백준 16928번 뱀과 사다리 게임
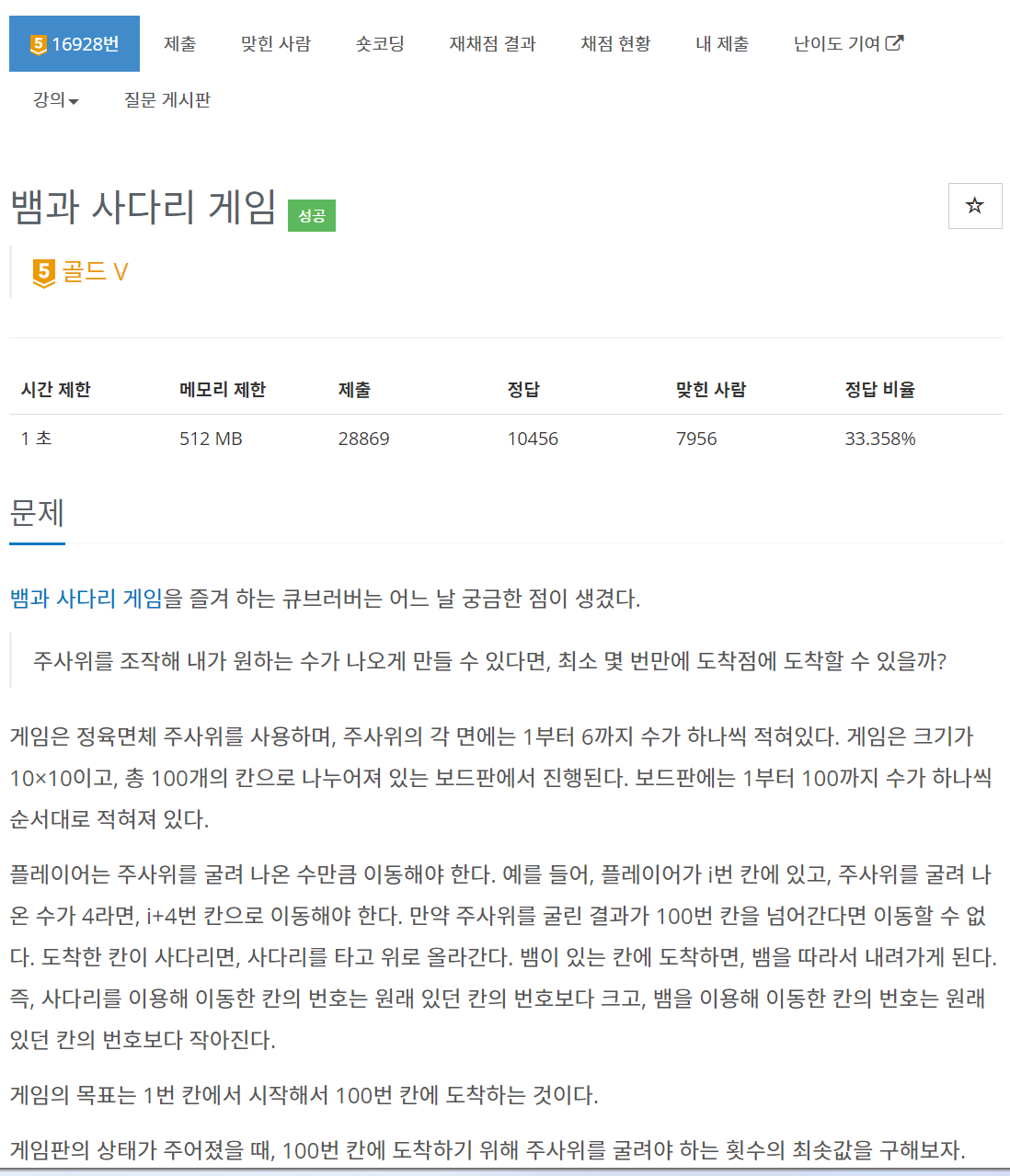
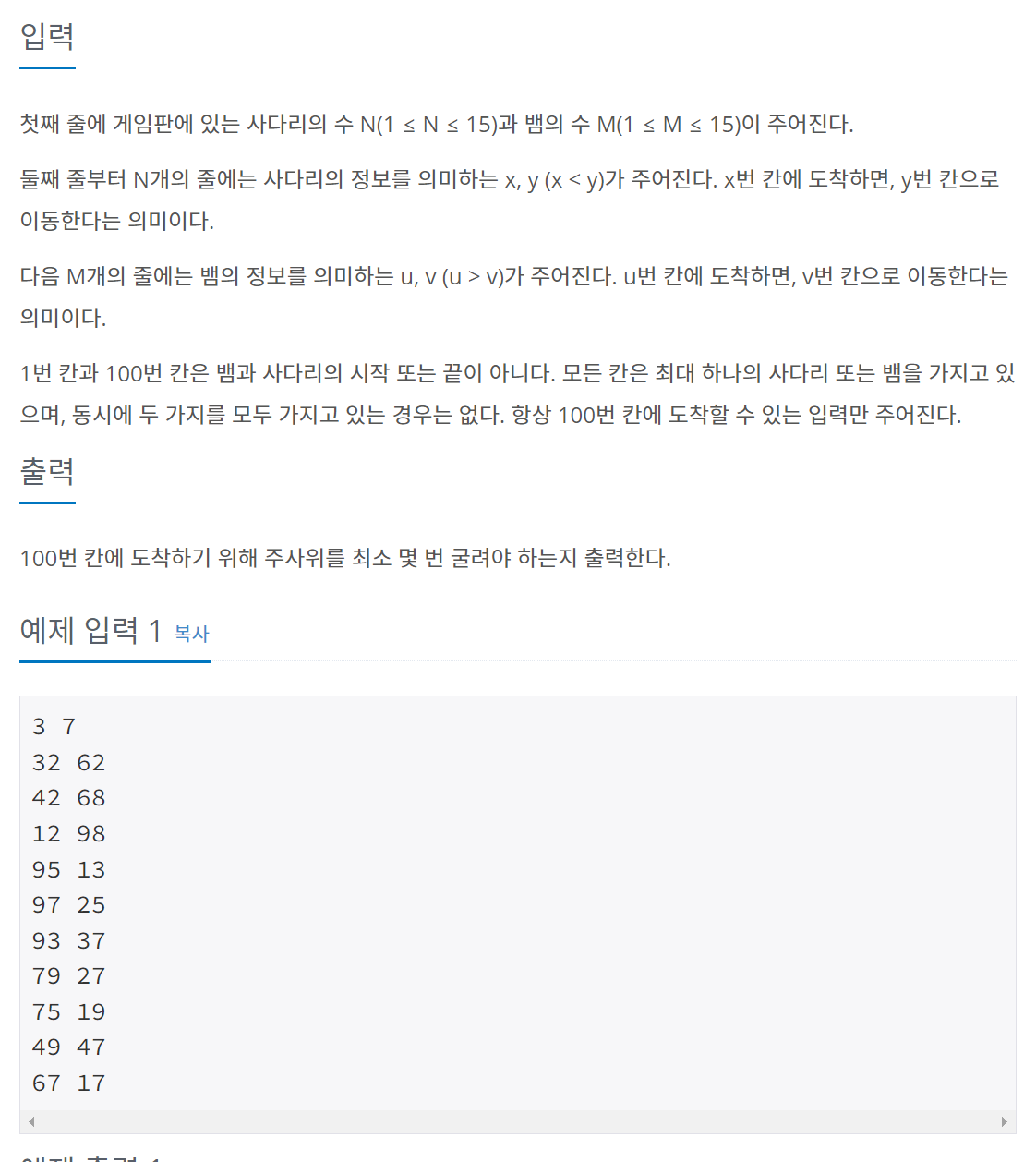
문제
나의 풀이
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int dist[] = new int[101];
int next[] = new int[101];
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
for(int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
next[i] = i;
dist[i] = -1;
}
for(int k = 0; k < n + m; k++) {
int x = sc.nextInt();
int y = sc.nextInt();
next[x] = y; // 사다리, 뱀인 경우 x 도착 이후 가야할 곳 저장
}
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(1);
dist[1] = 0; // 시작점 1
while(!q.isEmpty()) { // bfs
int x = q.poll();
for(int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) { // 주사위 1부터 6까지
int y = x + i;
if(y > 100) { // 범위 넘어가는 경우
continue;
}
y = next[y]; // 다음 칸으로
if(dist[y] == -1) { // 아직 방문하지 않은 경우
dist[y] = dist[x] + 1; // 거리 업데이트
q.add(y);
}
}
}
System.out.println(dist[100]);
}
}게임에서 뱀과 사다리의 구분은 중요하지만, 구현에서는 별로 중요하지 않다.
x->y로 간다는 점만 중요하다. 새로운 배열 next[x]를 만들어서, x에 도착한 이후에 가야할 곳을 모두 기록한다.
뱀이나 사다리인 경우는 next[x] = y, 일반 칸인 경우는 next[x] = x로 구분한다.
