백준 7576번 토마토
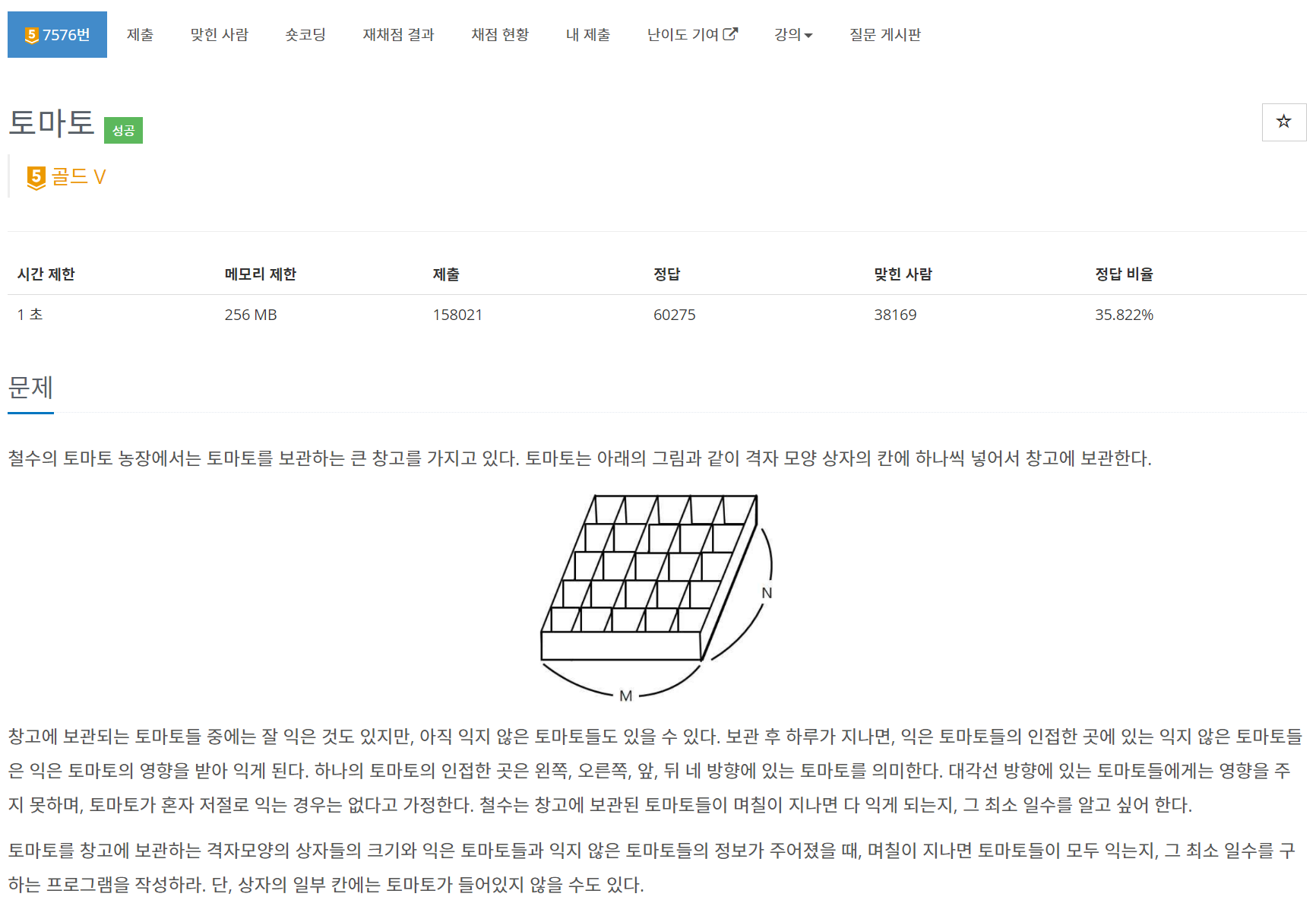
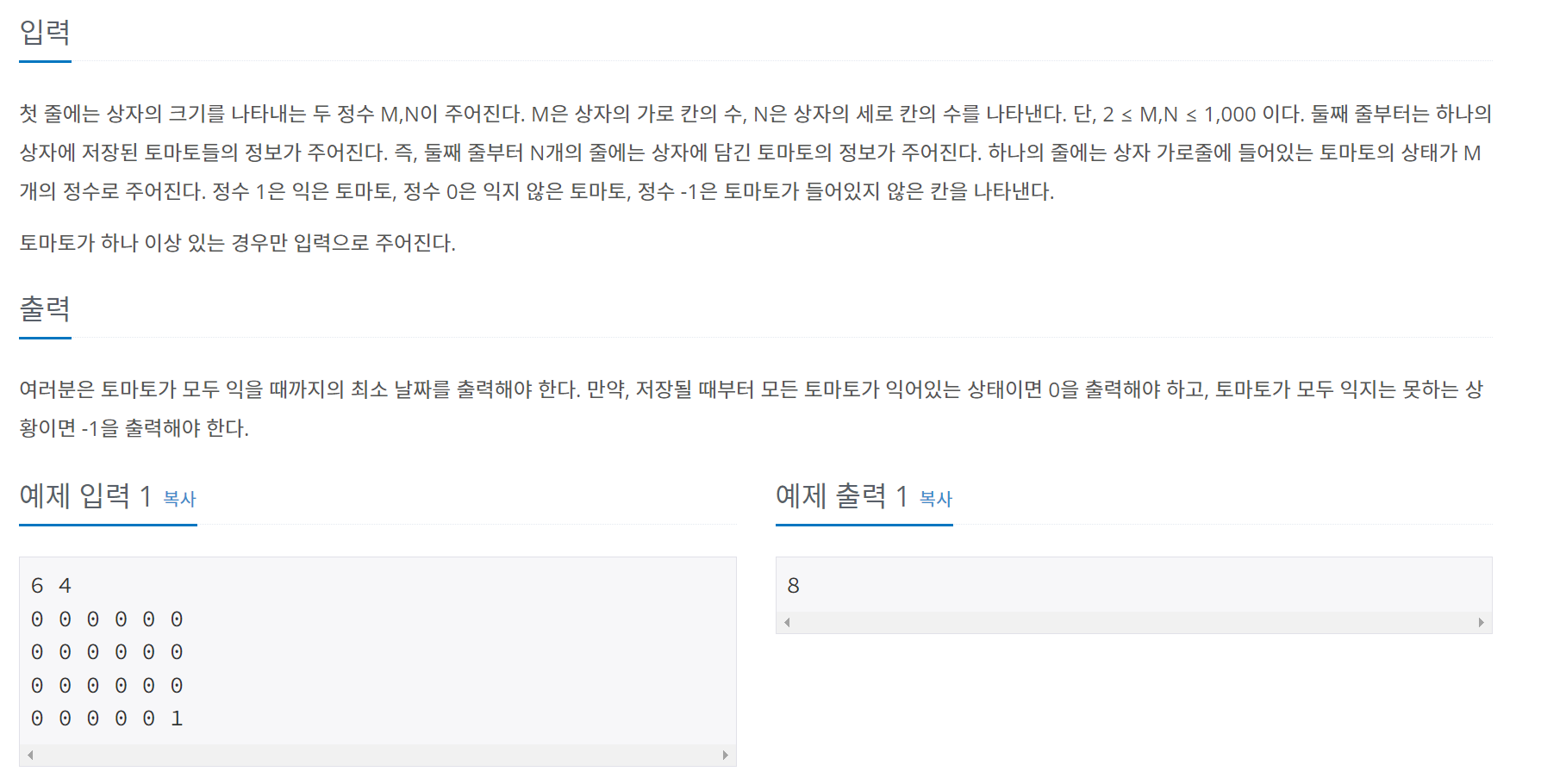
문제
나의 풀이
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static class Pair {
int x;
int y;
Pair(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
public static final int dx[] = { 0, 0, 1, -1 };
public static final int dy[] = { 1, -1, 0, 0 };
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int m = sc.nextInt();
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[][] a = new int[n][m];
int[][] dist = new int[n][m];
