리스트(List)
특징
- 선형적인 자료구조
- 데이터를 일렬로 늘여놓은 형태
- 순서가 있음
기능
- 데이터 추가
- 데이터 삽입
- 데이터 삭제
- 데이터 탐색
종류
- ArrayList
- LinkedList
- Single Linked List
- Doubly Linked List
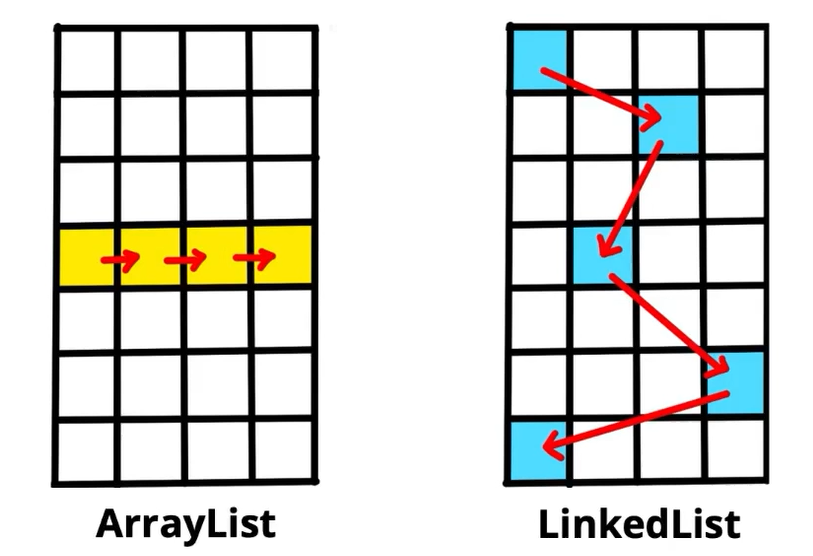 ArrayList와 LinkedList 비교
ArrayList와 LinkedList 비교
ArrayList
특징
- 연속되는 기억 장소에 데이터를 저장
- 배열 삽입하려는 위치부터 데이터를 하나씩 뒤로 이동한 후 데이터를 삽입
- 삭제도 마찬가지 (삭제하려는 위치의 다음부터 데이터를 하나씩 아프로 이동)
기능
- 추가
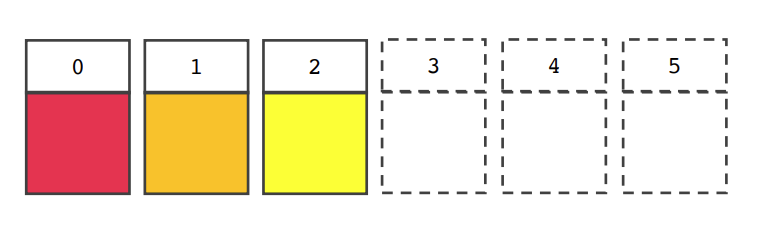 - 6개의 고정된 크기의 배열을 선언
- 6개의 고정된 크기의 배열을 선언
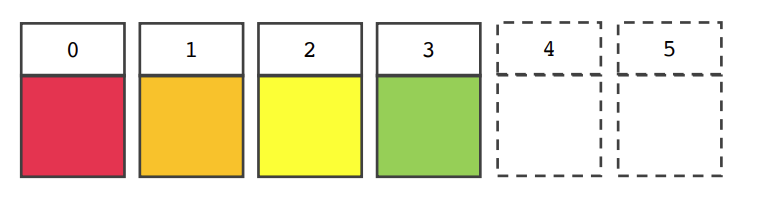 - 이전에 있던 데이터 바로 뒤에 데이터 삽입
- 이전에 있던 데이터 바로 뒤에 데이터 삽입
- 특징
- 마지막 데이터가 있는 곳 다음에 추가 됨
- 삽입
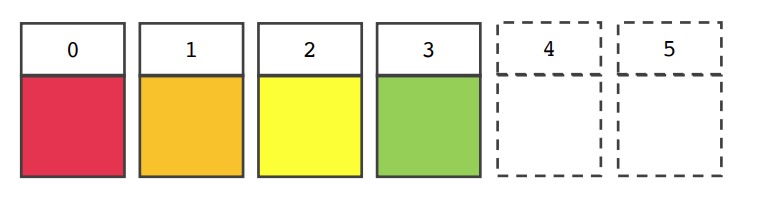 - 6개의 고정된 크기의 배열을 선언
- 6개의 고정된 크기의 배열을 선언
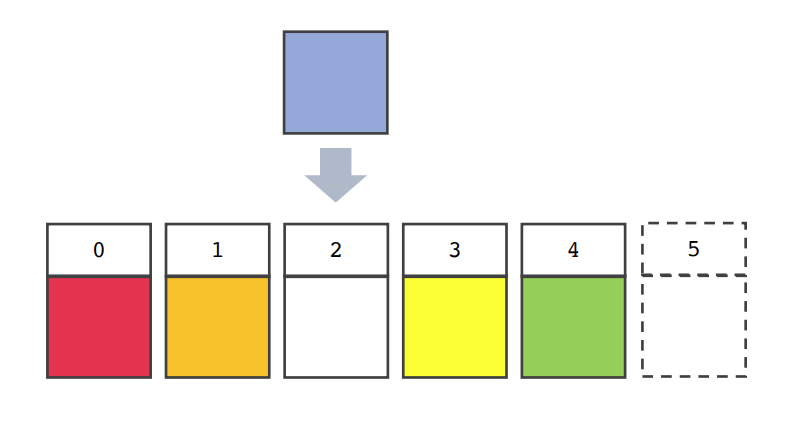 - 2번째 인덱스에 있는 데이터를 뒤로 한칸씩 미뤄주기
- 2번째 인덱스에 있는 데이터를 뒤로 한칸씩 미뤄주기
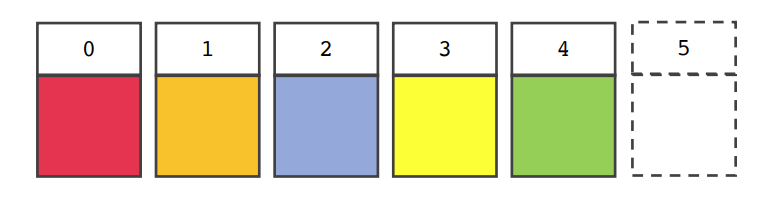 - 2번째 인덱스에 데이터 삽입
- 2번째 인덱스에 데이터 삽입
- 특징
- 삽입하고자 하는 인덱스의 위치로부터 데이터가 위치한 제일 뒤에 인덱스까지 한 칸 씩 뒤로 미뤄야 함
- 미루지 않고 데이터를 삽입시 기존 데이터 삭제됨
- 삭제
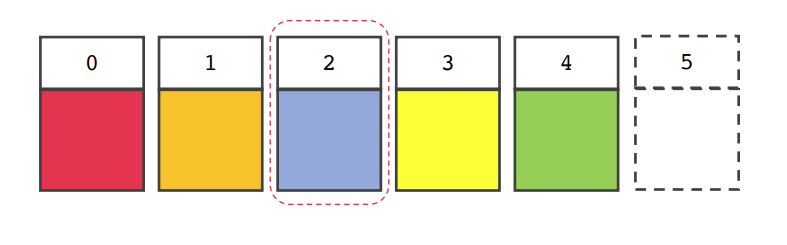 - 2번째 인덱스 데이터를 삭제하고자 할 때
- 2번째 인덱스 데이터를 삭제하고자 할 때
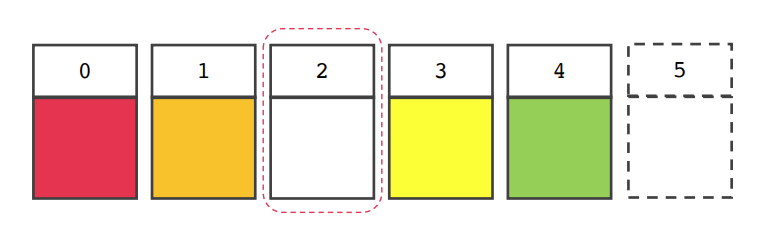 - 데이터를 삭제 후 그 앞으로 땡겨주는 작업 필요
- 데이터를 삭제 후 그 앞으로 땡겨주는 작업 필요
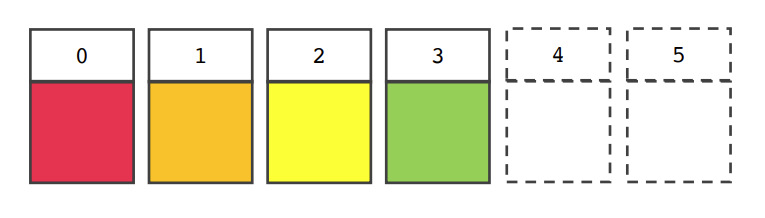 - 그림처럼 리스트에 빈공간이 없게 데이터를 앞으로 땡겨오는 작업 필요