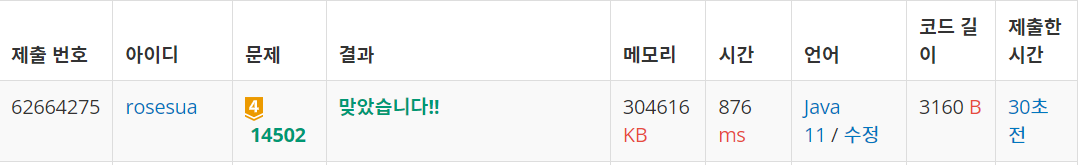
결과

백준 16948번 데스 나이트
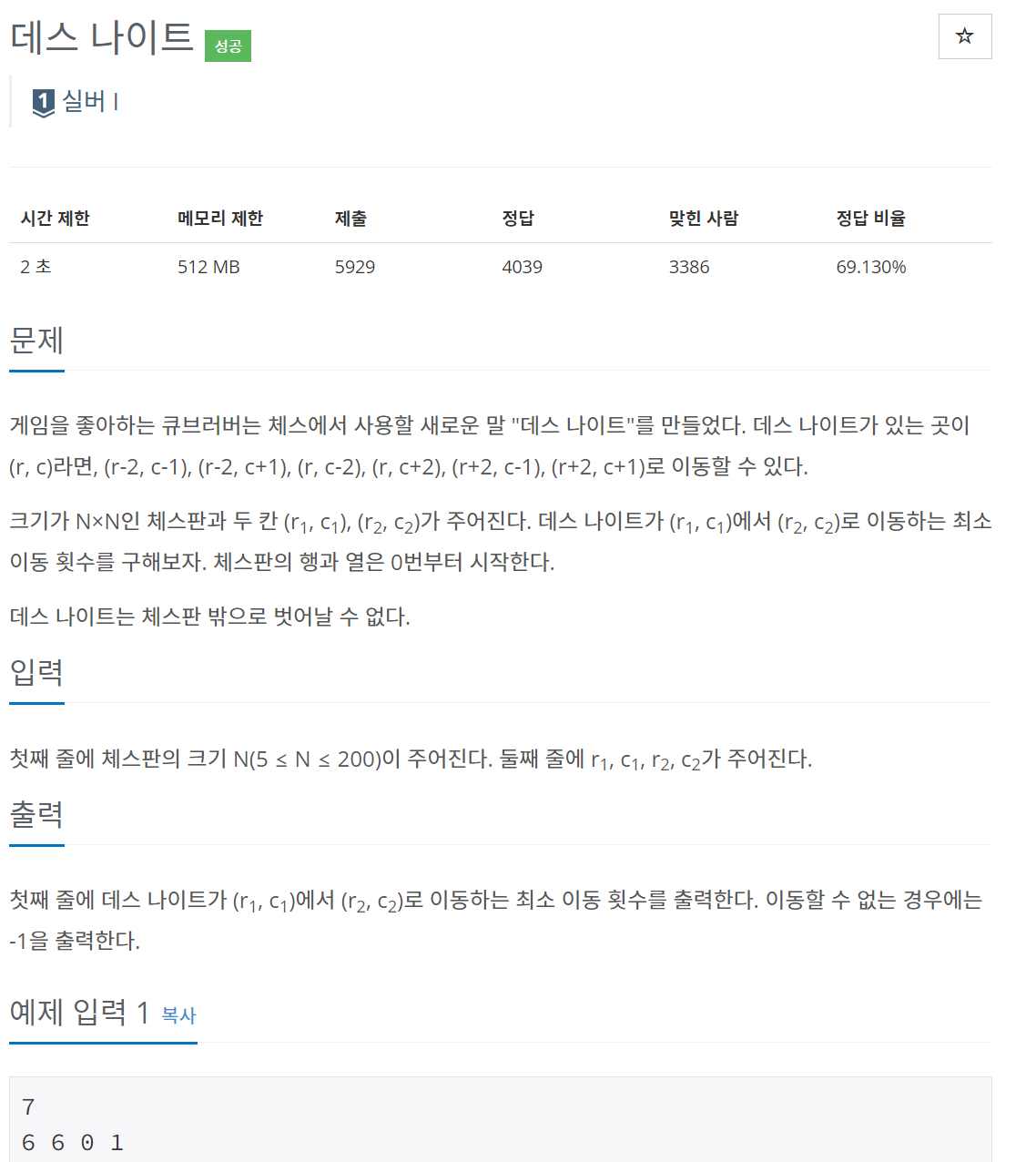
문제
나의 풀이
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
final static int dx[] = { -2, -2, 0, 0, 2, 2 };
final static int dy[] = { -1, 1, -2, 2, -1, 1 };
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int sx = sc.nextInt();
int sy = sc.nextInt();
int ex = sc.nextInt();
int ey = sc.nextInt();
int dist[][] = new int[n][n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Arrays.fill(dist[i], -1); // -1로 채우기
}
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(sx); q.add(sy); // 시작점
dist[sx][sy] = 0; // 시작점이므로 거리 0
while(!q.isEmpty()) { // bfs
int x = q.poll();
int y = q.poll();
for(int k = 0; k < 6; k++) { // 6방향에 대하여
int nx = x + dx[k];
int ny = y + dy[k];
if(0 <= nx && nx < n && 0 <= ny && ny < n) {
if(dist[nx][ny] == -1) { // 아직 방문하지 않은 경우
q.add(nx); q.add(ny);
dist[nx][ny] = dist[x][y] + 1; // 거리 업데이트
}
}
}
}
System.out.println(dist[ex][ey]);
}
}최소 이동횟수를 구하고 한칸에서 다른 칸으로 이동하기 때문에 BFS로 해결할 수 있다. 6가지의 상대적인 방향에 대해 dx, dy로 정의하고 bfs 탐색을 해주며 방문하지 않은 경우 거리를 업데이트 시켜서 방문 처리를 해주면 된다. 그런 다음 도착점의 dist 값을 구하면 된다.
