬한 후, 가중치가 최소인 간선부터 선택하여 MST를 만듭니다. 이 때, 이미 MST에 포함된 정점과 아닌 정점을 구분하기 위해서 Union-find를 사용합니다. 간선의 시작 정점과 끝 정점이 서로 다른 집합에 속할 때만 해당 간선을 선택합니다. 간선이 E개 존재한다고 할 때, Kruskal 알고리즘의 시간 복잡도는 O( E log E )입니다.
코드
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
//백준 6091 핑크 플로이드
/*
* 주어진 인접행렬을 통해 MST를 만들면 그것이 원본 인접리스트
* */
public class Main {
static class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
int from;
int to;
int cost;
public Node(int from, int to, int cost) {
super();
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
this.cost = cost;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) {
return this.cost - o.cost;
}
}
static int parent[];
private static boolean union(int a, int b) {
a = find(a);
b = find(b);
if(a != b) {
if(a < b) parent[b] = a;
else parent[a] = b;
return true;
}
return false;
}
private static int find(int a) {
if(parent[a] == a) return a;
else return parent[a] = find(parent[a]);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
parent = new int[N + 1];
for(int i = 0;i <= N;i++) parent[i] = i;
String str[];
PriorityQueue<Node> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
for(int i = 1; i < N;i++) {
str = br.readLine().split(" ");
for(int j = 0;j < str.length;j++) pq.add(new Node(i, j + i + 1, Integer.parseInt(str[j])));
}
ArrayList<Node> list = new ArrayList<>();
//크루스칼 알고리즘을 통한 MST 구하기
int cnt = 0;
while(!pq.isEmpty()) {
Node temp = pq.poll();
if(union(temp.from, temp.to)) {
cnt++;
list.add(temp);
if(cnt == N - 1) break;
}
}
//원본 인접 리스트 만들기
ArrayList<Integer> adjList[] = new ArrayList[N + 1];
for(int i = 0;i <= N;i++) adjList[i] = new ArrayList<>();
for(Node temp : list) {
adjList[temp.from].add(temp.to);
adjList[temp.to].add(temp.from);
}
for(int i = 1;i <= N;i++) {
sb.append(adjList[i].size()).append(" ");
Collections.sort(adjList[i]);
for(int a : adjList[i]) sb.append(a).append(" ");
sb.append("\n");
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
}
