JAVA의 제어문
- 프로그램의 흐름 변경 (+ 특정 조건)
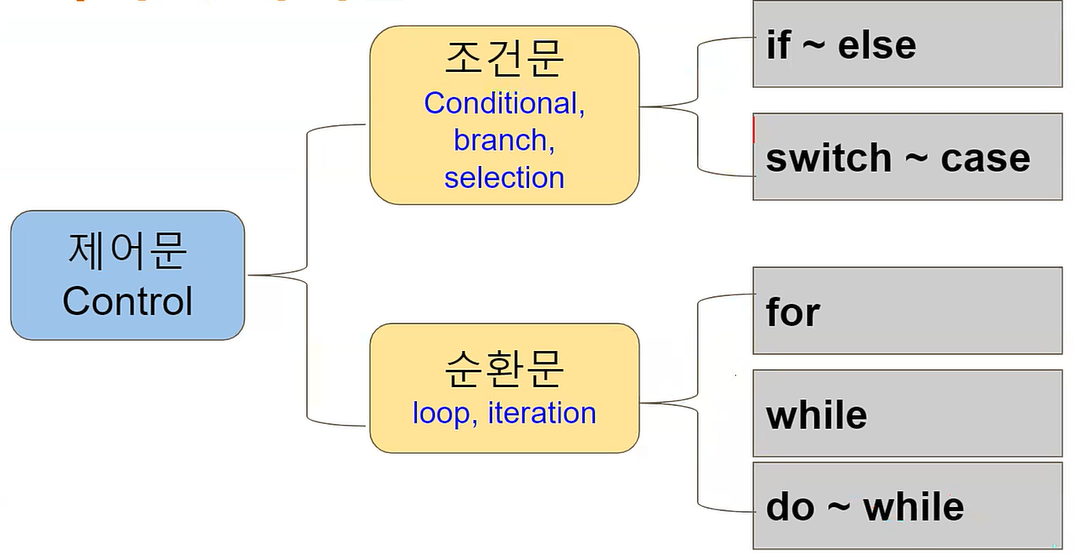
순환문(loop)
- for
- while
- do ~ while // 현재 프로그래밍 언어에서는 잘 사용하지 않음
- 순환문을 작성시 내가 만드는 순환문에 대해 다음을 확실하게 인지하고 작성해야 한다.
- 몇번 순환하는가?
- 순환중에 사용된 인덱스값의 시작값과 끝값은?
- 순환문이 끝난뒤 인덱스값은?
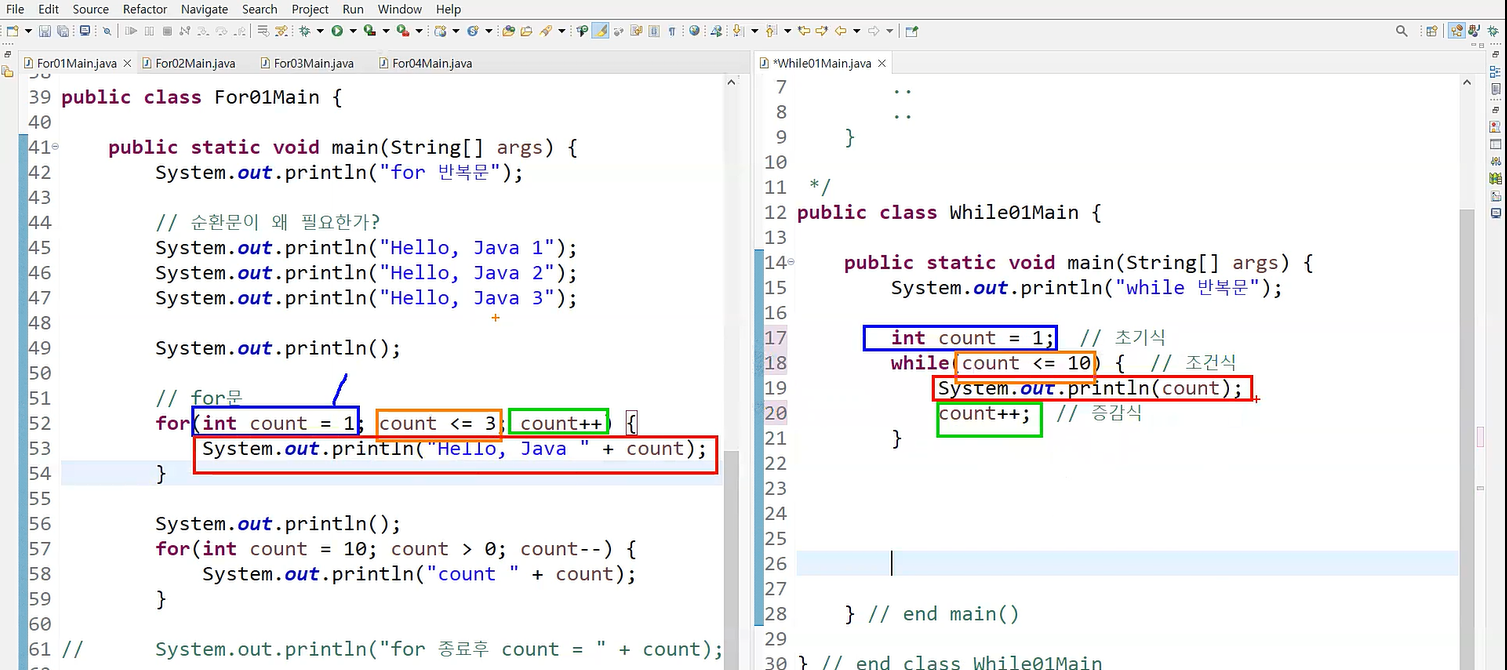
1. for문
- for 순환문 구문
for(①초기식; ②조건식; ④증감식){
③수행문;
..
}
①초기식 : 최초에 단한번 수행
②조건식 : true / false 결과값
-> 위 조건식의 결과가 false 이면 for문 종료
③수행문 : 위 조건식이 true 이면 수행
④증감식 : 수행문이 끝나면 증감식 수행
증감식이 끝나면 다시 ②조건식 으로..- 예시
for(int i = 2; i<10; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j<10; j++) {
System.out.print(i*j+" ");
}
System.out.println("");
}

for문 작성시 TIP
1) n번 순환 하는 경우 (즉 횟수가 촛점인 경우)
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){ .. }
2) a ~ b 까지 순환하는 경우 (즉 시작값과 끝값이 중요한 경우)
for(int i = a; i <= b; i++){ .. }
public class For01Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("for 반복문");
// 순환문이 왜 필요한가?
System.out.println("Hello, Java 1");
System.out.println("Hello, Java 2");
System.out.println("Hello, Java 3");
System.out.println();
// for문
for(int count = 1; count <= 3; count++) {
System.out.println("Hello, Java " + count);
}
System.out.println();
for(int count = 10; count > 0; count--) {
System.out.println("count " + count);
}
// System.out.println("for 종료후 count = " + count); // for{} 블럭의 local 에서 선언된 변수라 for{}가 끝나면 소멸된다.
// 초기식과 증감식에 식을 여러개 사용 가능.
int i, j;
for(i = 0, j = 10; i < j; i++, j-=2) {
System.out.println("i:" + i);
}
System.out.println("for 종료후 i: " + i + " j :" + j);
} // end main()
} // end class For01Main[연습1 : 구구단 출력]