Queue<Pair> q = new LinkedList<Pair>();
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<m; j++) {
a[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
dist[i][j] = -1;
if(a[i][j] == 1) {
q.add(new Pair(i, j));
dist[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
Pair p = q.remove();
int x = p.x;
int y = p.y;
for(int k=0; k<4; k++) {
int nx = x+dx[k];
int ny = y+dy[k];
if(0 <= nx && nx < n && 0 <= ny && ny < m) {
if(a[nx][ny] == 0 && dist[nx][ny] == -1) {
q.add(new Pair(nx, ny));
dist[nx][ny] = dist[x][y] + 1;
}
}
}
}
int answer = 0;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<m; j++) {
answer = Math.max(answer, dist[i][j]);
}
}
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<m; j++) {
if(a[i][j] == 0 && dist[i][j] == -1) {
answer = -1;
}
}
}
System.out.println(answer);
}
}bfs 탐색 최단거리 문제로, 미로탐색에서 풀이했던것과 유사하게 하면 된다.
즉, bfs 탐색을 하면서 거리를 재는 방식으로 진행하면 된다.
결과

백준 7562번 나이트의 이동
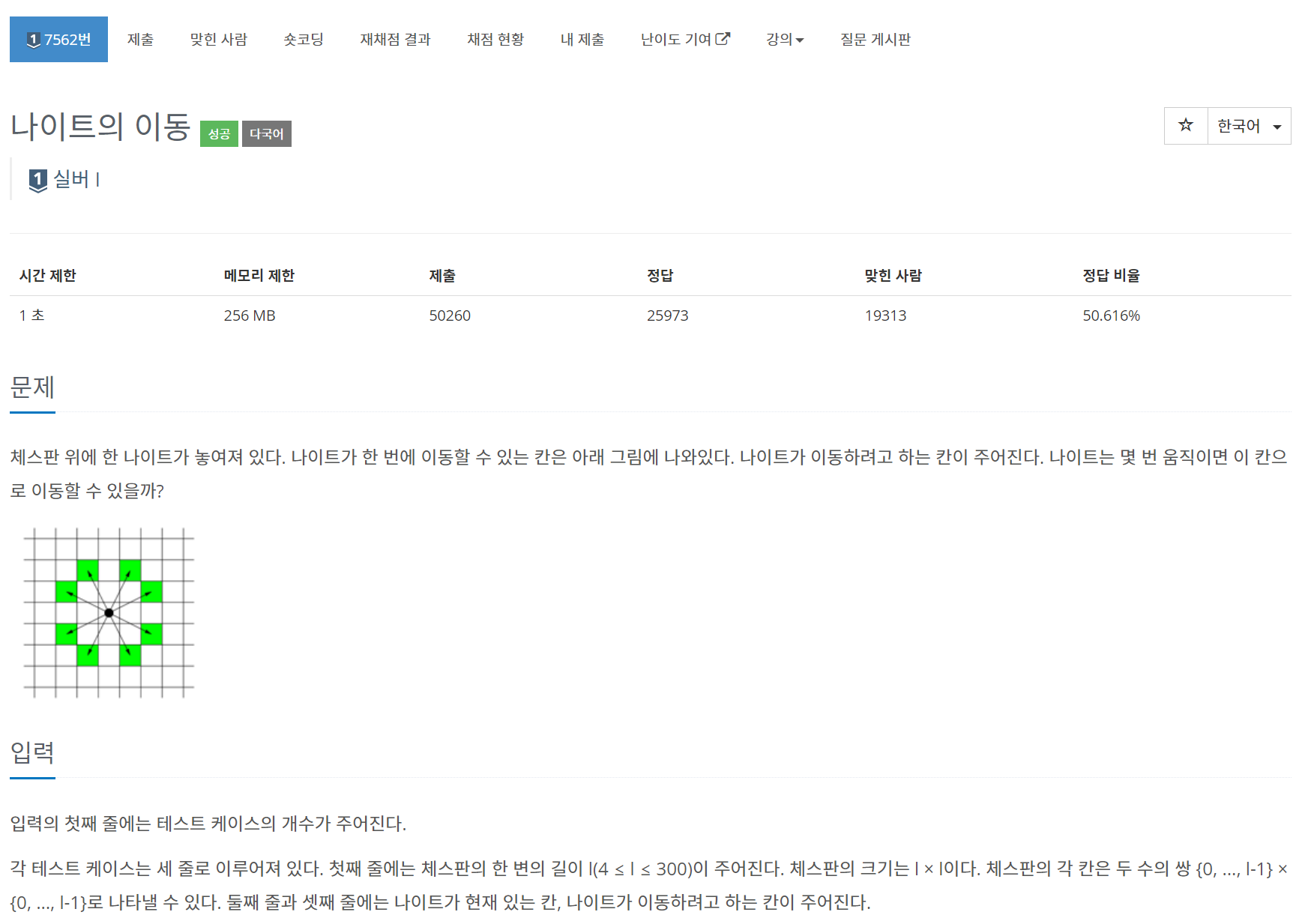
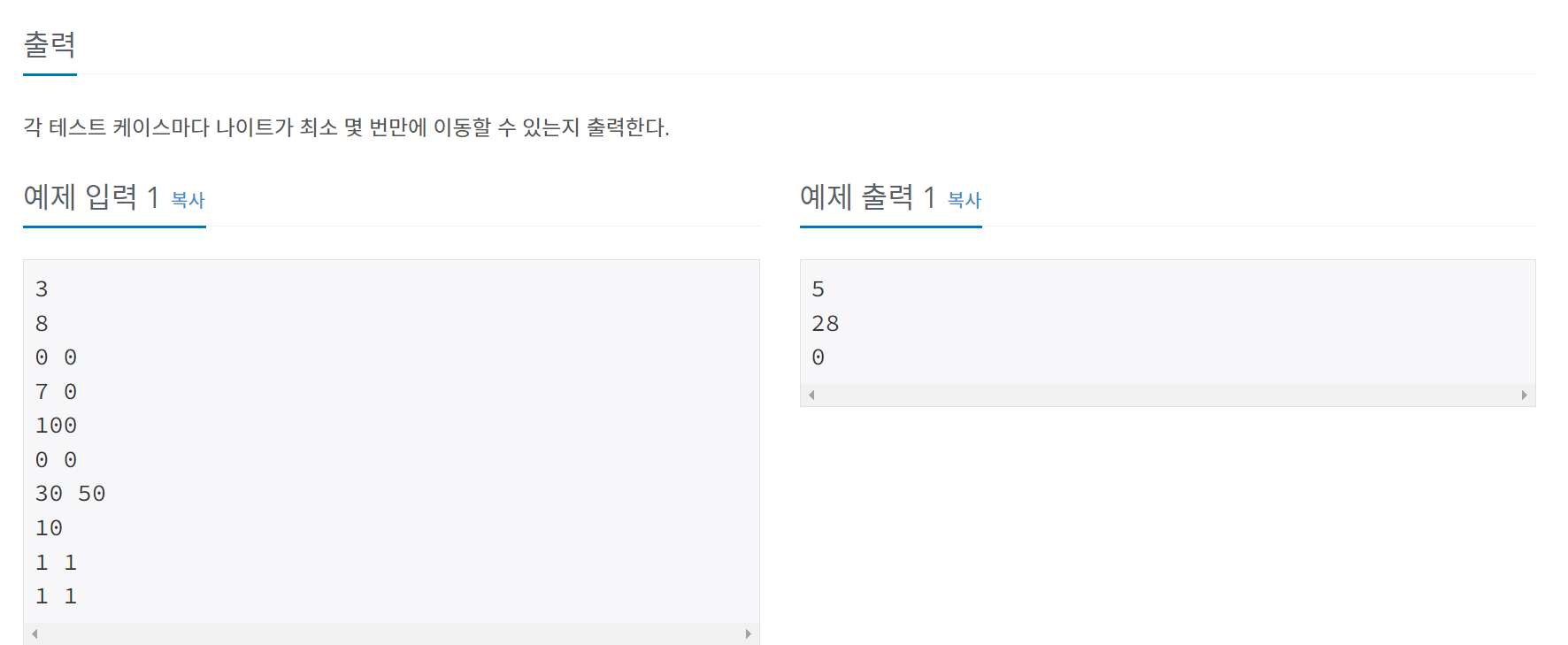
문제
나의 풀이
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static final int dx[] = { -2, -1, 1, 2, 2, 1, -1, -2 };
