문제
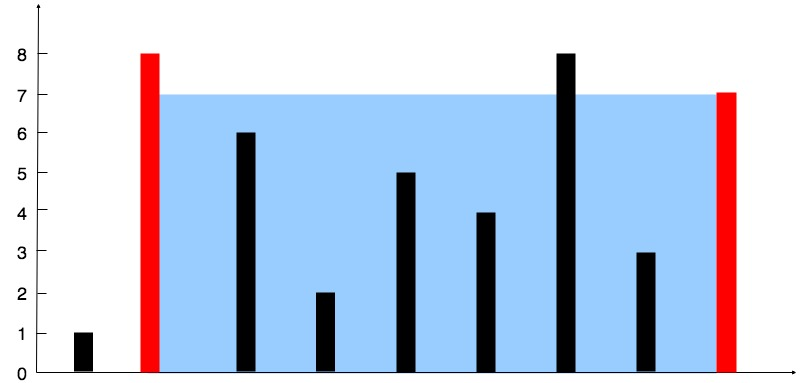
Given n non-negative integers a1, a2, ..., an , where each represents a point at coordinate (i, ai). n vertical lines are drawn such that the two endpoints of the line i is at (i, ai) and (i, 0). Find two lines, which, together with the x-axis forms a container, such that the container contains the most water.
Notice that you may not slant the container.
접근
가장 많은 물을 차지 할 수 있게 하는 두 컨테이너 바를 설치했을 때 물의 옆 쪽 면적?을 찾으면 된다. 간단하게 먼저 전체의 경우를 탐색하는 방법으로 풀어보았다.
var maxArea = function(height) {
let answer = 0;
for(let i=0; i<height.length; i++){
for(let j=i+1; j<height.length; j++){
const hei = Math.min(height[i], height[j]);
const wid = j-i;
const area = hei * wid;
if(area > answer){
answer = area;
}
}
}
return answer;
};두 개의 for문으로 모든 경우의 수의 넓이를 찾고 가장 큰 값을 저장해두었다가 리턴한다. 같은 크기(height)의 배열을 두 번 돌기 때문에 시간 복잡도는 O(N^2)이 될 것이다. 코드 제출하고 성공하지만
Runtime: 912 ms, faster than 24.54% of JavaScript online submissions for Container With Most Water.
Memory Usage: 41.7 MB, less than 11.30% of JavaScript online submissions for Container With Most Water.좀 느린 방법이다. 그래서 솔루션을 보니 Two Pointer라는 방법이 또 있다.
기본적으로 배열 양 쪽에 각각 포인터를 지정하고 하나의 조건(어떤 포인터에서의 높이가 더 높은지)를 걸고 그 조건의 결과에 따라 어떤 포인터를 가운데로 당겨 올지 정한다.
var maxArea = function(height) {
let answer = 0;
let forward = 0;
let backward = height.length-1;
while(forward < backward){
// 어떤 포인터를 당겨올지 정하는 조건
if(height[forward] < height[backward]){
answer = Math.max(height[forward] * (backward-forward), answer);
forward++;
}else{
answer = Math.max(height[backward] * (backward-forward), answer);
backward--;
}
}
return answer;
};이렇게 하면 반복문이 하나가 되므로 시간 복잡도가 O(N)이 되어 위에 내가 한 방법보다 더 효율적이다.
Runtime: 84 ms, faster than 67.90% of JavaScript online submissions for Container With Most Water.
Memory Usage: 40.8 MB, less than 11.30% of JavaScript online submissions for Container With Most Water.