- 그림처럼 리스트에 빈공간이 없게 데이터를 앞으로 땡겨오는 작업 필요
- 특징
- 삭제 후 데이터를 그냥 둔 다면 중간에 데이터가 뻥 뚫린 상태가 되기 때문에 앞으로 한칸씩 이동시켜야 함
- 삭제하고자 하는 인덱스의 위치로부터 뒤에 있는 데이터가 많아지면 많아질수록 처리 시간은 증가
- 탐색
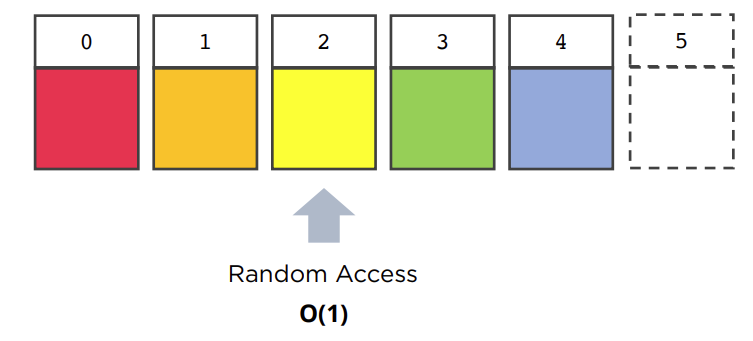 -
-
- 특징
- Random Access로 해당 위치에 다이렉트로 접근 가능 ⇒ 한번에 접근 가능
장단점
- 장점
- 인덱스를 통한 직접접근이 가능하므로 매우 빠르고 구현이 쉬움
- 단점
- 삽입 / 삭제 시 데이터가 이동해야 함 ⇒ 데이터 양이 많은 경우 부담
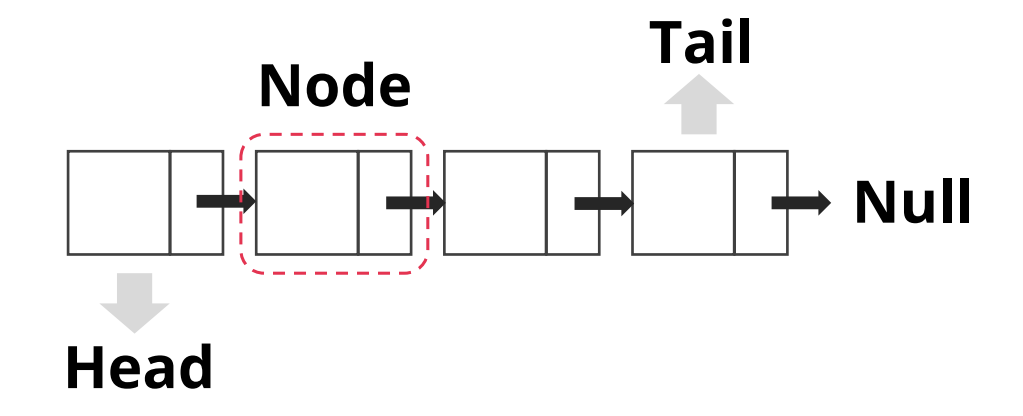
LinkedList
특징
- Node라는 객체로 구성되어 있음 ⇒ 데이터를 저장할 수 있는 필드, 다음 노드의 주소를 가지고 있는 필드
- 위 Node들이 연결되어 있는 형태를 LinkedList라고 함
- 가장 앞에 위치한 노드를 Head라고 부르고 가장 끝에 위치한것을 Tail이라고 함
- Tail의 next point는 null을 가리킨다
기능
- 추가
 -
-
 -
-
- 특징
- Head에서 부터 Tail까지 찾아간 뒤 Null을 가리키고 있는 Node를 찾아 데이터를 추가
- 탐색
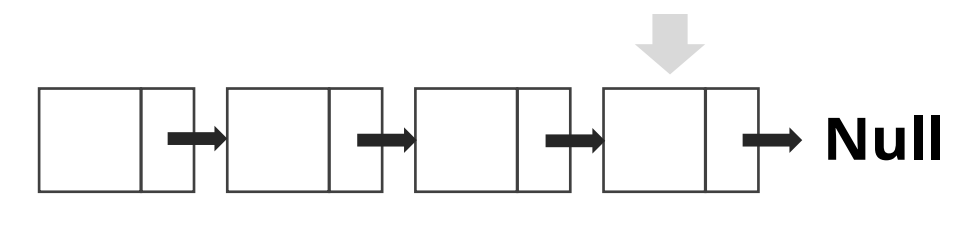 -
-
- 특징
- Array처럼 index를 통한 Random Accessr 불가능
- 자신을 가리키고있는 next point를 통해서 탐색 가능 즉 우리가 찾아가야하는 Node까지 Head에서 부터 하나씩 찾아가야 함
- 삽입
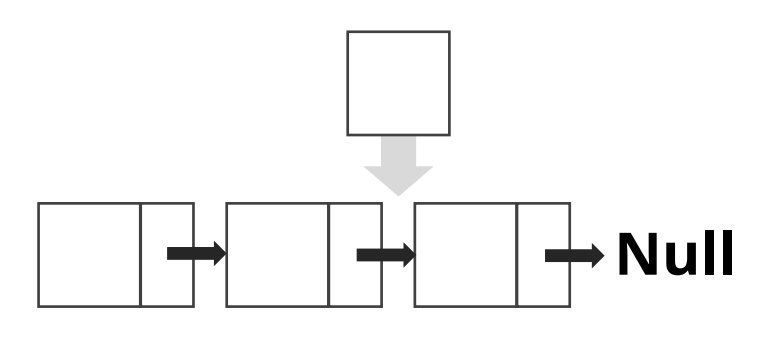 - 넣고자 하는 데이터를 기준으로
- 넣고자 하는 데이터를 기준으로
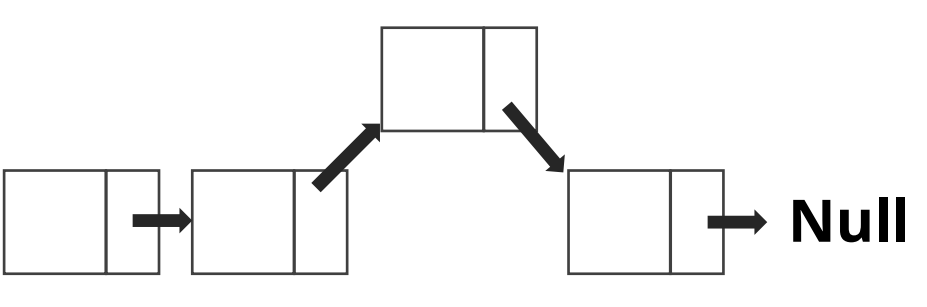 - next와 tail만 데이트에 연결해주면 된다
- next와 tail만 데이트에 연결해주면 된다
- 특징
- prev Node의 포인터를 자신을 가리키게 한 후 자신의 포인터는 prev Node가 가지고 있는 next 포인터로 연결함
- 제일 처음 위치에 데이터를 삽입하려고 하면 Array보다 더 나은 성능 가질 수 있음
- 삭제
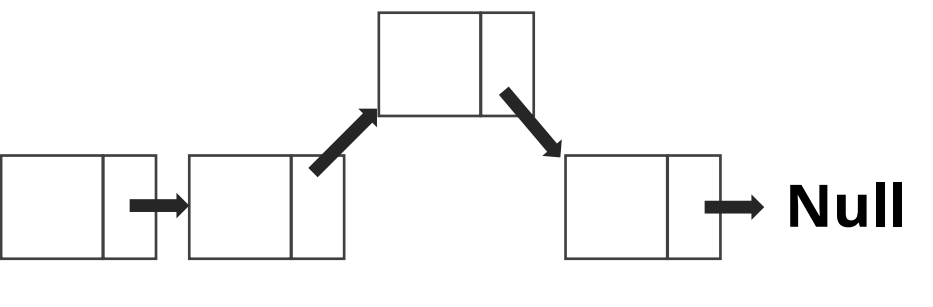 - 삭제하고자 하는 노드를 기준으로
