미로 탈출
https://school.programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/159993
문제
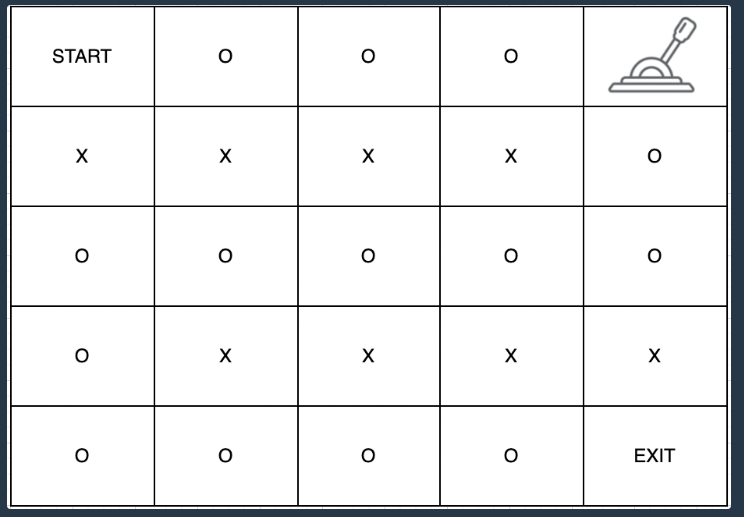
미로 탈출 (DFS -> 시간초과)
Start에서 레버로 가는 최단 거리를 구한다. 그리고 나서 레버에서 Exit까지 최단 거리를 구한다. 이 두 가지 경우에서 하나라도 float("inf")라면 -1을 리턴하고 그렇지 않으면 두 가지 최단거리를 더한 값을 리턴한다.
또한 탐색해야 하는 것은 4가지 방향으로 (상, 하, 좌, 우)가 될 것이다. 여기서 "X", 범위를 벗어날 경우 등 이럴 때에는 리턴을 해준다. "E", "L"이 될 경우 그 중에서 최단 경로를 찾는다.
이것을 DFS 코드로 나타내면 다음과 같다.
-
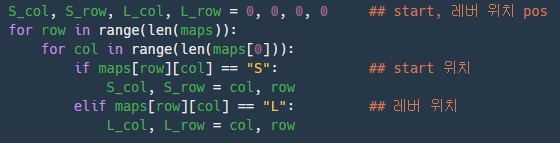
start, 레버 위치 찾는다.
-
Start에서 레버로 가는 최단 거리를 구한다.
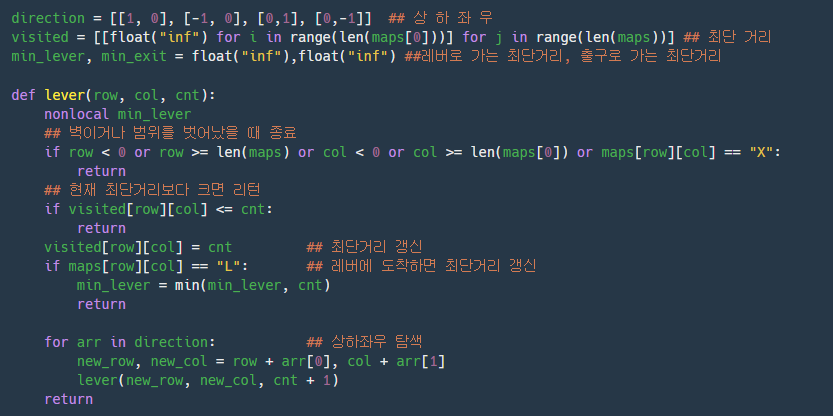
visited는 각 위치마다 최단 거리가 저장되어 있는 변수이다. 탐색 중에서 벽이거나, 범위를 벗어날 때만 리턴해주는 것이 아니라 최단 거리도 함께 조건에 추가하여 불필요한 탐색을 줄였다.
탐색 중에 레버에 도착하면 min_lever를 갱신해준다.
-
레버에서 Exit로 가는 최단 거리를 구한다.
