문법
-
컴퓨터가 처리 할 수 있는 데이터의 형태
(B) 숫자 -
15 를 2진수로
(1111) -
4bit 이므로
1111 << 1 = 1110 = 14
1111 << 2 = 1100 = 12
1111 << 3 = 1000 = 8 -
요구사항분석 -> 알고리즘의 개발 -> 코딩 -> 컴파일과 링크 -> 실행과 디버깅 -> 유지보수
-
컴파일 오류 / 런타임 오류 / 논리 오류
컴파일 오류 : 문법 오류 가장 찾기 쉽다. (ex. 세미콜론 빼먹기)
런타임 오류 : 실행 시간에 오류가 발생. (ex. 10 / 0 )
논리 오류 : 문제 해결 절차를 잘 못 기술함. - 다음의 코드에서 에러가 발생하는 이유는 무엇인가.
aP의 초기값이 없다. => aP는 아무것도 간접참조하고 있지 않다.
*aP = 10;
초기화 되어 있지 않은 포인터를 통해 값을 바꾸려고 하고 있다.
- 다음의 코드에서 에러가 발생하는 부분과 그 이유는 무엇인가
a의 타입이 const로 수식되어 있는데, a = 20 으로 값을 바꾸려고 시도하고 있다. 따라서 컴파일 오류가 발생한다.
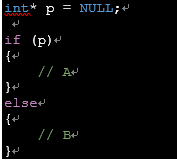
- A, B 중 어느부분이 실행될까?
p가 널 포인터이므로 진리값이 거짓으로 평가되어 B가 실행된다.
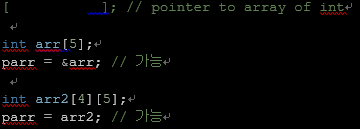
- 배열포인터를 선언 해 보자
int (*parr)[5];
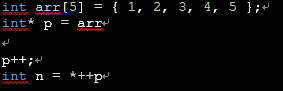
- 다음의 코드에서 n의 값은?
(3)
- 구조체의 BestFriend 멤버에 접근하는 코드를 두가지 방식으로 구현해보자
seonmun.BestFriend;
(&seonmun)->BestFriend;

구현
- 포인터와 레퍼런스를 활용해 함수 외부에서 선언된 두 정수형 변수의 값을 서로 바꾸는 Swap 함수를 각각 구현하시오
void Swap(int* a, int* b)
{
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
void Swap(int& a, int& b)
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}-
1000미만의 3의 승수를 차례대로 출력하는 코드를 구현 하시오
int main(void) { for (int i = 3; i < 1000; i *= 3) { printf("%d\n", i); } } -
다음의 형태로 * 을 출력하는 코드를 구현 하시오
-
배열의 값을 오름차순으로 정렬해서 반환하는 함수를 구현 하시오
나무위키 정렬 알고리즘 검색
한두개 정돈 암기하고 있는것이 좋다.
아래 방식은 버블 소트 방식이다.
한 사이클이 돌 때 마다 가장 큰 수가 맨 뒤로 정렬된다.
#define CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void sortArray(int* arr, int size)
{
// 버블 소트는 여러 페이즈로 이뤄지며
// 각 페이즈가 끝날 시 맨 끝 원소부터 정렬된 원소가 삽입된다.
for (int phase = 0; phase < size - 1; ++phase)
{
// 각 페이즈마다 해줘야 하는 일.
for (int i = 0; i < size - 1 - phase; ++i)
{
// 정렬 조건 : 현재 원소가 다음 원소보다 클 때 (오름차순)
if (arr[i] > arr[i + 1])
{
// 서로 바꾼다.
std::swap(arr[i], arr[i + 1]);
}
}
}
}
int main(void)
{
int arr[5] = { 5, 2, 4, 1, 3 };
sortArray(arr, 5);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
}- 로또 생성기
A. 최대 번호값과 생성 숫자 개수를 입력하면 해당 조건 내에서 중복되지 않는 숫자를 출력하는 로또 번호 생성기를 구현.
B. 최대값 : 60, 생성숫자 : 10 을 입력하면 1 ~ 60 사이의 중복되지 않는 숫자 10개를 생성한다.
int main()
{
// 입력 : 최대 번호값과 생성 숫자 개수 입력 받는다.
cout << "최대 번호 값을 입력하세요. : ";
int maxValue;
cin >> maxValue;
cout << "생성할 숫자의 개수를 입력하세요. : ";
int digitCount;
cin >> digitCount;
// 처리 : 로또 생성
// 1 ~ maxValue 사이의 값 중 중복되지 않게 digitCount만큼 뽑음.