- 삭제하고자 하는 노드를 기준으로
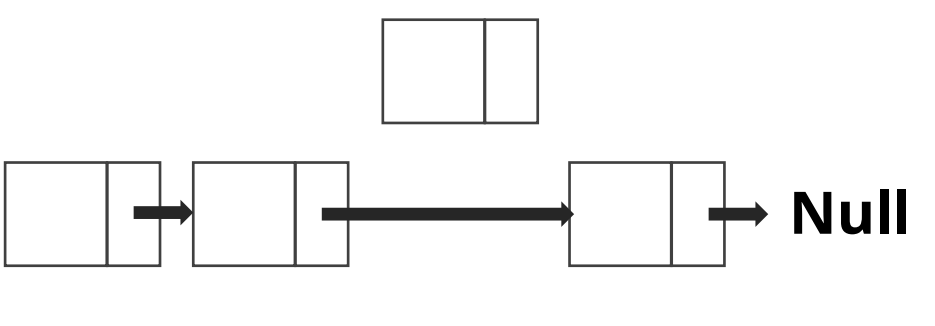 - 연결을 끊으면 됨
- 연결을 끊으면 됨
- 특징
- 삭제 하고자 하는 노드를 기준으로 prev 노드가 기준의 next 노드를 가리키게 함 또한 삭제 하고자 하는 노드의 next는 null로 표시
- Head, Tail 노드를 제외한 나머지 노드를 삭제할 때에는 탐색을 통해 해당 노드까지 찾아가야 함
장단점
- 장점
- 배열처럼 크기를 정하지 않아도 되기 때문에 데이터 추가, 삭제가 자유로움
- 배열의 복사나 재할당없이 데이터 추가 가능
- 단점
js 코드로 구현한 LinkedList
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.size = 0;
}
push(value) {
const newNode = new Node(value);
if (this.tail) this.tail.next = newNode;
else this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
this.size++;
}
insertAt(index, value) {
if (index < 0 || index > this.size) throw new RangeError('index out of range');
const newNode = new Node(value);
if (index === 0) {
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head = newNode;
if (!this.tail) this.tail = newNode;
} else {
let current = this.head;
let previous = null;
for (let i = 0; i < index; i++) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
newNode.next = current;
previous.next = newNode;
if (!newNode.next) this.tail = newNode;
}
this.size++;
}
pop() {
if (!this.head) return undefined;
let current = this.head;
let previous = null;
while (current.next) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