static final int dy[] = { 1, 2, 2, 1, -1, -2, -2, -1 };
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int t = sc.nextInt();
while(t-- > 0) {
int n = sc.nextInt();
int sx = sc.nextInt();
int sy = sc.nextInt();
int ex = sc.nextInt();
int ey = sc.nextInt();
int d[][] = new int[n][n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Arrays.fill(d[i], -1);
}
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(sx); q.add(sy);
d[sx][sy] = 0;
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
int x = q.poll();
int y = q.poll();
for(int k = 0; k < 8; k++) {
int nx = x + dx[k];
int ny = y + dy[k];
if(0 <= nx && nx < n && 0 <= ny && ny < n) {
if(d[nx][ny] == -1) {
d[nx][ny] = d[x][y] + 1;
q.add(nx); q.add(ny);
}
}
}
}
System.out.println(d[ex][ey]);
}
}
}토마토 문제와 유사하지만, 하나의 칸에서 이동할 수 있는 방향이 8방향이라는 점이 다르다.
dx, dy만 8방향으로 바꿔주면 된다.
결과

백준 16929번 Two Dots
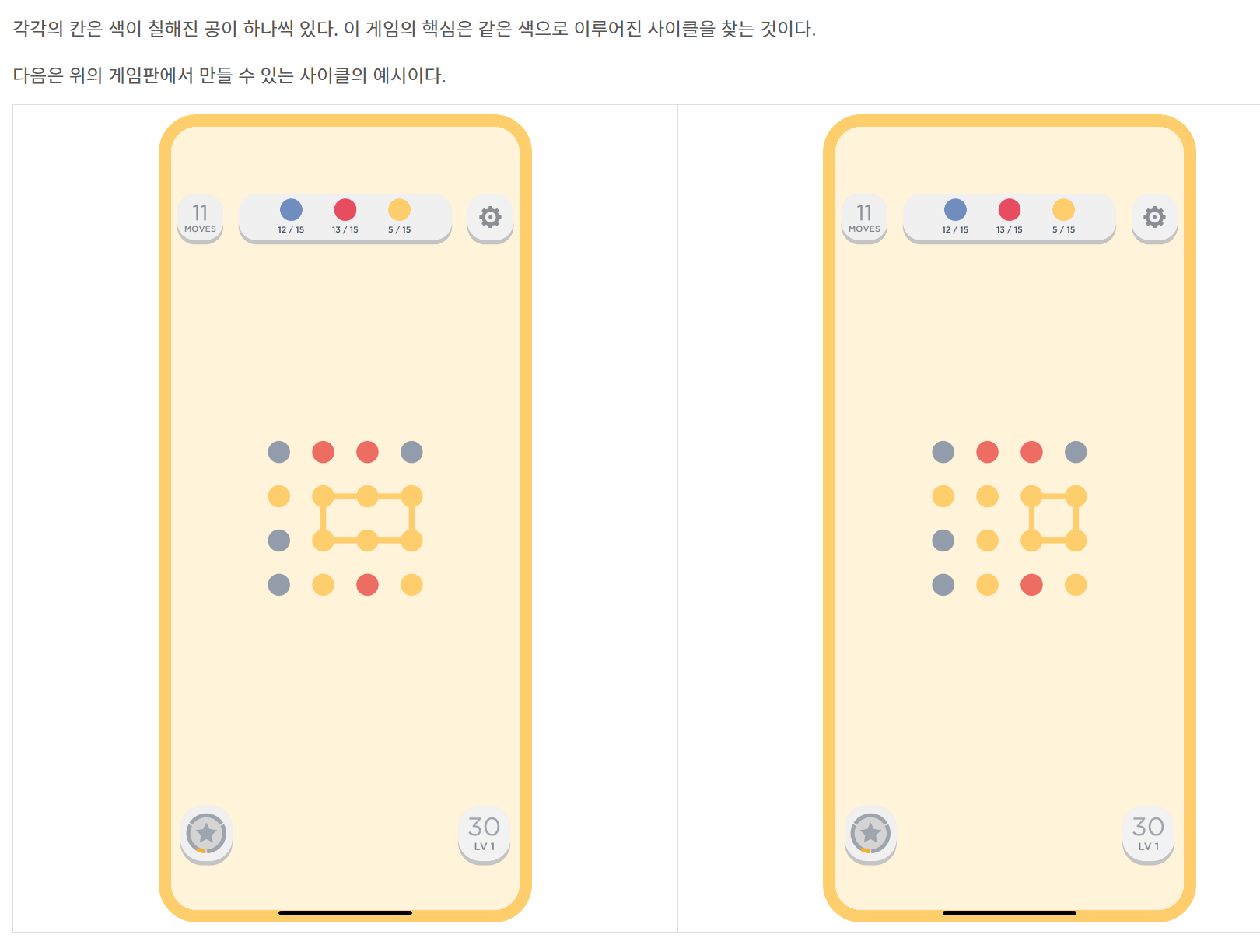
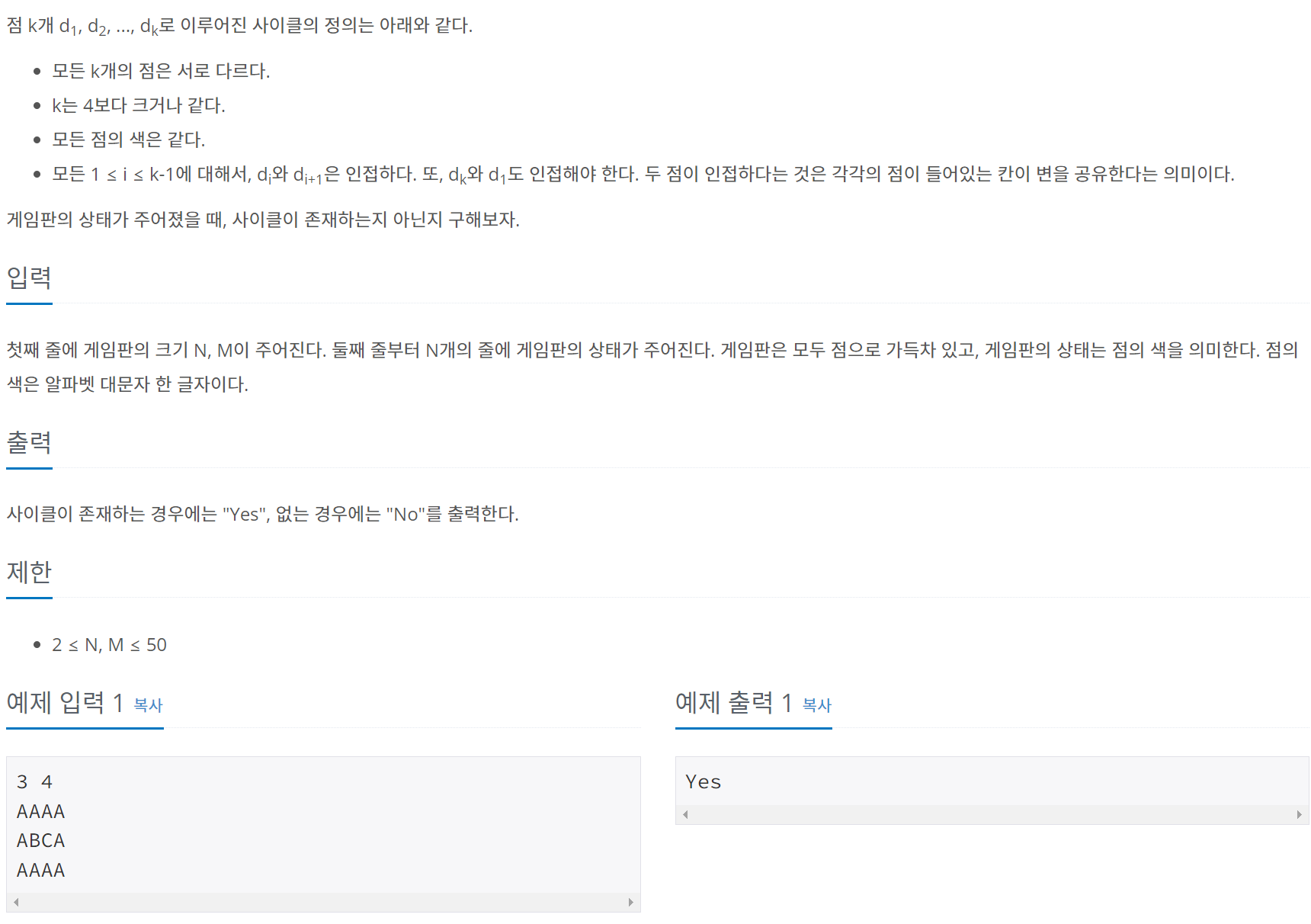
문제
나의 풀이
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static char a[][];
static boolean check[][];
static int n, m;
