백준 1991번 트리 순회
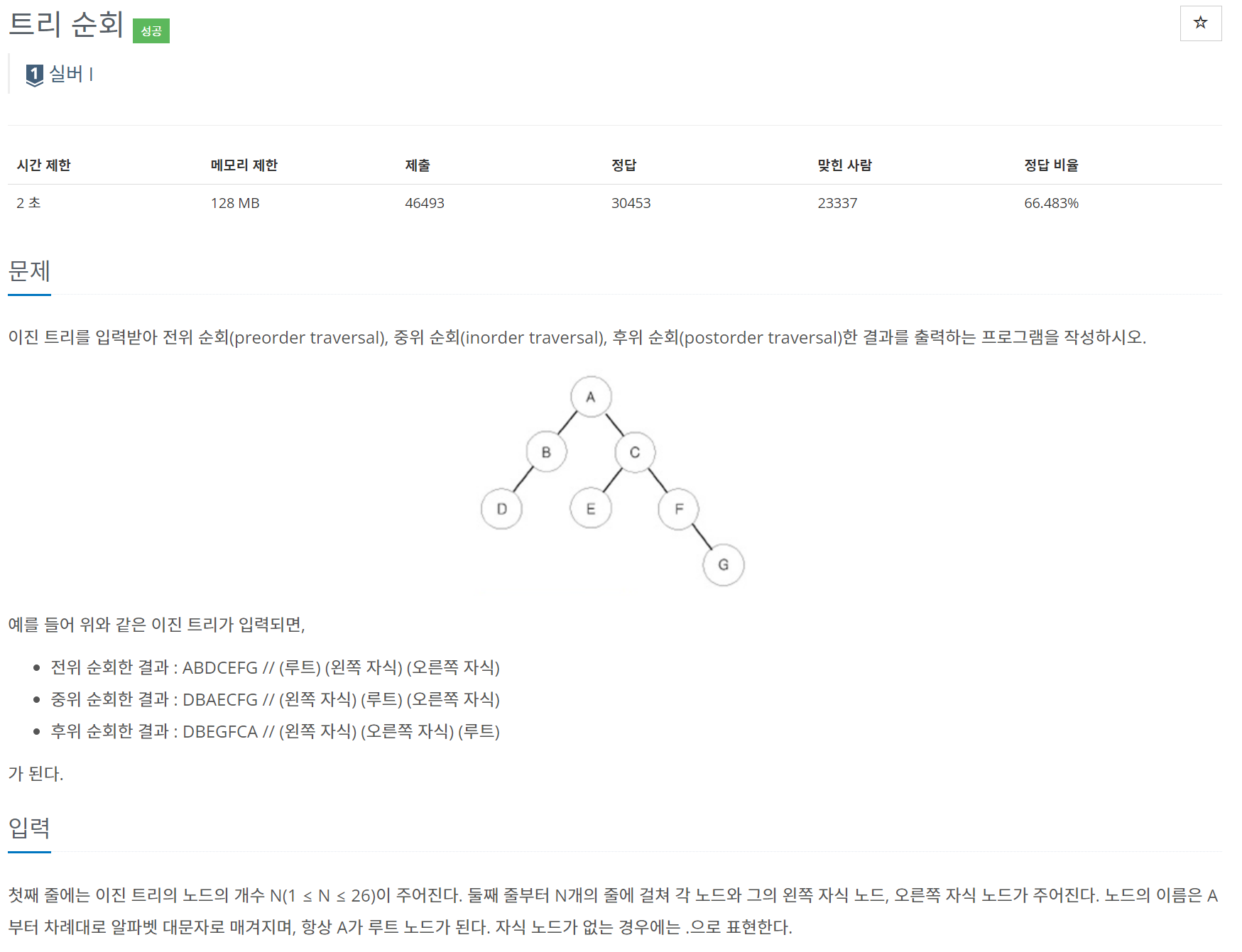
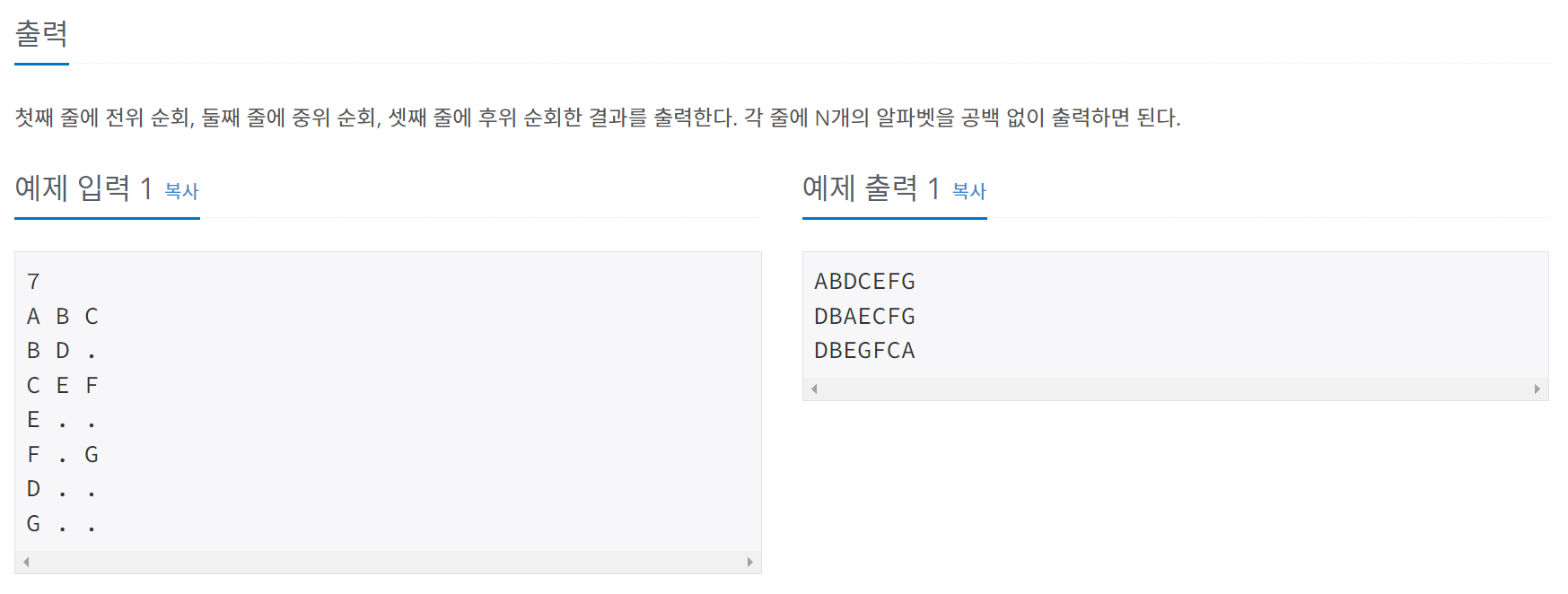
문제
나의 풀이
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static class Node {
int left, right;
Node(int left, int right) {
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
static void preorder(Node[] a, int x) {
if(x == -1) {
return;
}
System.out.print((char)(x + 'A'));
preorder(a, a[x].left);
preorder(a, a[x].right);
}
static void inorder(Node[] a, int x) {
if(x == -1) {
return;
}
inorder(a, a[x].left);
System.out.print((char)(x + 'A'));
inorder(a, a[x].right);
}
static void postorder(Node[] a, int x) {
if(x == -1) {
return;
}
postorder(a, a[x].left);
postorder(a, a[x].right);
System.out.print((char)(x + 'A'));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
Node a[] = new Node[26];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int x = sc.next().charAt(0) - 'A';
char y = sc.next().charAt(0);
char z = sc.next().charAt(0);
int left = -1;
int right = -1;
if(y != '.') {
left = y - 'A';
}
if(z != '.') {
right = z - 'A';
}
a[x] = new Node(left, right);
}
preorder(a, 0);
System.out.println();
inorder(a, 0);
System.out.println();
postorder(a, 0);
System.out.println();
}
}dfs를 이용하여 전위 순회, 중위 순회, 후위 순회한 결과를 출력시킨다.
순회 방법은 출력문의 위치가 어디냐에 따라 전위 순회, 중위 순회, 후위 순회로 나누어진다.
결과

백준 2250번 트리의 높이와 너비
문제


나의 풀이
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static class Node {