if (previous) {
previous.next = null;
this.tail = previous;
} else {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
this.size--;
}
removeAt(index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= this.size) throw new RangeError('index out of range');
let removedNode;
if (index === 0) {
removedNode = this.head;
this.head = this.head.next;
if (!this.head) this.tail = null;
} else {
let current = this.head;
let previous = null;
for (let i = 0; i < index; i++) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
removedNode = current;
previous.next = current.next;
if (!previous.next) this.tail = previous;
}
this.size--;
}
find(value) {
let current = this.head;
while (current) {
if (current.value === value) return current;
current = current.next;
}
return null;
}
getSize() {
return this.size;
}
}
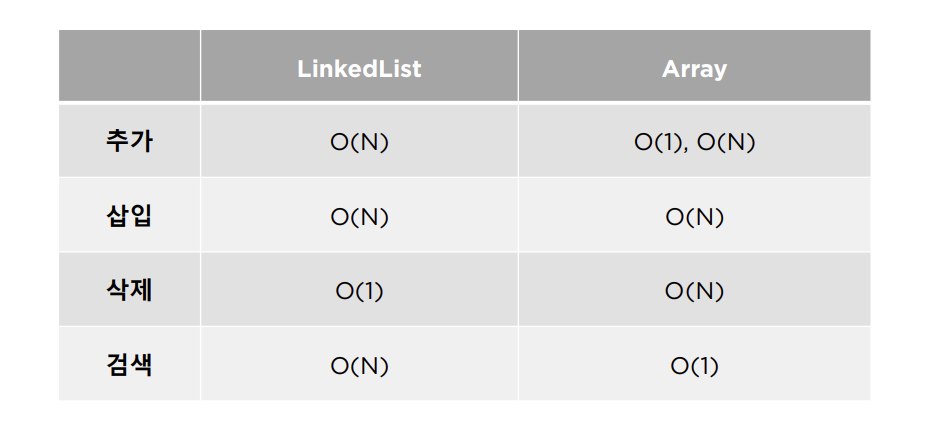
ArrayList VS LinkedList
- LinkedList는 삽입/삭제가 빠르지만, 데이터 접근에 대한 시간이 느림
- ArrayList는 데이터 접근 시간이 빠름
- 따라서, 데이터 삽입/삭제가 빈번하지 않은 경우 ArrayList가 유리하며, 이와 반대의 경우 LinkedList가 유리함
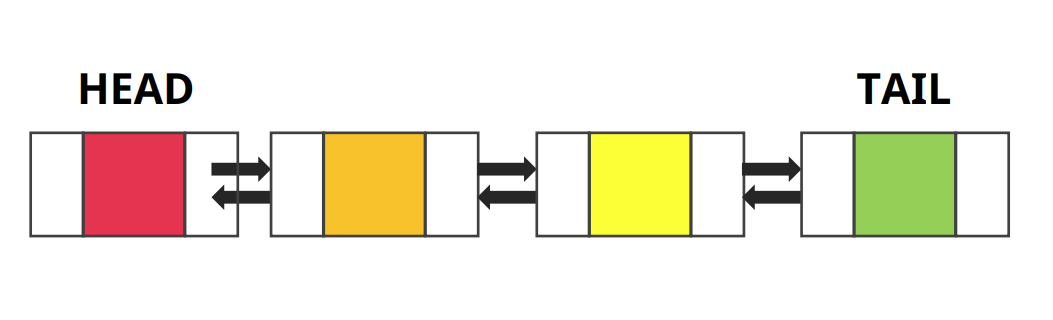
Doubly Linked List
특징
- 노드와 노드가 양방향으로 연결되어 있음
- 데이터를 탐색할 때
LinkedList 보다 ½ 이다
기능
- 추가
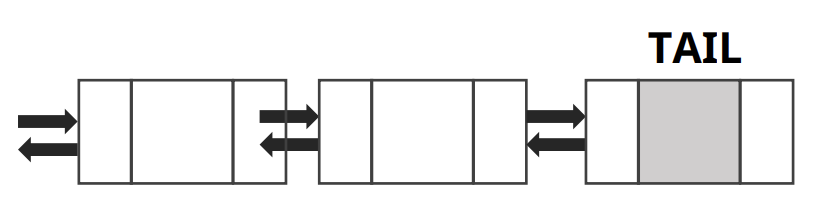 -
-
