Process Concept
*정의
프로그램 내에서 처리 부분을 맡고 있고, os의 unit of work이다.
*수행 task
- CPU time, Meomory, fiiles, I/O devices
*Memory layout
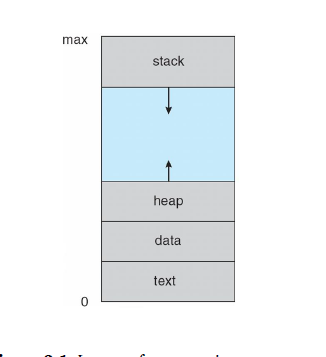
-
Text section: the executable code
-
Data section: global variables
-
Heap section: program run time하는 동안 메모리는 할당됩니다.
-
Stack section: invoking functions할 때 일시적인 데이터 저장소로 function parameters, return addresses, local variables이다
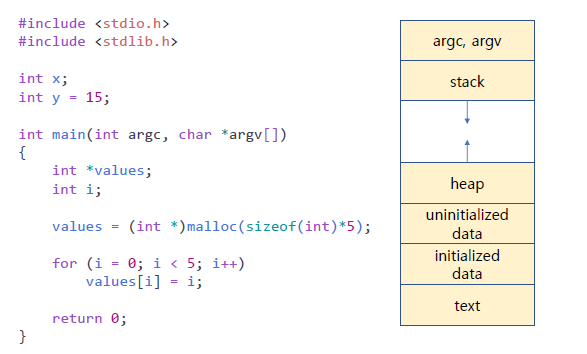
- process 실행 시 변화
-
New: process가 새로 생성됨
-
Running: Instructions가 실행됨
-
Waiting: process가 사건이 발생되길 기다림
- ex) I/O completion or reception of a signal.
-
Ready: process가 processor이 승인되길 기다림
-
Terminated: 실행 종료
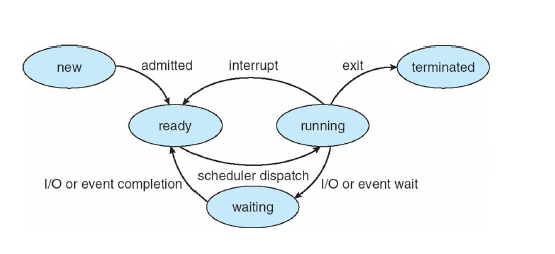
*PCB(Process Control Block) or TCB(Task Control Block)
-
각 프로세스는 PCB로 인해서 OS안에서 표현됨
-
Process of PCB
- Process state
- Porgram counter
- CPU registers
- CPU-scheduling information
- Memory-management information
- Accounting information
- I/O status information
*Summary
-
program은 하나의 스레드를 실행
-
스레드 제어는 process가 수행되도록 허락(only one task at a time)
-
현대 os는 process개념의 확장
- 다중 멀티 스레드 실행
- more than one task at a time
- 스레드는 higjweight process
Process Sheduling
-
멀티프로그래밍(The objective of multiprogramming)
- 동시에 여러 프로세스 진행
- CPU가동 범위 최대
-
타임 공유(The objective of time sharing)
- 프로세스들 사이의 CPU코어 변화
- Running, 유저와 프로그램은 상호작용
-
스케쥴링 큐(Sheduling Queues)
-
ready queue
- CPU코어 내에서 시작 위치와 시작을 기다리는 위치 파악
-
wait queue
- 확실한 event가 발생되어야 함
-
위의 큐들은 PCBs의 연결 리스트로 보충됨
-

- Queueing Diagram(process scheduling)

-
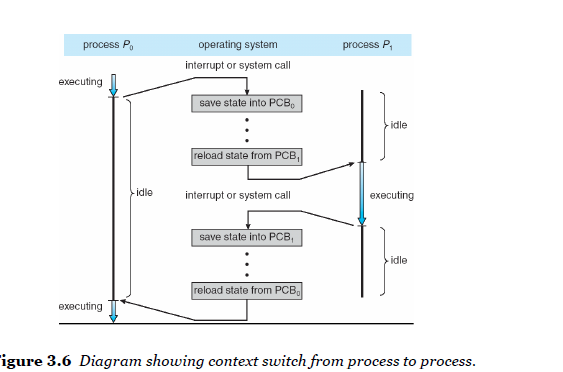
Context Switch
-
PCB, context process기 표현됨
-
Interrupt occurs
- 시스템은 돌아가는 프로세스의 현재 context 저장
- 그 후, 재 저장이 가능함
-
Context switch
- CPU코어를 다른 프로세스와 변환
- 현재 프로세스 저장
- 다른 프로세스에 재배치
-
Operations on Processes
-
Mechanism: process creation and termination
-
Create several new processes
- the creating process: a parent process
- a newly created process: a child process
- tree processes
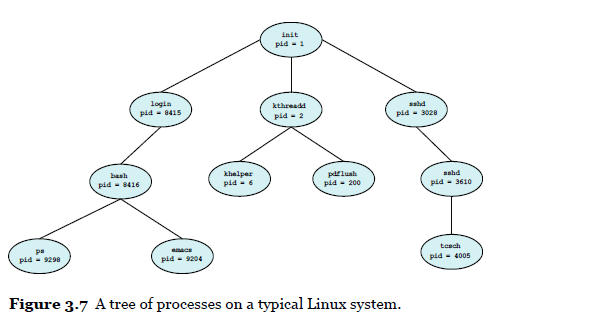
-
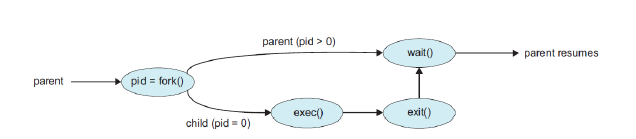
Two possibilities for execution
- 부모노드는 자식 노드가 실행되록 진행
- 부모노드는 자식 노드가 다 종료될 때가지 기다림
-
Two possibilities of address-space
- 자식 process는 부모 process를 복제
- 자식 process는 새로운 프로그램을 불러온다
-
CODE
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <wait.h>
int main()
{{
pid_t pid;
// fork a child process
pid = fork();
if (pid <0 ) { // error occurred
fprintf(stderr, "Fork Failed");
return 1;
}
else if (pid == 0) { // child process
execlp("/bin/ls", "ls", NULL);
}
else { // parent process
wait(NULL)
printf("Child Complete");
}
return 0;
}
-
프로세스 종결
-
최종 statement가 실행
-
exit()system call
-
OS deallocates and reclaims all the resources:
ex) allocated memories, open files, and I/O buffers, etc
-
-
Zombie and Orphan
- Zombie: 종결과정이지만 wait() call전
- Orphan: 현재 프로세스 wait()쓰지 않고 종결
-
UNIX-like O/S
-
fork()system call로 부터 새로운 process가 생성됨
-
A new process is created by the fork() system call.
- The child process consists of
-
a copy of the address space of the parent process.
-
• Both processes continue execution
- at the instruction after the fork() system call.
• With one difference:
- the return code for the fork() is zero for the child process, whereas
- the nonzero pid of the child is returned to the parent process.
-
After a fork() system call,
-
the parent can continue its execution ; or
-
if it has nothing else to do while the child runs,
-
it can issue a wait() system call
-
to move itself off the ready queue until the termination of the child.
-
-