package com.lec.java.for02;
public class For02Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("For문 - 구구단 출력");
// 구구단 2단
// 2 x 1 = 2
// 2 x 2 = 4
// 2 x 3 = 6
// 2 x 4 = 8
// 2 x 5 = 10
// 2 x 6 = 12
// 2 x 7 = 14
// 2 x 8 = 16
// 2 x 9 = 18
System.out.println("구구단 2단");
for(int i=1; i < 10 ; i++) {
System.out.println("2 x " + i + " = " + (2 * i));
}
} // end main()
} // end class For02Main[연습2 : 1 ~ 10 수 중에서 짝수(2의 배수)만 출력]
package com.lec.java.for03;
public class For03Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("for 연습");
// 1 ~ 10 수 중에서 짝수(2의 배수)만 출력
for(int i = 1; i <=10; i++) {
if(i % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
System.out.println("\n다른 방법");
for(int i = 2; i < =10; i += 2) {
System.out.println(i);
}
} // end main()
} // end class For03Main[연습3 : 1 ~ 100 수 중에서 2와 7의 공배수만 출력 / 1부터 n 가지의 합을 계산]
package com.lec.java.for04;
public class For04Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("for문 연습");
// 1 ~ 100 수 중에서 2와 7의 공배수만 출력
// 2와 7의 공배수: 2의 배수 && 7의 배수
System.out.println("\n2와 7의 공배수 출력");
// 1) 1 ~ 100 수를 모두 출력 (for문 이용)
// 2) 조건에 맞는 경우만 출력을 하도록 수정 (if문)
for(int i=1 ; i <= 100; i++) {
if((i % 2 == 0) && (i % 7 == 0)) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
// 1부터 n 가지의 합을 계산
int n = 1000;
System.out.printf("\n1 부터 %d까지의 합\n", n);
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
sum+= i; // 누적 합산
}
System.out.println("sum = " + sum);
} // end main ()
} // end class For04Main2. while문
- 조건식이 true 인 동안 while 블럭 반복
while(조건식 true / false) {
..