결과

백준 9019번 DSLR
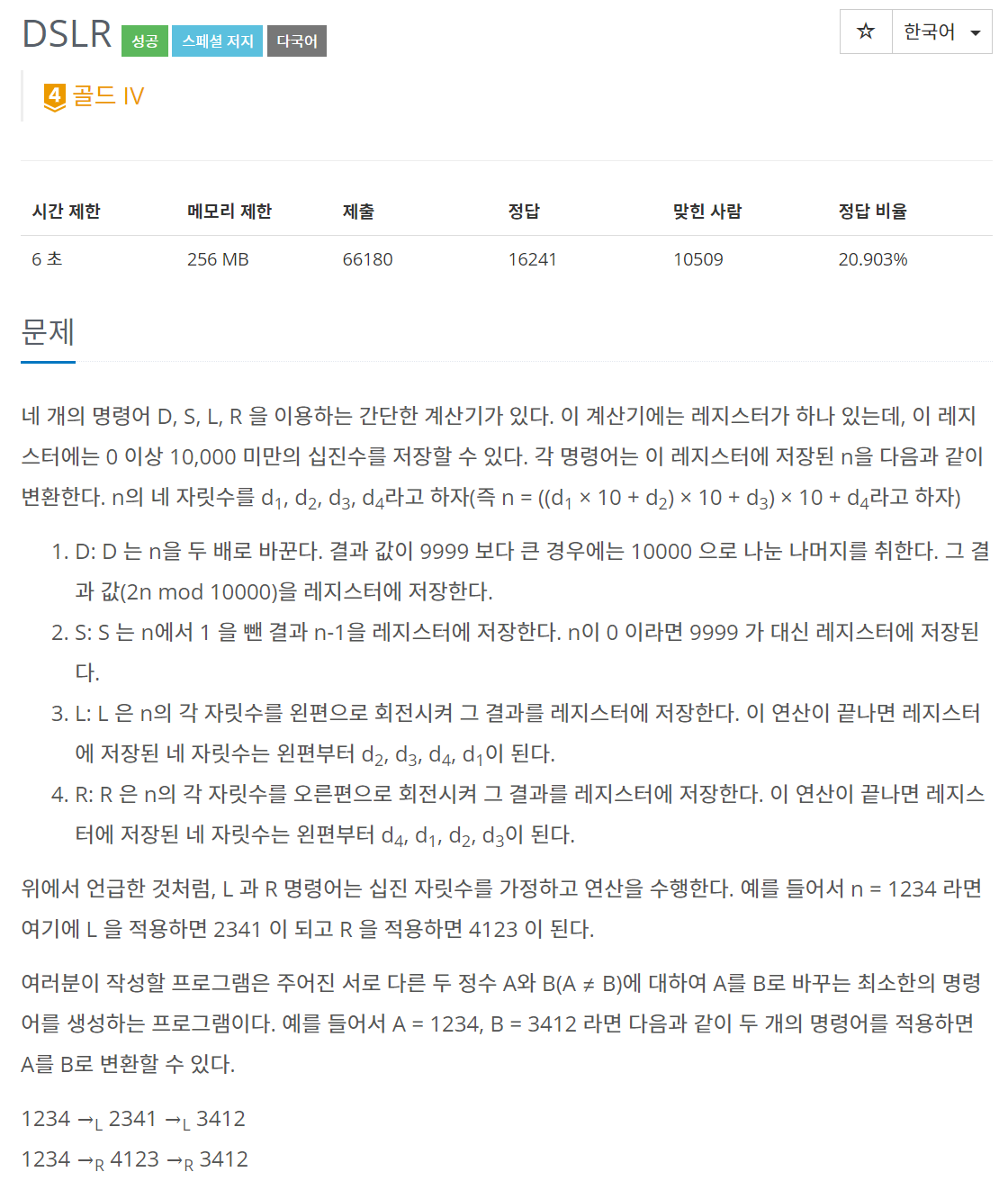
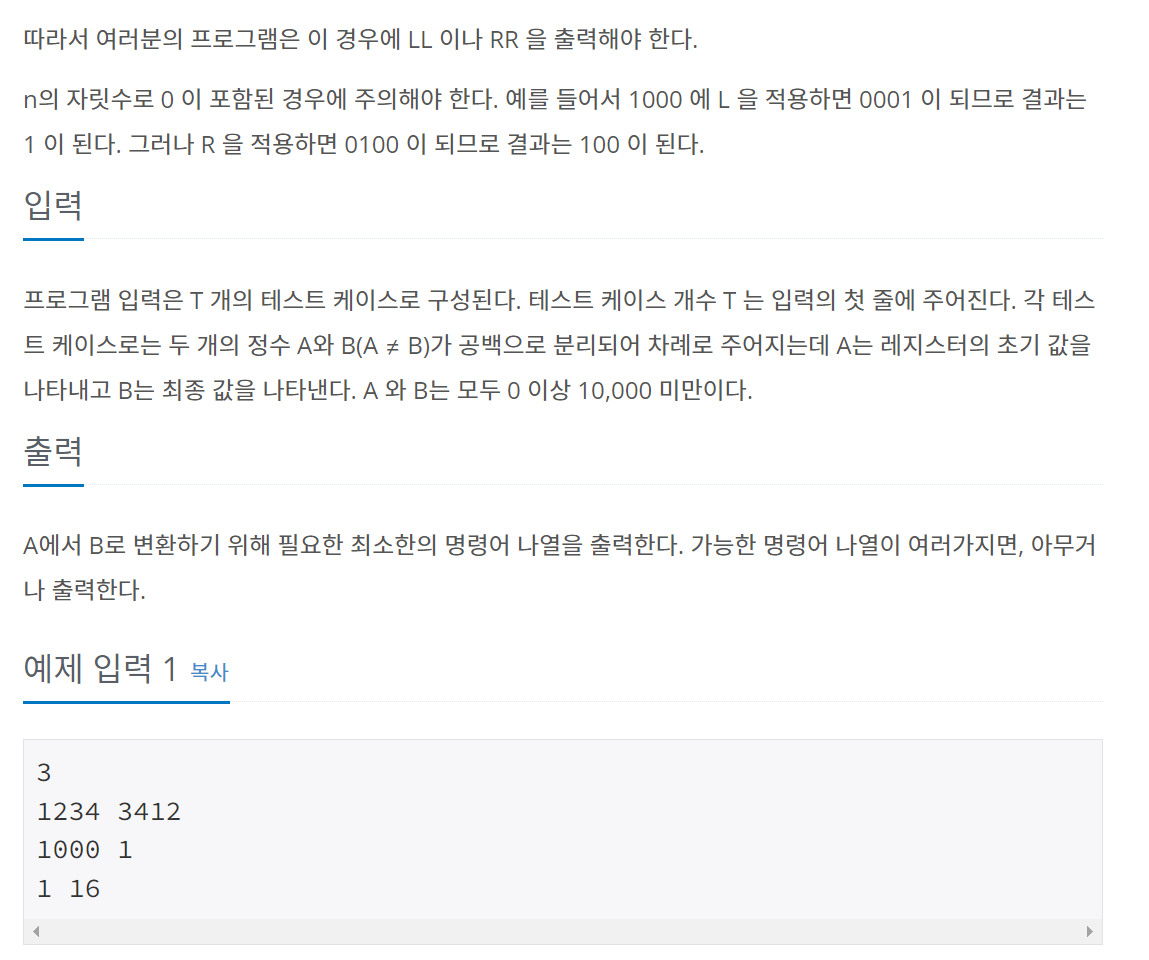
문제
나의 풀이
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int t = sc.nextInt();
while(t-- > 0) {
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
boolean check[] = new boolean[10001];
int dist[] = new int[10001];
char how[] = new char[10001];
int from[] = new int[10001];
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer>();
q.add(n); // 시작점은 초기 숫자
check[n] = true;
dist[n] = 0;
from[n] = -1;
while(!q.isEmpty()) { // bfs
int now = q.poll();
// D 연산
int next = (now * 2) % 10000;
if(check[next] == false) { // 방문하지 않은 경우
q.add(next);
check[next] = true;
dist[next] = dist[now] + 1; // 연산 횟수 업데이트
from[next] = now; // now에서 D연산을 통해 next가 만들어짐
how[next] = 'D'; // 전 단계에서 D연산을 통해 만들어짐
}
// S 연산
next = now - 1;
if(next == -1) {
next = 9999;
}
if(check[next] == false) { // 방문하지 않은 경우