 - Tail 더미 노드의 바로 앞 노드의 데이터 추가
- Tail 더미 노드의 바로 앞 노드의 데이터 추가
- 특징
- List에 데이터가 100개가 들어있든 100개가 들어있든 Tail만 찾으면 되기 때문에 시간복잡도는 O(1)
- 탐색
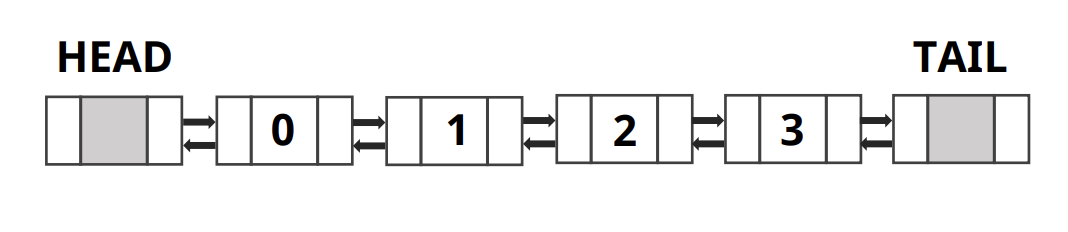 - 4개의 데이터가 있는 Doubly Linked List 리스트
- 4개의 데이터가 있는 Doubly Linked List 리스트
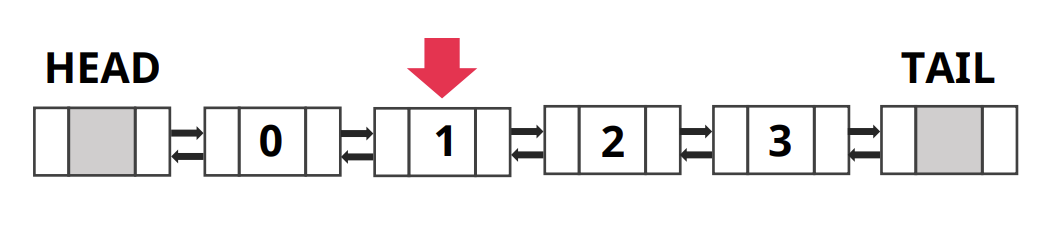 - 1번째 인덱스 데이터를 찾으려고 한다면
- 1번째 인덱스 데이터를 찾으려고 한다면
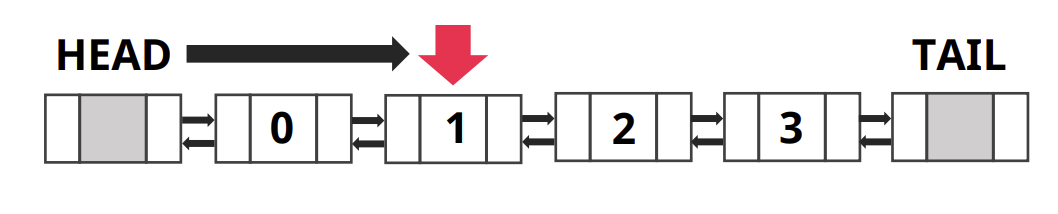 - 헤드부터 데이터 탐색하여 데이터 찾기
- 헤드부터 데이터 탐색하여 데이터 찾기
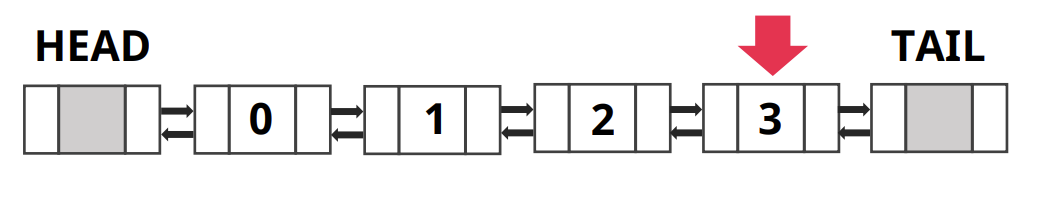 - 3번째 인덱스 데이터를 찾으려고 한다면
- 3번째 인덱스 데이터를 찾으려고 한다면
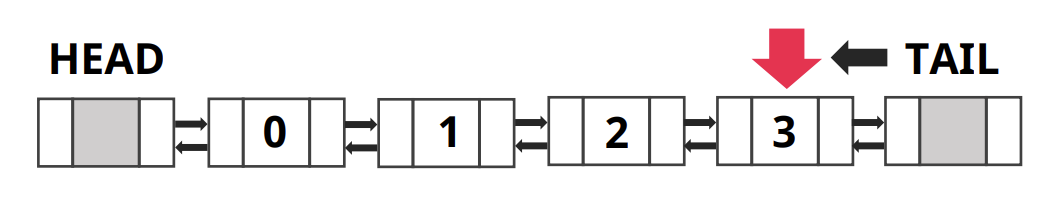 - 테일부터 데이터 탐색하여 데이터 찾기
- 테일부터 데이터 탐색하여 데이터 찾기
- 특징
- 데이터를 탐색할 때 Head에서 가까우면 Head에서부터 탐색하고 Tail에서 가까우면 Tail에서부터 탐색을 시작
- LinkedList의 비해 탐색 할 때의 시간복잡도는 O(n)으로 같지만 실제 연산 속도는 절반정도 소요됨
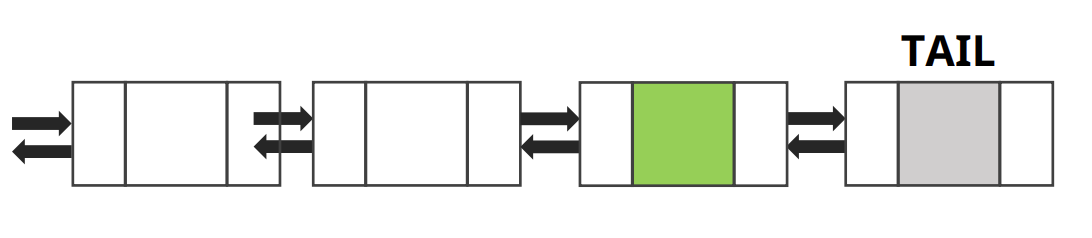
- 삽입
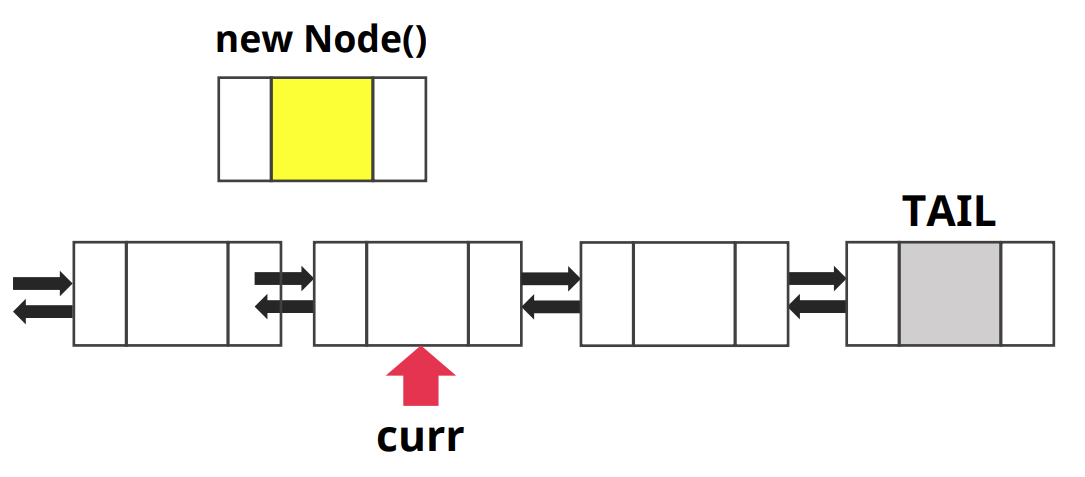 - 삽입 하고자 하는 노드 생성
- 삽입 하고자 하는 노드 생성
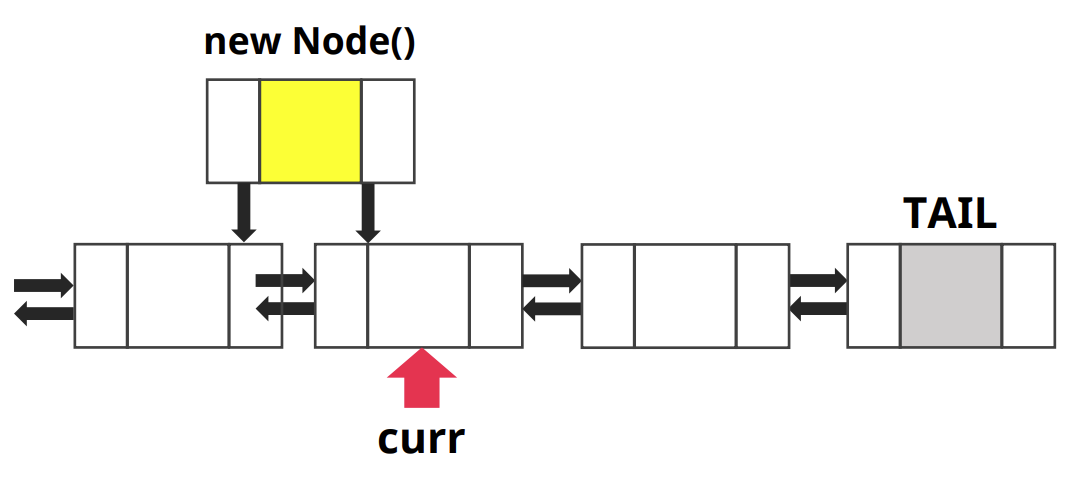 - new node의 prev는 curr가 가리키고 있는 위치의 노드의 이전노드로 가지고
- new node의 prev는 curr가 가리키고 있는 위치의 노드의 이전노드로 가지고
new node의 next는 현재 curr 노드를 가진다
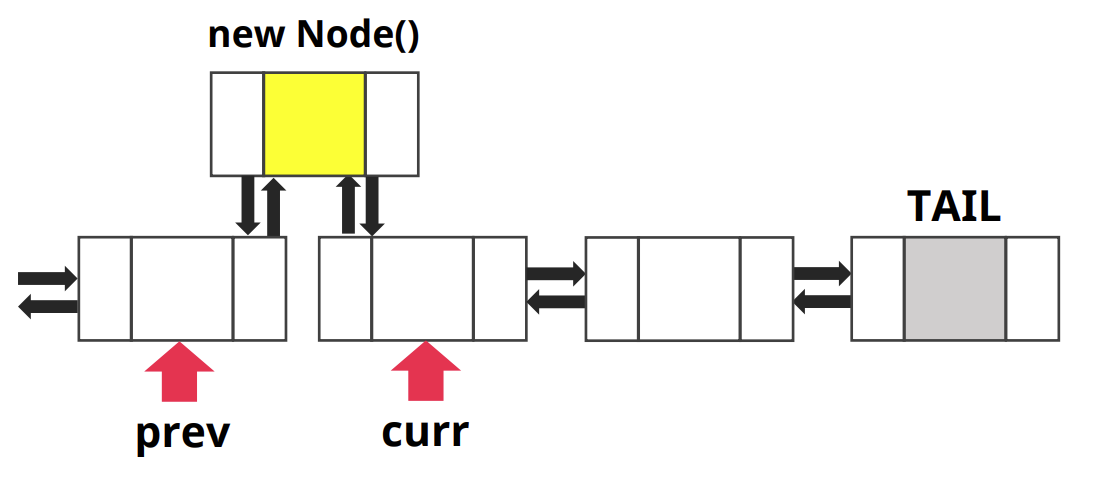 - curr의 포인터 정리
- curr의 포인터 정리
prev next = new node, curr prev = new node
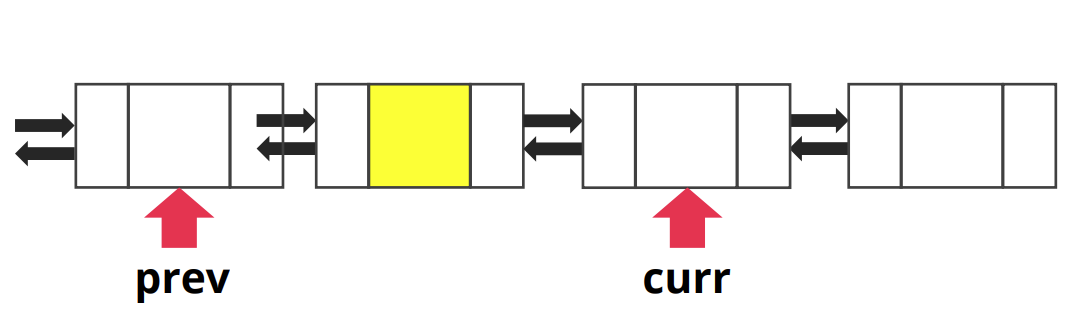 -
-
- 특징
- node끼리 잘 연결해야 함. 연결 실패시 데이터 날아감
