백준 깃허브 연동(백준허브)
백준에 제출한 풀이를 깃허브에 연동할수 있도록 도와주는 프로젝트이다. 여태까지 수동 push가 귀찮아서 깃허브 업로드를 미루고 있었는데 이런걸 진작 알았으면 좋았을 것 같다. 너무 편하다. *^____^*
이미 푼 문제는 트래픽 문제로 한꺼번에 업로드가 불가능하다고 한다.
2606 바이러스
DFS를 연습하려고 찾아낸 문제인데 BFS로 풀었다(?) 그래프의 개념은 알지만 문제에 나왔을 때 사용하는 방법은 막막했는데, vector를 사용해서 하나의 노드에 연결정보를 저장하고 이후에 stack이나 queue에 그 정보를 사용하면 됐다. 이 문제로 며칠을 고민했는데 옛날에 정리했던 자료에서 답을 얻었다.
- 최대 node의 갯수만큼 vector를 생성한 뒤 받아온 edge를 각 노드에 푸시했다. vector특성 상 이미 생성된 노드에 push_back하게 되면 다차원 배열처럼 사용할 수 있다.
- 1번째 노드의 연결정보를 알아내기 위해 bfs함수를 만들었다.
- 큐 버퍼에 1번째 노드를 푸시한 뒤 팝할 때 노드에 연결된 다른 노드를 푸시한다.
- 팝 할때마다 카운트를 1씩 증가시키면 연결된 모든 노드를 알 수 있다.
예를 들어 아래와 같은 그래프가 있다고 생각해보면
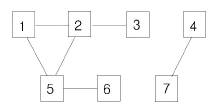
| 노드 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 연결된 노드 | 2, 5 | 1, 3, 5 | 2 | 7 | 1, 2, 6 | 5 | 4 |
이런 식으로 노드가 연결돼있다. 차례대로 queue버퍼의 연산과정을 표로 그려보면 처음에는 1번째 노드가 push된다.
| 노드 | 1 |
|---|
front인 1번노드가 pop되면 1번 노드의 인접노드인 2번, 5번 노드가 push된다.
| 노드 | 2 | 5 |
|---|
front인 2번 노드가 pop되면 2번 노드의 인접노드인 1번, 3번, 5번 노드가 push되지만 1번, 5번 노드는 이미 queue에 방문한 적이 있기 때문에 제외된다.
| 노드 | 5 | 3 |
|---|
front인 5번 노드가 pop되면 5번 노드의 인접노드인 1번, 2번, 6번 노드가 push되지만 1번, 2번 노드는 이미 queue에 방문한 적이 있기 때문에 제외된다.
| 노드 | 3 | 6 |
|---|
나머지 노드들도 같은 과정을 거친다.
| 노드 |
|---|
그래프 저장 방법을 알았기 때문에 BFS/DFS 모두 사용해서 풀 수 있을 것 같다. 알바 다녀온 다음에 1260번도 풀어야지ㅎㅎ
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
vector<int> node[101];
int visit[101];
int cnt = -1;
void bfs(int n)
{
queue<int> b;
b.push(n);
visit[n] = 1;
while (!b.empty())
{
int x = b.front();
b.pop();
cnt++;
for (int i = 0; i < node[x].size(); i++)
{
int y = node[x][i];
if (visit[y] == 0)
{
b.push(y);
visit[y] = 1;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int n, e;
cin >> n >> e;
for (int i = 0; i < e; i++)
{
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
node[a].push_back(b);
node[b].push_back(a);
}
bfs(1);
cout << cnt << endl;
return 0;
}1260 DFS와 BFS

bfs나 dfs나 거기서 거기라서 바로 풀어봤다. 결과는 틀렸다. dfs/bfs 구현은 했으나 문제가 요구하는 방향을 따라가지 못하는 코드라서 틀렸다. 각 노드의 연결순서 때문인가 싶어서 노드의 연결정보를 정렬한 뒤에 dfs/bfs를 실행했으나 여전히 틀렸다고 나온다.
그래서 결론은 다른 사람의 풀이 보고 수정했다.
수정전
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
vector<int>graph[1001];
int visit_bfs[1001];
int visit_dfs[1001];
void dfs(int n)
{
int visit[1001];
stack<int>b;
b.push(n);
visit_dfs[n] = 1;
while (!b.empty())
{
int x = b.top();
b.pop();
cout << x << " ";
for (int i = 0; i < graph[x].size(); i++)
{
int a = graph[x][i];
if (visit_dfs[a] == 0)
{
b.push(a);
visit_dfs[a] = 1;
}
}
}
}
void bfs(int n)
{
queue<int>b;
b.push(n);
visit_bfs[n] = 1;
while (!b.empty())
{
int x = b.front();
b.pop();
cout << x << " ";
for (int i = 0; i < graph[x].size(); i++)
{
int a = graph[x][i];
if (visit_bfs[a] == 0)
{
b.push(a);
visit_bfs[a] = 1;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int n, m, v;
cin >> n >> m >> v;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
graph[a].push_back(b);
graph[b].push_back(a);
}
dfs(v);
cout << "\n";
bfs(v);
return 0;
}수정후(re)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
vector<int>graph[1001];
int visit_bfs[1001];
int visit_dfs[1001];
void dfs(int n)
{
cout << n << " ";
visit_dfs[n] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < graph[n].size(); i++)
{
int a = graph[n][i];
if (visit_dfs[a] == 0)
{
visit_dfs[a] = 1;
dfs(a);
}
}
}
void bfs(int n)
{
queue<int>b;
b.push(n);
visit_bfs[n] = 1;
while (!b.empty())
{
int x = b.front();
b.pop();
cout << x << " ";
for (int i = 0; i < graph[x].size(); i++)
{
int a = graph[x][i];
if (visit_bfs[a] == 0)
{
b.push(a);
visit_bfs[a] = 1;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int n, m, v;
cin >> n >> m >> v;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
graph[a].push_back(b);
graph[b].push_back(a);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
sort(graph[i].begin(), graph[i].end());
}
dfs(v);
cout << "\n";
bfs(v);
return 0;
}수정후(rere)
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int c[1001];
vector<int> a[1001];
void insert_edge(int i, int j) {
a[i].push_back(j);
a[j].push_back(i);
}
void bfs(int start) {
queue<int> q;
q.push(start);
c[start] = true;
while (!q.empty()) {
int w = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << w << ' ';
for (int i = 0; i < a[w].size(); i++) {
int y = a[w][i];
if (!c[y]) {
q.push(y);
c[y] = true;
}
}
}
}
void dfs(int n) {
if (c[n]) return;
cout << n << ' ';
c[n] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < a[n].size(); i++) {
int y = a[n][i];
if (!c[y])
dfs(y);
}
}
int main(void) {
int N, M, V, x, y;
cin >> N >> M >> V;
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
cin >> x >> y;
insert_edge(x, y);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
sort(a[i].begin(), a[i].end());
}
dfs(V);
cout << endl;
memset(c, 0, sizeof(c));
bfs(V);
cout << endl;
}아 다르고 어 다른게 너무하다. memset함수는 처음 보는데 인자 분석정도는 해야겠다. 배열 초기화해줄 때 쓰는 함수같은데 자주 쓸수있을거같다.