int left, right;
public int order, depth;
Node(int left, int right) {
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
static Node a[] = new Node[10001];
static int left[] = new int[10001];
static int right[] = new int[10001];
static int count[] = new int[10001];
static int order = 0;
static void inorder(int node, int depth) {
if(node == -1) {
return;
}
inorder(a[node].left, depth + 1);
a[node].order = ++order;
a[node].depth = depth;
inorder(a[node].right, depth + 1);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int x = sc.nextInt();
int y = sc.nextInt();
int z = sc.nextInt();
a[x] = new Node(y, z);
if(y != -1) {
count[y] += 1;
}
if(z != -1) {
count[z] += 1;
}
}
int root = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if(count[i] == 0) {
root = i;
}
}
inorder(root , 1);
int maxdepth = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int depth = a[i].depth;
int order = a[i].order;
if(left[depth] == 0) {
left[depth] = order;
} else {
left[depth] = Math.min(left[depth], order);
}
right[depth] = Math.max(right[depth], order);
maxdepth = Math.max(maxdepth, depth);
}
int answer = 0;
int ans_level = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= maxdepth; i++) {
if(answer < right[i] - left[i] + 1) {
answer = right[i] - left[i] + 1;
ans_level = i;
}
}
System.out.println(ans_level + " " + answer);
}
}행을 레벨, 깊이를 나타내고 열은 인오더 방문 순서를 나타낸다.