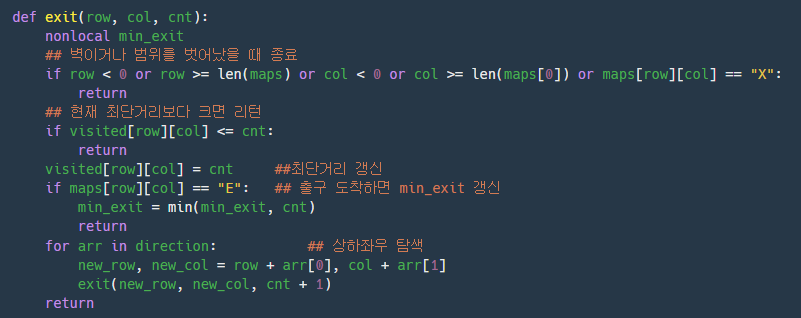
레버와 마찬가지로 Exit로 가는 최단거리를 구한다. -
결과 도출
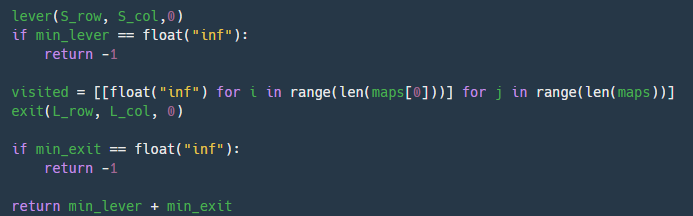
min_lever or min_exit가 float("inf) => 탐색할 수 없으면 -1을 리턴하고 그렇지 않으면 두가지 더한 값을 리턴한다.
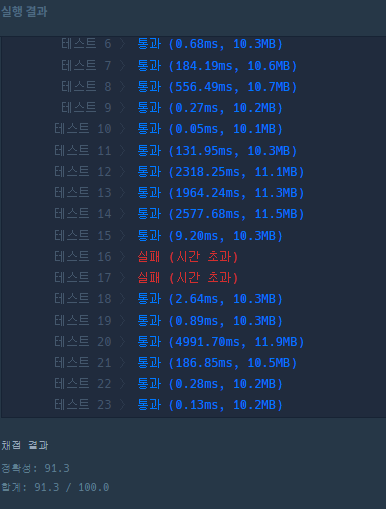
결과
import sys
sys.setrecursionlimit(10**6)을 사용했더니 5개에서 2로 에러가 줄었다. 하지만 시간초과 에러가 발생하였다. 그 이유는 DFS는 메모리제이션 기법을 사용하지 않으면 불필요한 계산을 하게 되는데 이 때매 시간 초과가 발생한 것 같다. 메모리제이션 기법대신 visited를 사용해서 불필요한 연산을 줄였다고 생각해지만 결과는 그렇지 않았다.
import sys
sys.setrecursionlimit(10**6)
def solution(maps):
S_col, S_row, L_col, L_row = 0, 0, 0, 0
for row in range(len(maps)):
for col in range(len(maps[0])):
if maps[row][col] == "S":
S_col, S_row = col, row
elif maps[row][col] == "L":
L_col, L_row = col, row
direction = [[1, 0], [-1, 0], [0,1], [0,-1]]
visited = [[float("inf") for i in range(len(maps[0]))] for j in range(len(maps))]
min_lever, min_exit = float("inf"),float("inf")
def lever(row, col, cnt):
nonlocal min_lever
if row < 0 or row >= len(maps) or col < 0 or col >= len(maps[0]) or maps[row][col] == "X":
return
if visited[row][col] <= cnt:
return
visited[row][col] = cnt
if maps[row][col] == "L":
min_lever = min(min_lever, cnt)
return
for arr in direction:
new_row, new_col = row + arr[0], col + arr[1]
lever(new_row, new_col, cnt + 1)
return
def exit(row, col, cnt):
nonlocal min_exit
if row < 0 or row >= len(maps) or col < 0 or col >= len(maps[0]) or maps[row][col] == "X":
return
if visited[row][col] <= cnt:
return
visited[row][col] = cnt
if maps[row][col] == "E":
min_exit = min(min_exit, cnt)
return
for arr in direction:
new_row, new_col = row + arr[0], col + arr[1]
exit(new_row, new_col, cnt + 1)
return
lever(S_row, S_col,0)
if min_lever == float("inf"):
return -1
visited = [[float("inf") for i in range(len(maps[0]))] for j in range(len(maps))]
exit(L_row, L_col, 0)
if min_exit == float("inf"):
return -1
return min_lever + min_exit
미로 탈출 (BFS -> heapq)
BFS 같은 경우 최단 거리를 보장 한다. 즉 "L", "E"에 먼저 도착한 경우가 가장 최단 거리라는 의미이다. 최단 거리는 DFS보단 BFS를 사용해야 할 것 같다.
