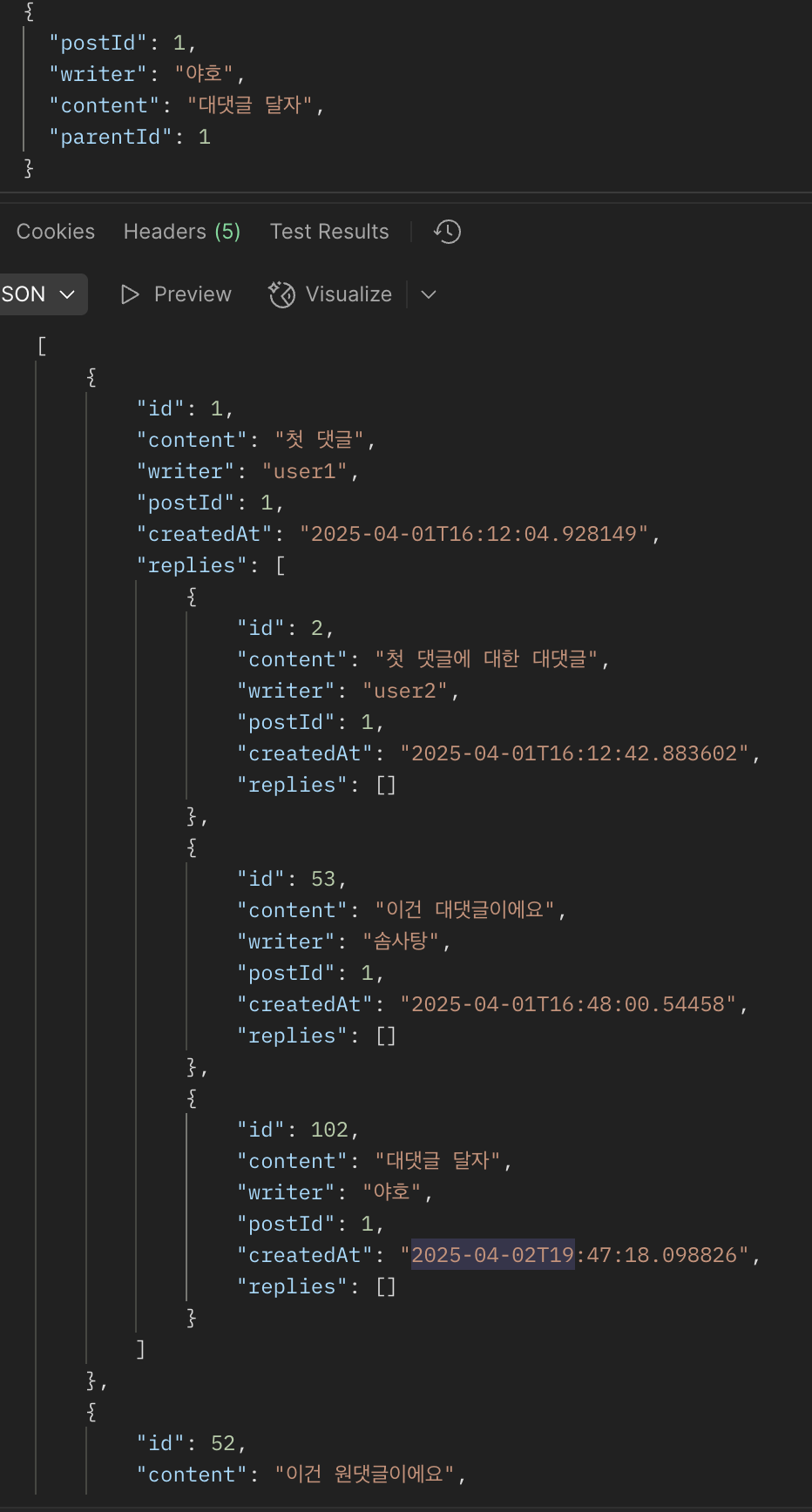
이전 프로젝트를 진행해보면서는 1뎁스의 댓글만 구현해보고 대댓글 구현은 해보지 못했다.
마지막 프로젝트에서 대댓글 형식과 같은 구조를 만들었는데 정확히는 대댓글이 되는게 아니었다.
면접에서
'댓글 구현하셨던데 몇 뎁스까지 가능하게 했나요?'와 같은 질문을 할 줄 몰랐고
'대댓글 구현하려면 DB어떻게 할지'에 대한 생각까지 해보지도 못한 것 같다.
대댓글 구현을 한거라 생각했던 프로젝트가 진짜 대댓글로 구현한 거였다면 알았겠지만
면접 후 다시 생각해보고 알아보니 형식은 대댓글 구조처럼 짜여져 있으나 실제 대댓글이 아닌.. 그런 구조였다.