- 삭제
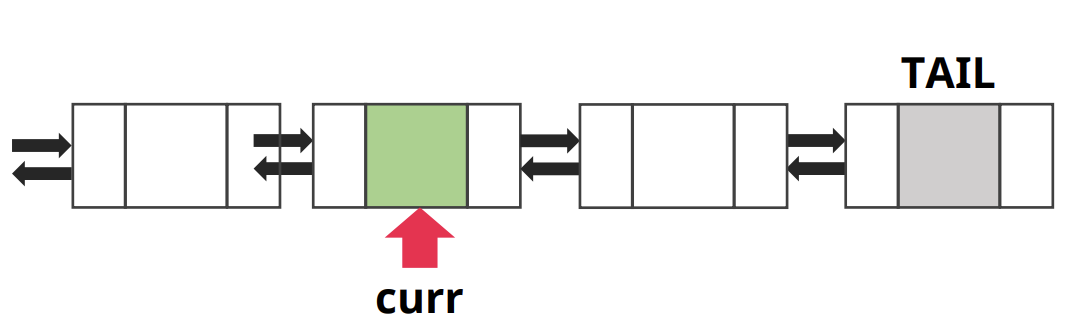 - 삭제 하고자 할 노드
- 삭제 하고자 할 노드
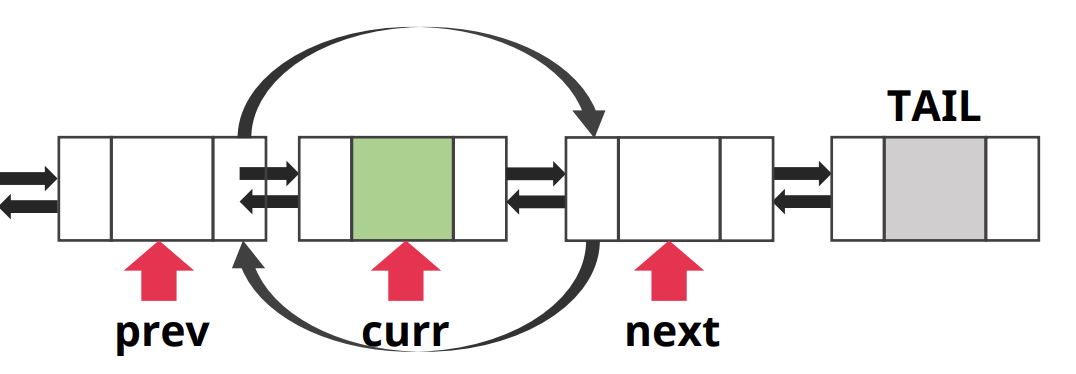 - 삭제할 curr을 기준으로 curr의 prev와 next를 연결해주는 작업
- 삭제할 curr을 기준으로 curr의 prev와 next를 연결해주는 작업
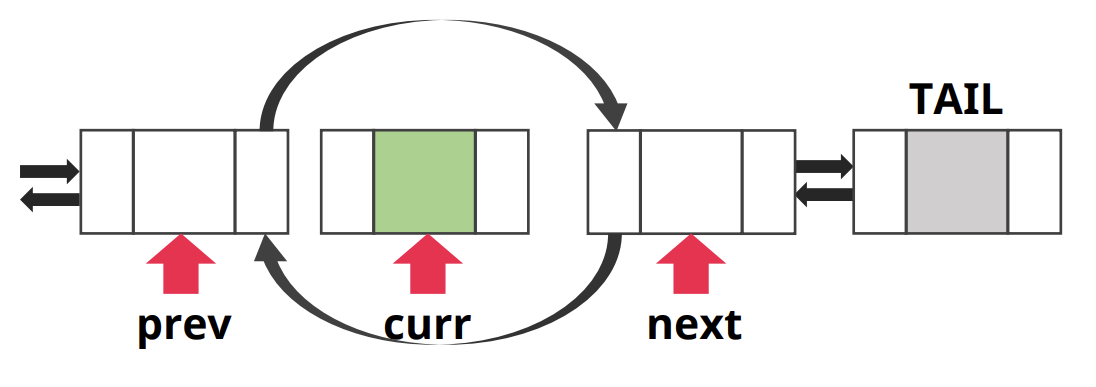 - prev, next 포인터 정리
- prev, next 포인터 정리
prev next = next, next prev = prev
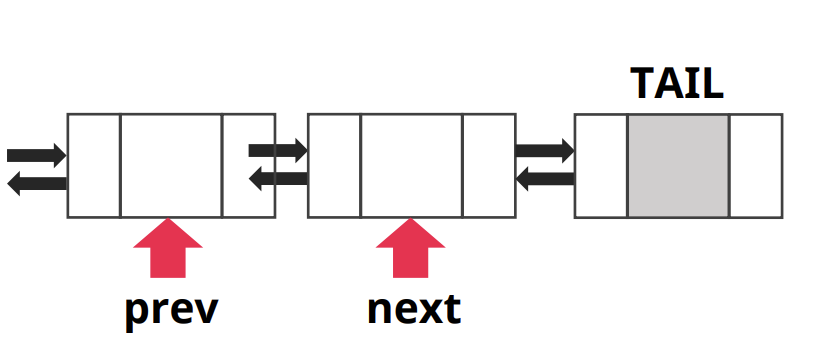 -
-
- 특징
- node끼리 잘 연결해야 함. 연결 실패시 데이터 날아감
js 코드로 구현한 Doubly Linked List
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
}
class DoublyLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.size = 0;
}
push(value) {
const newNode = new Node(value);
if (this.tail) {
this.tail.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = this.tail;
} else this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
this.size++;
}
insertAt(index, value) {
if (index < 0 || index > this.size) throw new RangeError("index out of range");
if (index === this.size) return this.push(value);
const newNode = new Node(value);
if (index === 0) {
if (this.head) {
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head.prev = newNode;
} else this.tail = newNode;
this.head = newNode;
} else {
let current = this.head;
for (let i = 0; i < index; i++) {
current = current.next;