q.add(next);
check[next] = true;
dist[next] = dist[now] + 1; // 연산 횟수 업데이트
from[next] = now; // now에서 S연산을 통해 next가 만들어짐
how[next] = 'S'; // 전 단계에서 S연산을 통해 만들어짐
}
// L 연산
next = (now % 1000) * 10 + now / 1000;
if(check[next] == false) { // 방문하지 않은 경우
q.add(next);
check[next] = true;
dist[next] = dist[now] + 1; // 연산 횟수 업데이트
from[next] = now; // now에서 L연산을 통해 next가 만들어짐
how[next] = 'L'; // 전 단계에서 L연산을 통해 만들어짐
}
// R 연산
next = (now % 10) * 1000 + (now / 10);
if(check[next] == false) { // 방문하지 않은 경우
q.add(next);
check[next] = true;
dist[next] = dist[now] + 1; // 연산 횟수 업데이트
from[next] = now; // now에서 R연산을 통해 next가 만들어짐
how[next] = 'R'; // 전 단계에서 R연산을 통해 만들어짐
}
}
StringBuilder answer = new StringBuilder();
while(m != n) { // 역추적
answer.append(how[m]);
m = from[m];
}
System.out.println(answer.reverse());
}
}
}A->B로 바꾸는 최소 연산 횟수를 구하는 것이므로 bfs로 풀이할 수 있다.