final static int dx[] = { 0, 0, 1, -1 };
final static int dy[] = { 1, -1, 0, 0 };
static boolean go(int x, int y, int px, int py, char color) {
if (check[x][y]) { // 이미 방문했던 칸을 또 방문한 경우 (길이가 4 이상인 사이클)
return true;
}
check[x][y] = true;
for (int k=0; k<4; k++) {
int nx = x+dx[k];
int ny = y+dy[k];
if (0 <= nx && nx < n && 0 <= ny && ny < m) {
if (!(nx == px && ny == py)) { // 이전 칸과 다른 칸인 경우
if (a[nx][ny] == color) { // 이전 칸과 똑같은 색인 경우
if (go(nx, ny, x, y, color)) { // 다음 칸이 true를 리턴한 경우
return true;
}
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
a = new char[n][m];
check = new boolean[n][m];
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
a[i] = sc.next().toCharArray();
}
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<m; j++) {
if (check[i][j]) continue; // 이미 방문했던 경우
boolean ok = go(i, j, -1, -1, a[i][j]);
if (ok) { // 존재하는 경우
System.out.println("Yes");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
System.out.println("No");
}
}이전 칸과 다른 칸으로 연속해서 이동했을 때, 이미 방문한 칸을 방문했으면 사이클이 존재한다고 볼 수 있다. (길이가 4 이상)
이를 이용하여 방문한 칸을 방문한 경우 true를 리턴시키면 된다.
결과