}
newNode.next = current;
newNode.prev = current.prev;
current.prev.next = newNode;
current.prev = newNode;
}
this.size++;
}
pop() {
if (!this.tail) return undefined;
this.tail = this.tail.prev;
if (this.tail) this.tail.next = null;
else this.head = null;
this.size--;
}
removeAt(index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= this.size) throw new RangeError("index out of range");
if (index === this.size - 1) return this.pop();
let removedNode;
if (index === 0) {
removedNode = this.head;
this.head = this.head.next;
if (this.head) this.head.prev = null;
else this.tail = null;
} else {
let current = this.head;
for (let i = 0; i < index; i++) {
current = current.next;
}
removedNode = current;
current.prev.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = current.prev;
}
this.size--;
}
find(value) {
let current = this.head;
while (current) {
if (current.value === value) return current;
current = current.next;
}
return null;
}
getSize() {
return this.size;
}
}
 ArrayList와 LinkedList 비교
ArrayList와 LinkedList 비교
 - 6개의 고정된 크기의 배열을 선언
- 6개의 고정된 크기의 배열을 선언
 - 이전에 있던 데이터 바로 뒤에 데이터 삽입
- 이전에 있던 데이터 바로 뒤에 데이터 삽입
 - 6개의 고정된 크기의 배열을 선언
- 6개의 고정된 크기의 배열을 선언
 - 2번째 인덱스에 있는 데이터를 뒤로 한칸씩 미뤄주기