이 문제는 최소값을 구해야 하는건 맞지만 어떠한 과정을 거쳐야 하는지를 구해야 한다. 따라서, 배열을 하나 더 이용해서 어떤 과정을 거쳤는지를 저장해야 한다.
how[i] = i를 어떻게 만들었는지 저장하는 배열로 둔다. (마지막 한단계만 기록해서 from배열을 통해 역추적할 수 있도록 한다.)
역추적 방법은 B가 A가 될때까지 반복하면서 B를 어떻게 만들었느지 기록하고 B를 from[B]의 값으로 업데이트해주어 반복한다.
결과
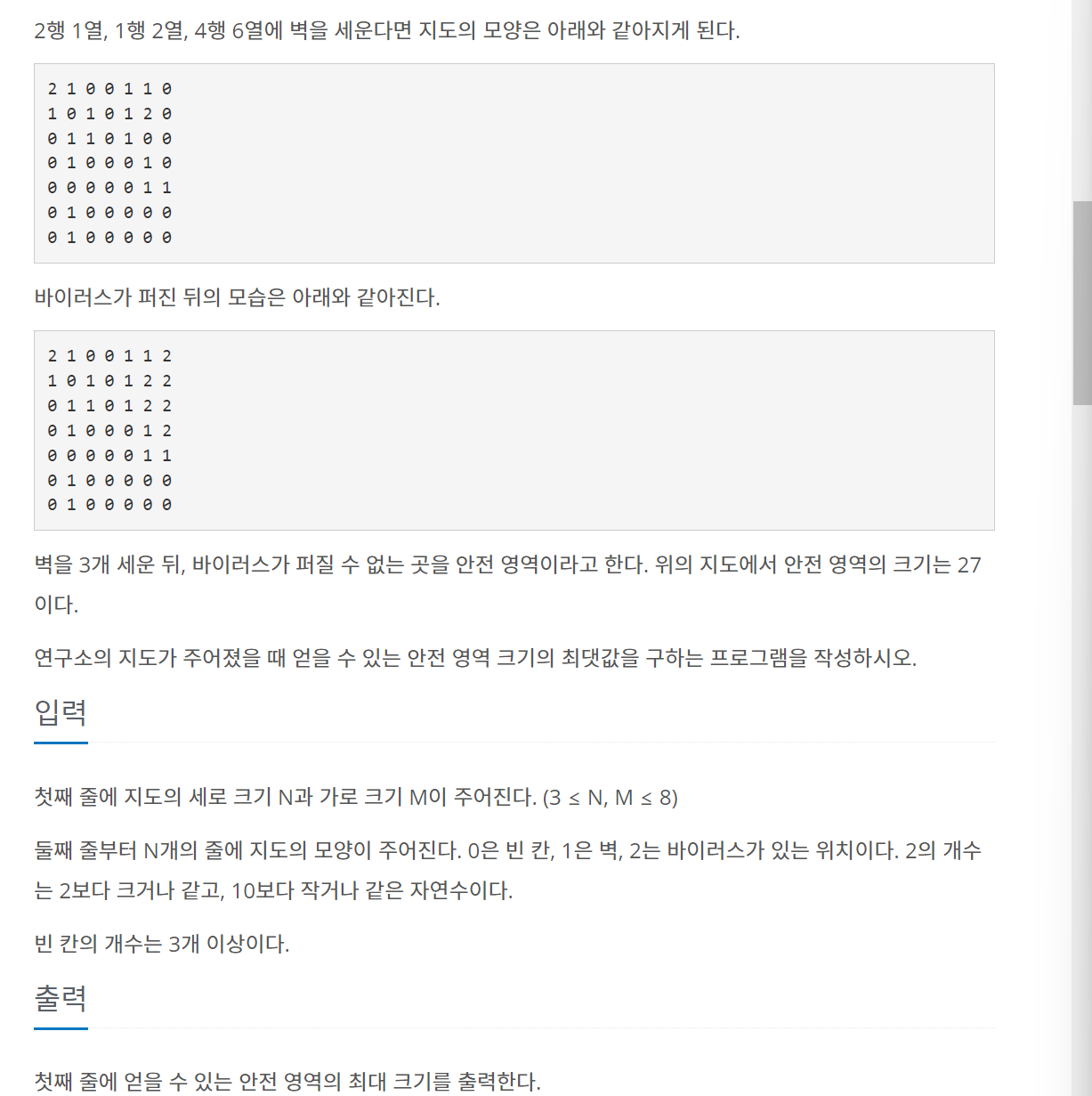
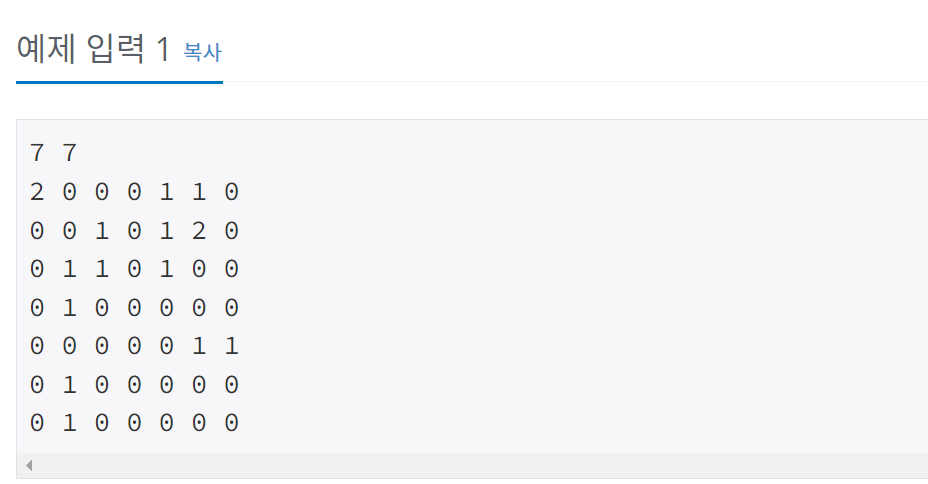
백준 14502번 연구소
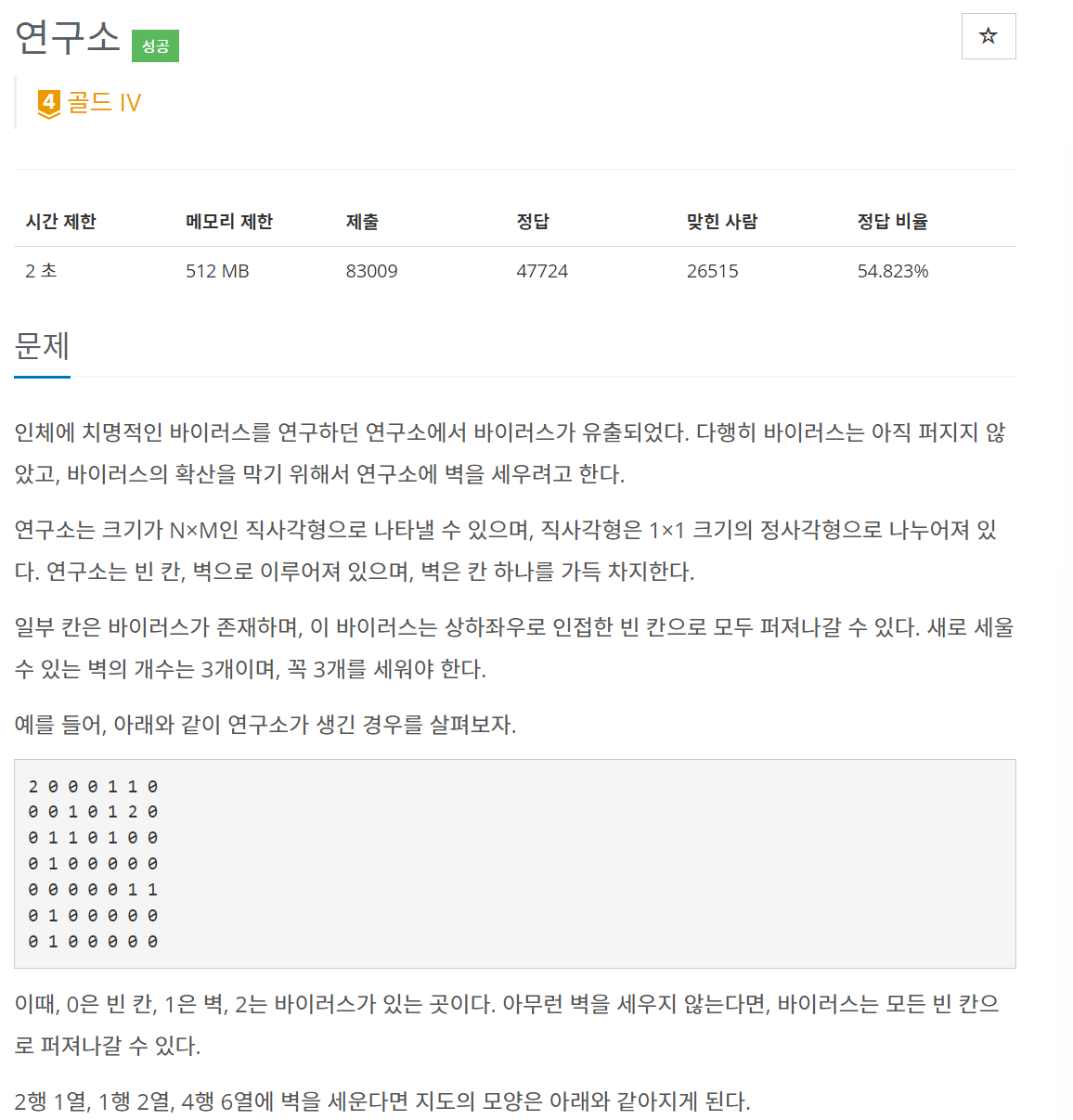
문제
나의 풀이
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static class Pair {
int x; int y;
Pair(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
static int n, m;
static int a[][] = new int[10][10];
static int b[][] = new int[10][10];
static int dx[] = { 0, 0, 1, -1 };
static int dy[] = { 1, -1, 0, 0 };
static int bfs() {
Queue<Pair> q = new LinkedList<Pair>();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
b[i][j] = a[i][j];