int* lotto = new int[digitCount]; // 동적할당
// 로또 번호 정하기
srand(time(NULL));
for (int curPos = 0; curPos < digitCount; ++curPos)
{
int candidate = 0;
bool isExist = false;
do
{
candidate = 1 + rand() % maxValue;
isExist = false;
for (int i = 0; i < curPos; ++i)
{
if (candidate == lotto[i])
{
isExist = true;
break;
}
}
} while (isExist);
}}
- 7포커
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
bool isUsedCard[53] = { false }; // 정적, 동적 할당 2개 다 할거기 때문에 파일범위에 놓음
/// <summary>
/// 카드 7장을 뽑는다.
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
/*
int* PickCard()
{
int* arr = new int[7];
int pickCard = 0;
while (pickCard < 7)
{
int rand_card_num = rand() % 53;
if (isUsedCard[rand_card_num])
{
rand_card_num = rand() % 53;
}
else
{
arr[pickCard] = rand_card_num;
isUsedCard[rand_card_num] = true;
++pickCard;
}
}
}
*/
/// <summary>
/// 카드 7장을 뽑는다.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="deck"></param>
void PickCard(int* deck)
{
// 중복되지 않게 카드를 뽑아야함.
// 카드는 정수값. [0, 53)
int pickCard = 0;
while (pickCard < 7)
{
int rand_card_num = rand() % 53;
if (isUsedCard[rand_card_num])
{
rand_card_num = rand() % 53;
}
else
{
deck[pickCard] = rand_card_num;
isUsedCard[rand_card_num] = true;
++pickCard;
}
}
}
// 0 ~ 12 : 스페이드
// 13 ~ 25 : 클로버
// 26 ~ 38 : 하트
// 39 ~ 51 : 다이아
// 52 : 조커
std::string ConvertToCardString(int cardIndex)
{
int cardType = cardIndex / 13;
int cardNumber = cardIndex % 13;
static const string CARD_TYPE[] = {"♠", "♣", "♥", "◆" };
static const string CARD_NUMBER[] = {"A", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "10", "J", "Q", "K"};
if (cardType == 4)
{
return "Joker";
}
else
{
return CARD_TYPE[cardType] + CARD_NUMBER[cardNumber];
}
}
int main()
{
srand(time(NULL));
int player1[7] = { 0 };
PickCard(player1);
int player2[7] = { 0 };
PickCard(player2);
cout << "Player1 : ";
for (int i = 0; i < 7; ++i)
{
cout << ConvertToCardString(player1[i]) << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "Player2 : ";
for (int i = 0; i < 7; ++i)
{
cout << ConvertToCardString(player2[i]) << " ";
}
}- 빙고게임
#define CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <string.h>
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
srand(time(NULL));
int board[5][5] = { 0 };
bool isUsed[26] = { false };
for (int r = 0; r < 5; ++r)
{
for (int c = 0; c < 5; ++c)
{
int number = 0;
do
{
number = rand() % 25 + 1;
} while (isUsed[number]);
board[r][c] = number;
isUsed[number] = true;
}
}
int bingoCount = 0;
while (1)
{
// 1. 출력
for (int r = 0; r < 5; ++r)
{
for (int c = 0; c < 5; ++c)
{
if (board[r][c] == 0)
{
cout << " \t";
}
else
{
cout << board[r][c] << "\t";
}
}
cout << "\n";
}
cout << "현재" << bingoCount << "줄의 빙고가 완성되었습니다." << endl;
// 2. 사용자로부터 입력을 받는다.
cout << "숫자를 입력해주세요 : ";
int input;
cin >> input;
// 3. 사용자의 입력이 유효한지 판단.
if (input < 0 || input > 25)
{
continue;
// 3-1. 오입력을 했다면? 2번부터 다시
}
// 4. 숫자를 지워준다.
for (int r = 0; r < 5; ++r)
{
bool isExit = false;
for (int c = 0; c < 5; ++c)
{
if (board[r][c] == input)
{
board[r][c] = 0;
isExit = true;
break;
}
}
if (isExit)
{
break;
}
}
// 5. 빙고 개수를 센다
// 빙고 ?