-
start, 레버 위치 찾는다.

-
BFS를 구현한다.
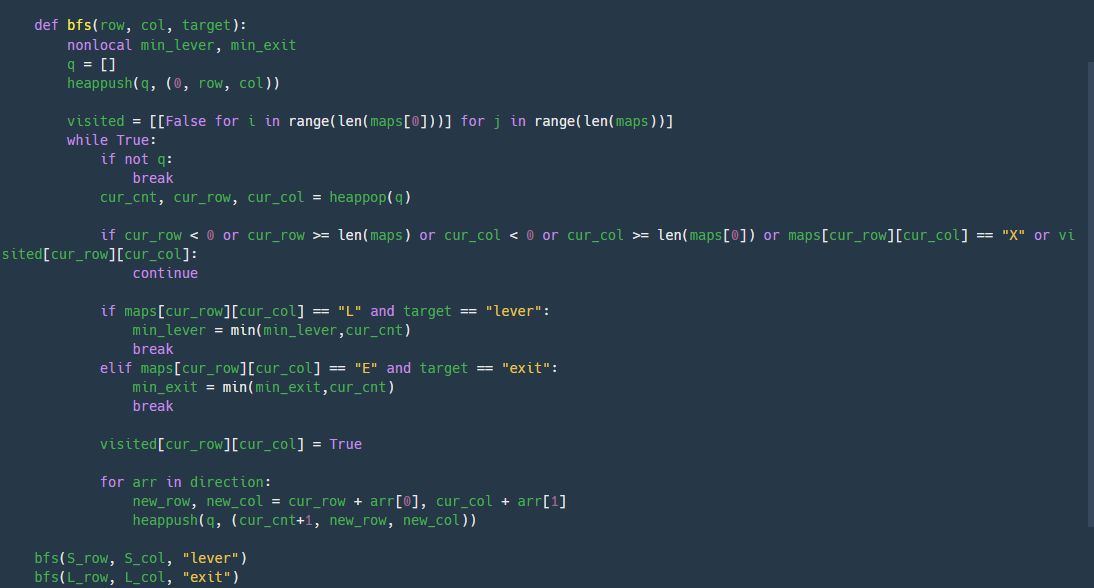
from heapq import heappush, heappop
def solution(maps):
S_col, S_row, L_col, L_row = 0, 0, 0, 0
for row in range(len(maps)):
for col in range(len(maps[0])):
if maps[row][col] == "S":
S_col, S_row = col, row
elif maps[row][col] == "L":
L_col, L_row = col, row
direction = [[1, 0], [-1, 0], [0,1], [0,-1]]
min_lever, min_exit = float("inf"), float("inf")
def bfs(row, col, target):
nonlocal min_lever, min_exit
q = []
heappush(q, (0, row, col))
visited = [[False for i in range(len(maps[0]))] for j in range(len(maps))]
while True:
if not q:
break
cur_cnt, cur_row, cur_col = heappop(q)
if cur_row < 0 or cur_row >= len(maps) or cur_col < 0 or cur_col >= len(maps[0]) or maps[cur_row][cur_col] == "X" or visited[cur_row][cur_col]:
continue
if maps[cur_row][cur_col] == "L" and target == "lever":
min_lever = min(min_lever,cur_cnt)
break
elif maps[cur_row][cur_col] == "E" and target == "exit":
min_exit = min(min_exit,cur_cnt)
break
visited[cur_row][cur_col] = True
for arr in direction:
new_row, new_col = cur_row + arr[0], cur_col + arr[1]
heappush(q, (cur_cnt+1, new_row, new_col))
bfs(S_row, S_col, "lever")
bfs(L_row, L_col, "exit")
if min_lever == float("inf") or min_exit == float("inf"):
return -1
return min_lever + min_exit