if(b[i][j] == 2) { // 바이러스인 경우
q.add(new Pair(i, j)); // 퍼지도록 하기 위해 큐에 넣기
}
}
}
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
Pair p = q.poll();
int x = p.x;
int y = p.y;
for(int k = 0; k < 4; k++) { // 상하좌우로 퍼짐
int nx = x + dx[k];
int ny = y + dy[k];
if(0 <= nx && nx < n && 0 <= ny && ny < m) {
if(b[nx][ny] == 0) { // 빈칸인 경우(벽 아니므로 퍼짐)
b[nx][ny] = 2; // 바이러스 퍼짐
q.add(new Pair(nx, ny));
}
}
}
}
// 안전 영역의 크기 구하기
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if(b[i][j] == 0) { // 빈칸인 경우
count += 1;
}
}
}
return count;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
a = new int[n][m];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
a[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
int answer = 0;
for(int x1 = 0; x1 < n; x1++) {
for(int y1 = 0; y1 < m; y1++) {
if(a[x1][y1] != 0) continue;
for(int x2 = 0; x2 < n; x2++) {
for(int y2 = 0; y2 < m; y2++) {
if(a[x2][y2] != 0) continue;
for(int x3 = 0; x3 < n; x3++) {
for(int y3 = 0; y3 < m; y3++) {
if(a[x3][y3] != 0) continue;
if(x1 == x2 && y1 == y2) continue;
if(x1 == x3 && y1 == y3) continue;
if(x2 == x3 && y2 == y3) continue;
a[x1][y1] = 1;
a[x2][y2] = 1;
a[x3][y3] = 1;
answer = Math.max(answer, bfs());
a[x1][y1] = 0;
a[x2][y2] = 0;
a[x3][y3] = 0;
}
}
}
}
}
}
System.out.println(answer);
}
}벽을 3개 세우는 부분과 바이러스가 퍼질 수 없는 곳의 크기를 구하는 부분 크게 두 가지다. 벽을 세운다는 내용을 잠시 제외하면 바이러스가 퍼질 수 없는 영역의 크기를 BFS로 구할 수 있다. BFS의 목적은 한 정점에서 시작해 연결된 모든 정점을 방문하는 것이다. 이제 벽을 고려해보면 for문을 통해서 벽을 세운 다음 안전 영역의 크기를 구하는 것을 BFS를 이용하면 된다. 바이러스가 퍼질 위치 3개를 고른 뒤 해당 위치에 벽을 세운다. 맵 정보에 1로 값을 변경한다. 그런 다음 bfs 탐색을 해서 안전영역의 크기를 구하고 다시 맵 정보에 0로 값을 변경한다. 이 과정을 6중 for문을 통해 반복해주면 된다.
결과