ArrayList
while + iterator
package jcf;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class PhoneNumFinder {
public static void main(String[] args) {
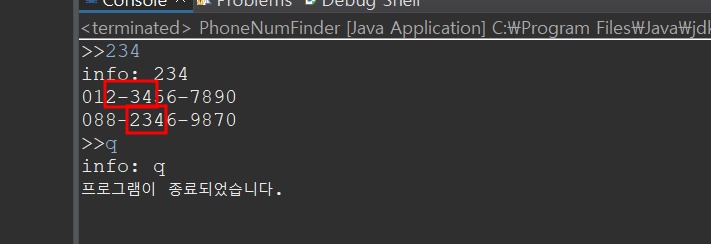
String[] phoneNumArr = {"012-3456-7890", "099-2456-7980", "088-2346-9870", "013-3456-7890"};
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
System.out.print(">>");
String input = s.nextLine().trim(); // trim()으로 입력내용에서 공백을 제거
System.out.println("info: " + input);
if (input.equals("")) {
continue;
}
else if (input.equalsIgnoreCase("Q")) {
System.out.println("프로그램이 종료되었습니다.");
s.close();
System.exit(0);
}
for (int i=0; i<phoneNumArr.length; i++) {
String phoneNum = phoneNumArr[i];
String tmp = phoneNum.replace("-", "");
if (tmp.contains(input)) {
list.add(phoneNum);
}
}
if (list.size() > 0) {
print(list);
list.clear();
}
else {
System.out.println("일치하는 번호가 없습니다.");
}
} // end while
} // end main
// while + iterator
public static void print(List<String> list) {
Iterator<String> iter = list.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
String num = iter.next();
System.out.println(num);
}
}
}for each
// 개선 for
public static void print2(List<String> list) {
for (String num : list) {
System.out.println(num);
}
}for each를 통해 성능 개선
Stream
FileInputStream
- test.txt 생성
- test.txt
ABC
123
가나다- FileReaderTest.java
package io;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileReader {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String fileName = "test.txt";
// 파일 오픈
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(fileName);
int data = 0;
// read(): 읽을 바이트 없으면 -1 리턴
while ((data = fis.read()) != -1) { // 문자가 정수로 인코딩(ex. A -> 65)
System.out.println((char)data); // 정수가 문자로 디코딩(ex. 65 -> A)
}
// 파일닫기(스트림 자원 해제)
fis.close();
}
}- 결과
A
B
C
1
2
3
ê
°
ë
ë
¤FileReader
- FileReaderTest.java
package io;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileReaderTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String fileName = "test.txt";
int data = 0;
// 한글(UTF-16) 포함 데이터 읽기
FileReader fr = new FileReader(fileName);
// read(): 읽을 바이트 없으면 -1 리턴
while ((data = fr.read()) != -1) { // 문자가 정수로 인코딩(ex. A -> 65)
System.out.println((char)data); // 정수가 문자로 디코딩(ex. 65 -> A)
}
// 파일닫기(스트림 자원 해제)
fr.close();
}
}- 결과
A
B
C
1
2
3
가
나
다BufferedReader
- FileReaderTest2.java
package io;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileReaderTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String fileName = "test.txt";
String data = ""; // BufferedReader는 String으로!
// 한글(UTF-16) 포함 데이터 읽기
// 파일(Stream 자원) 오픈
FileReader fr = new FileReader(fileName);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
// readLine(): 읽을 바이트 없으면 null 리턴
while ((data = br.readLine()) != null) { // 라인 읽기
System.out.println(data);
}
// 파일닫기(스트림 자원 해제)
fr.close();
}
}- 결과
ABC
123
가나다FileWriter
- FileCopyTest.java
package io;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileCopyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String fileName = "test.txt";
String fileName2 = "test2.txt"; // 생성할 파일 이름
String data = ""; // BufferedReader는 String으로!
// 한글(UTF-16) 포함 데이터 읽고 쓰기
// 파일(Stream 자원) 오픈
FileReader fr = new FileReader(fileName);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(fileName2);
// readLine(): 읽을 바이트 없으면 null 리턴
while ((data = br.readLine()) != null) { // 라인 읽기
data += "\r\n"; // 줄바꿈
fw.write(data); // 라인 쓰기
}
br.close();
fw.close(); // close는 flush를 포함함. flush를 해야 파일에 쓰여짐
}
}
- 결과(test2.txt)
ABC
123
가나다System
package sys;
public class SystemTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(System.getenv("PATH"));
System.out.println(System.getProperty("java.version"));
System.out.println(System.getProperty("os.name"));
System.out.println(System.getProperty("user.home"));
}
}
Exception
- ExceptionTest.java
package except;
import java.util.Date;
public class ExceptionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date date = new Date();
if (date != null) { // null 검증
System.out.println(date.getTime());
}
}
}- ExceptionTest2.java
package except;
import java.io.*;
public class ExceptionTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
print();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
static void print() throws Exception {
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(new File("test.txt"));
}
}printStackTrace()는 Java에서 예외가 발생했을 때 그 예외의 상세 정보를 출력하는 메소드입니다. 이 메소드는 예외의 종류와 메시지, 그리고 예외가 발생한 위치와 메소드 호출 순서를 포함한 스택 트레이스를 콘솔에 출력합니다. 디버깅에 매우 유용하지만, 실제 운영 환경에서는 로그 파일에 기록하는 것이 일반적입니다.
InputMismatchException
- ExceptionTest3.java
package except;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.InputMismatchException;
import java.util.Scanner;
// 입력 정수 1 증가
// 정수 입력할 때까지 재입력 반복
public class ExceptionTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
while (true) {
try {
int num = readInt();
System.out.println(num + 1);
break;
} catch (Exception e) {
//
}
}
}
private static int readInt() {
try {
System.out.print("정수 입력: ");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = scanner.nextInt();
return num;
}
catch (InputMismatchException e) {
System.out.println("정수 미입력");
throw new InputMismatchException("정수 미입력");
}
}
}Thread
- AddThread.java
package thread;
public class MyAddThread implements Runnable {
int begin, end;
int hap;
public int getHap() {
return hap;
}
public void setHap(int hap) {
this.hap = hap;
}
public MyAddThread() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
hap = 0;
}
public MyAddThread(int begin, int end) {
this(); // MyAddThread() 호출
this.begin = begin;
this.end = end;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
for (int i=begin; i<=end; i++) {
hap += i;
}
}
}
- MyAddThreadTest.java
package thread;
public class MyAddThreadTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyAddThread mat1 = new MyAddThread(1, 50);
MyAddThread mat2 = new MyAddThread(51, 100);
Thread th1 = new Thread(mat1);
Thread th2 = new Thread(mat2);
th1.start();
th2.start();
// 다른 thread가 종료할 때까지 wait
try {
th1.join();
th2.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("총함: " + (mat1.getHap() + mat2.getHap()));
}
}- 결과
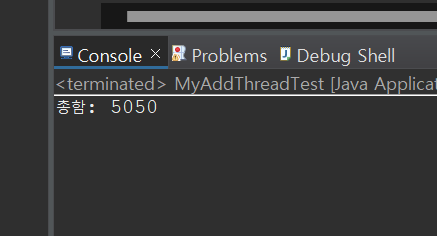


오늘도 공부 열심히 하시네요 ^~^