..
}
package com.lec.java.while01;
public class While01Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("while 반복문");
int count = 1; // 초기식
while(count <= 10) { // 조건식
System.out.println(count);
count++; //증감식
}
} // end main()
} // end class While01Main
[연습1 : 구구단 출력]
package com.lec.java.while02;
public class While02Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("while 연습");
// 구구단 2단
// 2 x 1 = 2
// 2 x 2 = 4
// 2 x 3 = 6
// 2 x 4 = 8
// 2 x 5 = 10
// 2 x 6 = 12
// 2 x 7 = 14
// 2 x 8 = 16
// 2 x 9 = 18
int i = 1;
while (i <= 9) {
System.out.println("2 x " + i + " = " + (2 * i));
i++;
}
} // end main()
} // end class While02Main3. for문과 while문의 호환

[예시]
4. 자주하는 실수
- 제어문 뒤에 ';' 붙이지 않기
package com.lec.java.while03;
public class While03Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("while 연습");
int n = 34;
if(n % 1 == 0); // if, for, while 뒤에 ; 붙이지 마세요
System.out.println("홀수입니다");
System.out.println("프로그램 종료");
} // end main()
} // end class While03Main5. break
순환문(for, while, do~while) 안에서 break를 만나면 break를 감싸는 가장 가까운 순환문 종료

public class Loop01Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Break");
int num = 1;
while(num <= 10) {
System.out.println(num);
if(num == 3) {
break;
}
num++;
}
System.out.println("while 끝난후 num = " + num);
System.out.println();
// 2와 7의 최소공배수를 출력
// 최소공배수: 공배수 중에서 가장 작은 수
// TODO
System.out.println();
System.out.println("무한 루프와 break;");
num = 1;
while(true) {
System.out.println(num);
num++;
if(num == 5) break; // 무한루프 종료 조건
}
System.out.println();
// 2단은 x 2 까지 출력
// 3단은 x 3 까지 출력
// TODO
System.out.println("\n프로그램 종료");
} // end main()
} // end class[연습문제1]
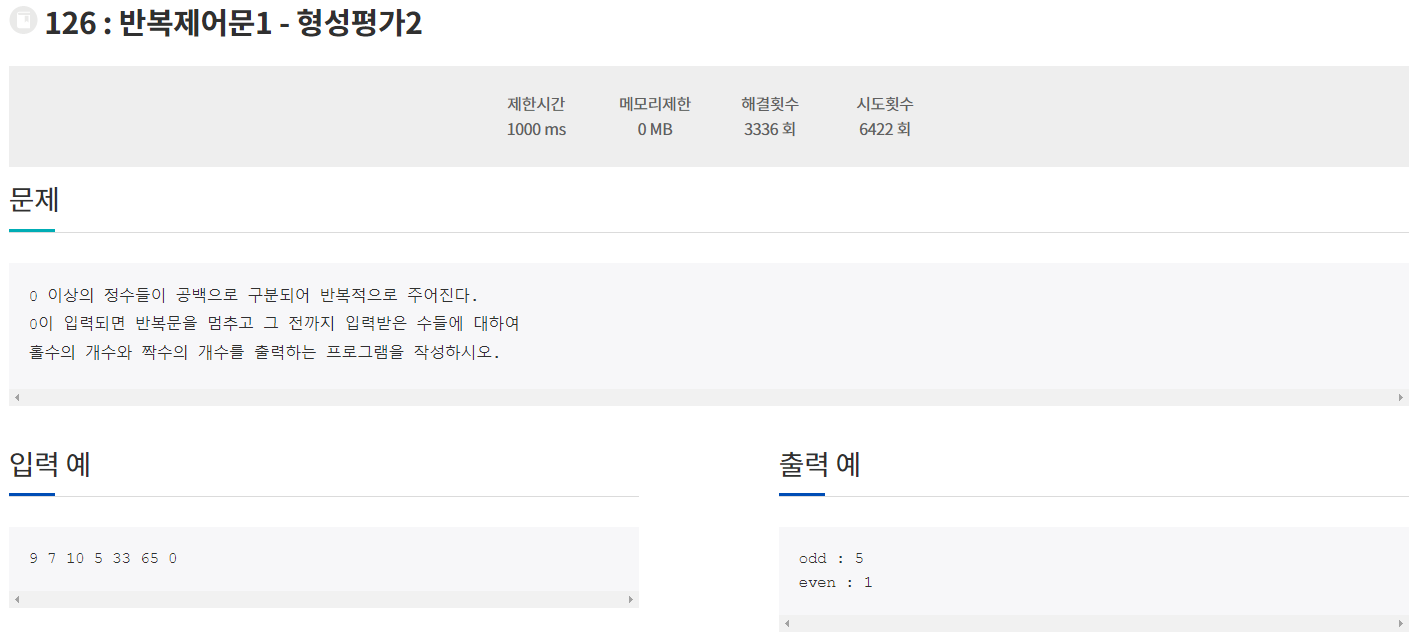
package 반복제어문1.형성평가02;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int i;
int cntOdd = 0;
int cntEven = 0;
while(true) {
i = sc.nextInt();
if(i == 0) break; // 종료조건
if(i % 2 == 0) cntEven++;
else cntOdd++;
}
sc.close();
System.out.println("odd : " +cntOdd);
System.out.println("even : "+cntEven);
}
}[연습문제2]
package com.lec.java.loop03;