그래서 한 번 구현을 해보는게 좋겠어서 해봤다:)
controller
@RestController
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/comments")
public class CommentController {
private final CommentService commentService;
@PostMapping
public ResponseEntity<CommentResponseDto> write(@RequestBody CommentRequestDto requestDto) {
Comment saved = commentService.save(requestDto);
return ResponseEntity.ok(CommentResponseDto.fromEntity(saved));
}
@GetMapping("/{postId}")
public ResponseEntity<List<CommentResponseDto>> getComments(@PathVariable Long postId) {
return ResponseEntity.ok(commentService.getCommentsByPost(postId));
}
}@RestController + @RequestMapping으로 REST API 정의
/comments POST: 댓글 등록
/comments/{postId} GET: 해당 게시글의 댓글 트리 조회
service
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class CommentService {
private final CommentRepository commentRepository;
public Comment save(CommentRequestDto requestDto) {
Comment comment = new Comment();
comment.setPostId(requestDto.getPostId());
comment.setContent(requestDto.getContent());
comment.setWriter(requestDto.getWriter());
comment.setCreatedAt(LocalDateTime.now());
if (requestDto.getParentId() != null) {
Comment parent = commentRepository.findById(requestDto.getParentId())
.orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException("부모 댓글 없음"));
comment.setParent(parent);
}
return commentRepository.save(comment);
}
public List<CommentResponseDto> getCommentsByPost(Long postId) {
List<Comment> roots = commentRepository.findByPostIdAndParentIsNullOrderByCreatedAtAsc(postId);
return roots.stream()
.map(CommentResponseDto::fromEntity)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}- 부모 ID가 null이면 ‘원댓글’, 아니면 ‘대댓글’
Entity를 직접 반환하지 않고DTO로 변환해서 전달
처음 setter로 진행
실무에서는 setter를 직접 호출하기보다는 Builder 패턴이나 생성자 주입 방식 사용.
Comment comment = Comment.builder()
.postId(requestDto.getPostId())
.content(requestDto.getContent())
.writer(requestDto.getWriter())
.createdAt(LocalDateTime.now())
.build();이렇게 바꾸고 요청해보니 DB에 데이터는 저장되는데 500에러나 나왔다.
문제 원인
Builder 사용 시 replies = new ArrayList<>()가 무시된다.
private List<Comment> replies = new ArrayList<>();이렇게 해놔도 Builder를 쓰면 이 기본값이 무시돼서 null로 들어가버린다.
그래서 .stream() 호출 시 NPE가 발생
왜 이런 현상이 생기까?
Lombok의 @Builder는 필드를 하나하나 명시적으로 설정하는 빌더 객체를 생성하기 때문에,
빌더가 replies를 설정하지 않으면 초기값을 무시하고 null로 남겨버린다.
해결방법
방법 1: Builder에서 기본값 설정
@Builder.Default
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "parent", cascade = CascadeType.ALL, orphanRemoval = true)
private List<Comment> replies = new ArrayList<>(); @Builder.Default 를 붙이면 Lombok이 기본값도 빌더에 반영하도록 해준다.

성공!
repository
public interface CommentRepository extends JpaRepository<Comment, Long> {
List<Comment> findByPostIdAndParentIsNullOrderByCreatedAtAsc(Long postId);
}entity
@Entity
@Getter @Setter
@Builder
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Comment {
@Id @GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String content;
private String writer;
private Long postId; //게시글 ID
private LocalDateTime createdAt;
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY)
@JoinColumn(name = "parent_id")
private Comment parent;
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "parent", cascade = CascadeType.ALL, orphanRemoval = true)
private List<Comment> replies = new ArrayList<>(); //대댓글 목록
}컬렉션(List) 필드는 반드시 new ArrayList<>()로 초기화! (null 방지 목적, 실무 필수)
자기참조(parent, replies)를 이용한 “특수구조” 구조(parent, replies)를 이용한 “특수구조” 구조
orphanRemoval = true: 부모에서 제거 시 자식도 삭제됨
cascade = ALL: 댓글 저장 시 대댓글도 자동 저장 가능 (현재 꼭 필요한건 아님)
@Builder: 생성자 대체로 객체를 더 명확하게 생성할 수 있음
dto
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class CommentRequestDto {
private Long postId;
private String content;
private String writer;
private Long parentId; //null 이면 기본 댓글
}@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class CommentResponseDto {
private Long id;
private String content;
private String writer;
private Long postId;
private LocalDateTime createdAt;
private List<CommentResponseDto> replies = new ArrayList<>();
public static CommentResponseDto fromEntity(Comment comment) {
return new CommentResponseDto(
comment.getId(),
comment.getContent(),
comment.getWriter(),
comment.getPostId(),
comment.getCreatedAt(),
comment.getReplies().stream()
.map(CommentResponseDto::fromEntity)
.collect(Collectors.toList())
);
}
}응답에서 순환 참조 방지 (Entity -> DTO 변환)
orphanRemoval = true란?
- 부모 엔티티에서 연관된 자식 엔티티를 제거했을 때, DB에서도 해당 자식 레코드를 자동으로 삭제해주는 기능.
orphanRemoval 작동 조건
@OneToMany 또는 @OneToOne 관계
- 양방향 연관관계에서만 의미 있다.
부모 객체의 컬렉션에서 자식 제거
.remove()했을 때만 작동
orphanRemoval = true 설정 필요
- 안 하면 DB에서 삭제되지 않음
orphanRemoval = true 부모에서 자식 제거 시 DB에서도 삭제됨
cascade = REMOVE 부모가 삭제될 때 자식도 삭제됨