- 2번째 인덱스에 있는 데이터를 뒤로 한칸씩 미뤄주기
 - 2번째 인덱스에 데이터 삽입
- 2번째 인덱스에 데이터 삽입
 - 2번째 인덱스 데이터를 삭제하고자 할 때
- 2번째 인덱스 데이터를 삭제하고자 할 때
 - 데이터를 삭제 후 그 앞으로 땡겨주는 작업 필요
- 데이터를 삭제 후 그 앞으로 땡겨주는 작업 필요
 - 그림처럼 리스트에 빈공간이 없게 데이터를 앞으로 땡겨오는 작업 필요
- 그림처럼 리스트에 빈공간이 없게 데이터를 앞으로 땡겨오는 작업 필요
 -
-
 -
-
 -
-
 -
-
 - 넣고자 하는 데이터를 기준으로
- 넣고자 하는 데이터를 기준으로
 - next와 tail만 데이트에 연결해주면 된다
- next와 tail만 데이트에 연결해주면 된다
 - 삭제하고자 하는 노드를 기준으로
- 삭제하고자 하는 노드를 기준으로
 - 연결을 끊으면 됨
- 연결을 끊으면 됨
 -
-
 - Tail 더미 노드의 바로 앞 노드의 데이터 추가
- Tail 더미 노드의 바로 앞 노드의 데이터 추가
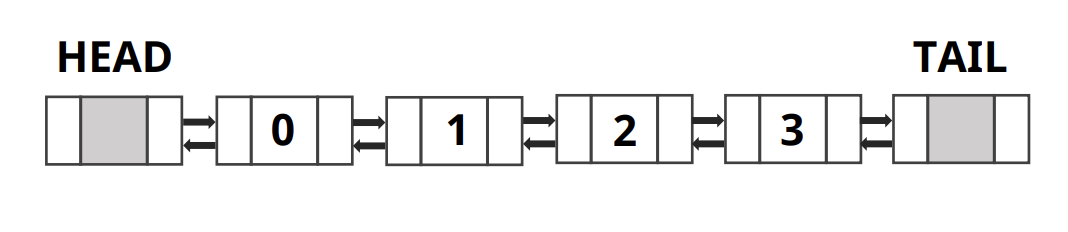 - 4개의 데이터가 있는 Doubly Linked List 리스트
- 4개의 데이터가 있는 Doubly Linked List 리스트
 - 1번째 인덱스 데이터를 찾으려고 한다면
- 1번째 인덱스 데이터를 찾으려고 한다면
 - 헤드부터 데이터 탐색하여 데이터 찾기
- 헤드부터 데이터 탐색하여 데이터 찾기
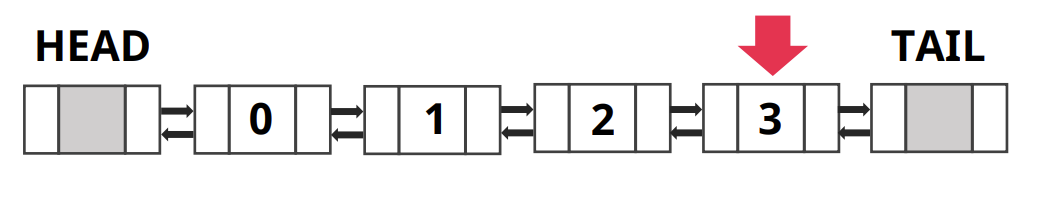 - 3번째 인덱스 데이터를 찾으려고 한다면
- 3번째 인덱스 데이터를 찾으려고 한다면
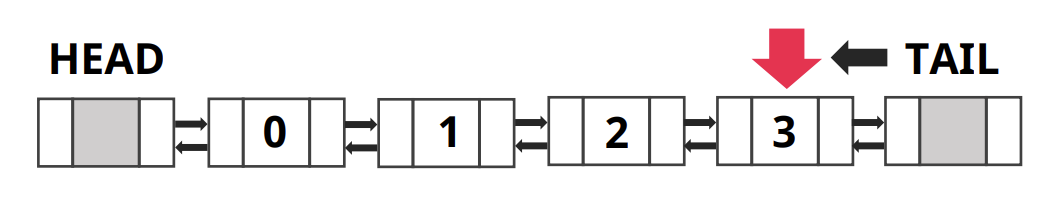 - 테일부터 데이터 탐색하여 데이터 찾기
- 테일부터 데이터 탐색하여 데이터 찾기
 - 삽입 하고자 하는 노드 생성
- 삽입 하고자 하는 노드 생성
 - new node의 prev는 curr가 가리키고 있는 위치의 노드의 이전노드로 가지고
- new node의 prev는 curr가 가리키고 있는 위치의 노드의 이전노드로 가지고 - curr의 포인터 정리
- curr의 포인터 정리 -
-
 - 삭제 하고자 할 노드
- 삭제 하고자 할 노드
 - 삭제할 curr을 기준으로 curr의 prev와 next를 연결해주는 작업
- 삭제할 curr을 기준으로 curr의 prev와 next를 연결해주는 작업
 - prev, next 포인터 정리
- prev, next 포인터 정리 -
-