// - 가로의 모든 숫자를 지운 것
int count = 0;
for (int r = 0; r < 5; ++r)
{
bool isBingo = true;
for (int c = 0; c < 5; ++c)
{
if (board[r][c] != 0)
{
isBingo = false;
break;
}
}
if (isBingo)
{
++count;
}
}
// - 세로의 모든 숫자를 지운 것
for (int r = 0; r < 5; ++r)
{
bool isBingo = true;
for (int c = 0; c < 5; ++c)
{
if (board[c][r] != 0)
{
isBingo = false;
break;
}
}
if (isBingo)
{
++count;
}
}
// - 대각선의 모든 숫자를 지운 것
// [0][0] / [1][1] / [2][2] / [3][3] / [4][4]
{
bool isBingo = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
if (board[i][i] != 0)
{
isBingo = false;
break;
}
}
if (isBingo)
{
++count;
}
}
// [0][4] / [1][3] / [2][2] / [3][1] / [4][0]
{
bool isBingo = true;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
if (board[i][4 - i] != 0)
{
isBingo = false;
break;
}
}
if (isBingo)
{
++count;
}
}
bingoCount = count;
// 6. 2번부터 반복한다.
system("cls");
}}
- 달팽이
#include
#include
#define NOT_VISITED 0
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// 1. 배열만들기
cout << "배열의 크기를 입력하세요 : ";
int size;
cin >> size;
// 이중배열 할당을 하지 않는 이유
// 메모리가 연속적으로 할당되지 않아 메모리 파편화가 될 수 있기때문
int* arr = new int[size * size];
// arr[2][3]
// arr[2 * size + 3];
memset(arr, 0, sizeof(int) * size * size); // 메모리 초기화
// 2. 달팽이 배열 세팅
// 2-1. 달팽이 데이터 초기화
int r = 0; // 달팽이의 위치 (y좌표)
int c = 0; // 달팽이의 위치 (y좌표)
int footstep = 1; // 달팽이 발자국
enum Direction
{
DIR_RIGHT,
DIR_DOWN,
DIR_LEFT,
DIR_UP,
DIR_MAX
};
Direction direction = DIR_RIGHT; // 달팽이가 움직이는 방향
for (int i = 0; i < size * size; ++i)
{
// 2-2. 발자국을 남긴다.
arr[r * size + c] = footstep;
++footstep;
static const int dr[] = { 0, 1, 0, -1 };
static const int dc[] = { 1, 0, -1, 0 };
// DIR_RIGHT(0) : r = r + dr[0] = r + 0 / c = c + dc[0] = c + 1
// DIR_DOWN(0) : r = r + dr[1] = r + 1 / c = c + dc[1] = c + 0
// DIR_LEFT(0) : r = r + dr[2] = r + 0 / c = c + dc[2] = c - 1
// DIR_UP(0) : r = r + dr[3] = r - 1 / c = c + dc[3] = c + 0
// 2-3. 이동할 위치를 계산한다.
int nc = c + dc[(int)direction]; // => 아래 스위치문이랑 같은 용도
int nr = r + dr[(int)direction];
/*switch (direction)
{
case DIR_RIGHT:
++c;
break;
case DIR_DOWN:
++r;
break;
case DIR_LEFT:
--c;
break;
case DIR_UP:
--r;
break;
}*/
// 2-3-1. 오른쪽으로 갈 때 => c += 1
// 2-3-2. 밑으로 갈 때 => r += 1
// 2-3-3. 왼쪽으로 갈 때 => c -= 1
// 2-3-4. 위쪽으로 갈 때 => r -= 1
// 오른쪽 : r = r + 0/ c = c + 1 / direction == DIR_RIGHT(0)
// 밑 : r = r + 1/ c = c + 0 / direction == DIR_DOWN(1)
// 왼쪽 : r = r + 0/ c = c - 1 / direction == DIR_LEFT(2)
// 위 : r = r - 1/ c = c + 0 / direction == DIR_UP(3)
// 2-4. 이동이 가능한지 판별한다.
// 2-4-1. 벽에 닿았을 때 => r, c의 위치가 [0, size)
// 2-4-2. 이미 지나온 곳일 때 => arr[nr][nc] != 0
if (nr < 0 || nr >= size || nc < 0 || nc >= size || arr[nr * size + nc] != NOT_VISITED)
{
// 2-5. 이동이 불가능하므로 방향 전환을 한다.
direction = (Direction)((direction + 1) % DIR_MAX);
// 2-6. 위치값을 다시 계산한다.
nc = c + dc[(int)direction];
nr = r + dr[(int)direction];
}
// 2-7. 이동한다.
r = nr;
c = nc;
}
// 3. 출력
for (int r = 0; r < size; ++r)
{
for (int c = 0; c < size; ++c)
{
cout << arr[r * size + c] << "\t";
}
cout << "\n\n";
}
delete[] arr;}