public class Loop03Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("중첩 for 문 nested for");
// 2 x 1 = 2
// ..
// 2 x 9 = 18
// 3 x 1 = 3
// ..
// 3 x 9 = 27
// ...
// 9 x 1 = 9
// ..
// 9 x 9 = 81
// 구구단 출력 : 중첩 for 사용
// 2단 ~ 9단
for(int dan = 2; dan <= 9; dan++) {
System.out.println(dan + "단");
// x 1 ~ x 9
for(int mul = 1; mul <= 9; mul++) {
System.out.println(dan + " x " + mul + " = " + (dan * mul));
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
// 구구단 출력 : 중첩 while 문 사용
int dan = 2;
while (dan < 10) {
System.out.println("구구단 " + dan + "단");
int mul = 1;
while (mul <9) {
System.out.println(dan + " x " + mul + " = " + (dan * mul));
mul++;
} // end while (n)
System.out.println();
dan++;
} // end while (dan)
System.out.println("\n프로그램 종료");
} // end main()
} // end class
[연습문제3]

package 반복제어문3.자가진단02;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
sc.close();
}
}
[연습문제4]


package practice.game369;
public class Game369Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// // 방법1
// {
// System.out.println("1의 자리와 10의 자리만 확인");
// int number = 100;
//
// int i = 1;
// while(i <= number) {
//
// int d1 = i % 10; // 일의 자리 숫자
// int d10 = i / 10; // 십의 자리 숫자
//
// if(d1 == 3 || d1 == 6 || d1 == 9
// || d10 == 3 || d10 == 6 || d10 == 9) {
// System.out.printf("%4s", "*");
// } else {
// System.out.printf("%4d", i);
// }
//
// if(i % 10 == 0) System.out.println();
//
// i++;
// }
// }
//
// 방법2: 임의 숫자까지 369 만들기
{
System.out.println("자릿수를 하나씩 깍아 내려오면서 3의 배수가 있는지 확인");
int number = 1000;
int i = 1;
while(i <= number) {
int k = i;
while(k > 0) {
int d1 = k % 10;
if(d1 == 3 || d1 == 6 || d1 == 9) {
System.out.printf("%5s", "*");
break;
}
k /= 10; // 한자리씩 깍아와
}
if(k == 0) { // 모든 자릿수를 다 깍아내었는데도 3, 6, 9를 발견 못하면 출력
System.out.printf("%5d", i);
}
if(i % 10 == 0) System.out.println();
i++;
}
}
}
}🎇Tips!
- 동일한 변수 하이라이트 선택 & 변경
- 단축키 : alt + shift + r
- 마우스 오른쪽 클릭 -> Refactor -> Rename
(이클립스에서의 사각형 의미 : 지금부터 키보드로만 움직여라! 마우스 사용 X)
- 찾아바꾸기
- Find/Replae
- 단축키 : crtl + f