각 노드가 배치되는 순서가 인오더와 같으므로 인오더를 수행하면서 몇번인지 몇번째 레벨인지 기록하게 하여 각 레벨 마다 너비를 구해서 너비가 가장 넓은 레벨과 그 레벨의 너비를 출력시키면 된다.
결과

백준 11725번 트리의 부모 찾기
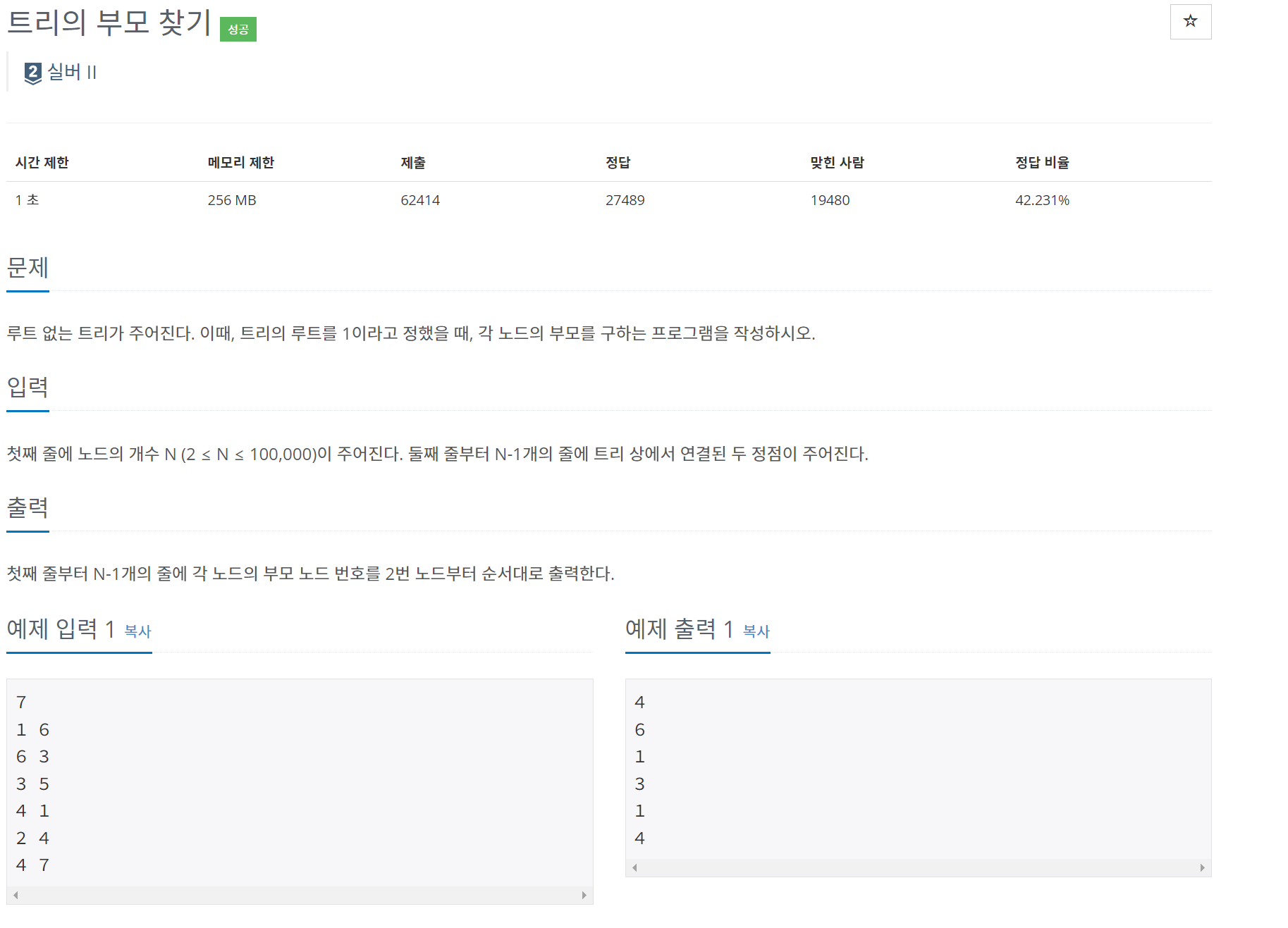
문제
나의 풀이
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
ArrayList<Integer>[] a = (ArrayList<Integer>[]) new ArrayList[n + 1];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
a[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>();
}
for(int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
int u = sc.nextInt();
int v = sc.nextInt();
a[u].add(v);
a[v].add(u);
}
boolean check[] = new boolean[n + 1];
int parent[] = new int[n + 1];
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(1);
check[1] = true;
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
int x = q.poll();
for(int y : a[x]) {
if(check[y] == false) {
check[y] = true;
parent[y] = x; // 부모 기록
q.add(y);
}
}
}
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
System.out.println(parent[i]);
}
}
}bfs 탐색을 하면서 방문할 때 해당 노드의 부모를 parent 배열에 저장시켜주면 해결할 수 있는 문제다.
결과

