복합체 패턴이란, 복합 객체(composite)와 단일 객체(Leaf)를 동일하게 취급하여 클라이언트가 이 둘을 구분하지 않고 동일한 인터페이스를 통해 사용하는 구조 패턴이다.
예를들어서, 복합 객체를 폴더, 단일 객체를 파일로 정의한파일 시스템 구조라고 생각하면된다.
이 폴더와 파일 동일한대상으로 생각하고 재귀동작을 통해 구분없이 처리하는 것을 의미한다.
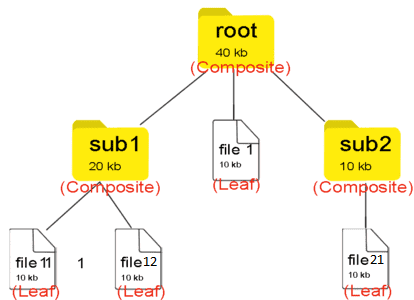
구조
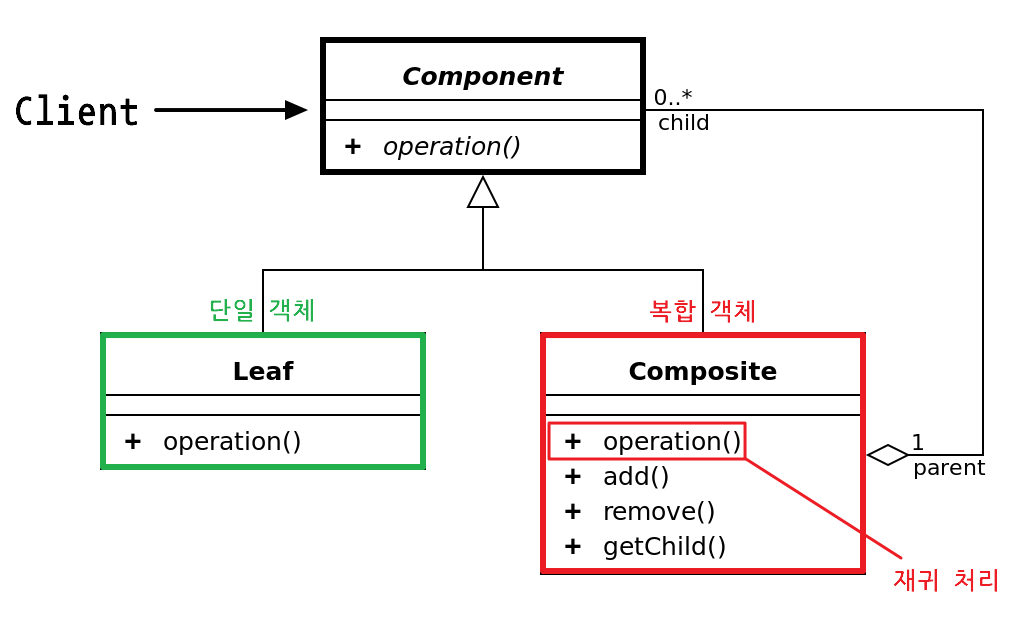
Composite는
List<Component>를 소유.
Composite와 Leaf가 동시에 구현하는(operation()) 추상 메서드를 정의하고 Composite 객체의 operation()은 하위 객체(List<Component>)를 순회하게된다.
Composite와 Leaf는 동일한 인터페이스로 구현되어있기 때문에List<Component>에 저장 가능
Leaf의 operation()은 그저 자신의 값을 호출한다.
이는 재귀 형태로 나타나기 때문에 Composite와 Leaf를 동일한 대상으로 처리할 수 있게된다.
장점
- 단일체와 복합체 관계를 묶어서 관리하기 편함
- 트리 구조를 편리하게 구성 가능
- 클라이언트는 추상화된 인터페이스만 바라보기 때문에 OCP 원칙 준수
단점
- 트리의 깊이가 깊어지면 디버깅 어려움
- 인터페이스 설계가 까다로움
예시 코드
interface Component {
void operation();
}
class Leaf implements Component {
@Override
public void operation() {
System.out.println(this + " 호출");
}
}
class Composite implements Component {
// Leaf 와 Composite 객체 모두를 저장하여 관리하는 내부 리스트
List<Component> components = new ArrayList<>();
public void add(Component c) {
components.add(c); // 리스트 추가
}
public void remove(Component c) {
components.remove(c); // 리스트 삭제
}
@Override
public void operation() {
System.out.println(this + " 호출");
// 내부 리스트를 순회하여, 단일 Leaf이면 값을 출력하고,
// 또다른 서브 복합 객체이면, 다시 그 내부를 순회하는 재귀 함수 동작이 된다.
for (Component component : components) {
component.operation(); // 자기 자신을 호출(재귀)
}
}
public List<Component> getChild() {
return components;
}
}복합객체와 단일객체를 동일한 인터페이스로 구현
복합객체 안에 단일객체를 갖는 구조에서 같은 인터페이스를 사용하여 관리
Ex. Component안에 여러 Component가 존재 -> 반복

