MVVM Architecture & LiveData, ViewModel, LifeCycle Components
📗 단어 정리 📘
OBS BUILD
| 영어 | 한글 |
|---|---|
| interacts | 통신하다, 상호작용을 하다 |
| relevant | 관련 있는 |
| populated | (데이터를) 덧붙이다 |
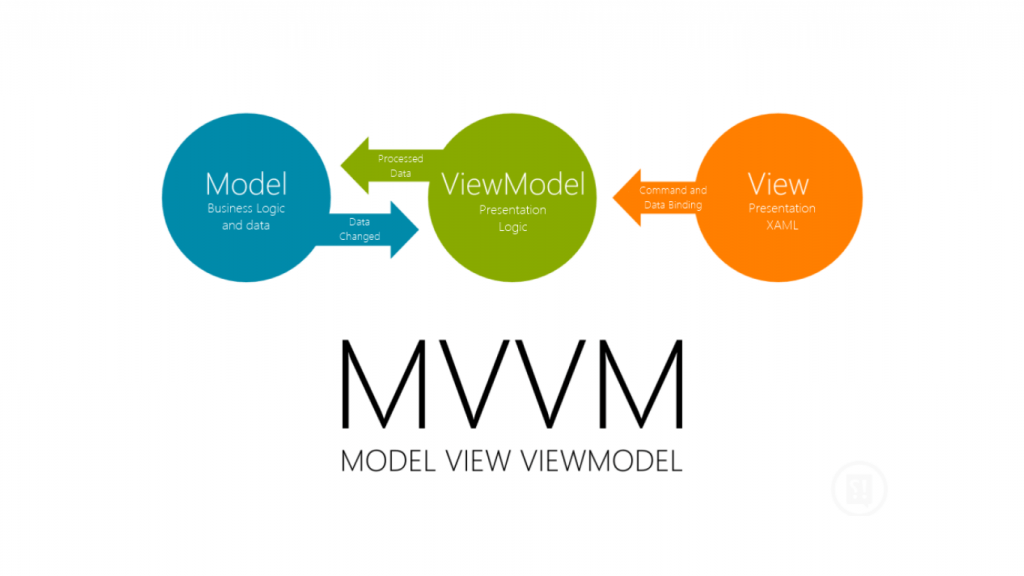
#Model-View-ViewModel
DataModel
DataModel contains the data from different sources, can be API or can be from database.
데이터모델은 다른 소스로부터 데이터를 포함합니다. api거나 다른 데이터베이스가 될 수 있습니다.
It is the Single entry point to your data. Most of the times datamodel contains API or DataBase Logic.
데이터에 단일 진입점이 있고 대부분의 경우 데이터모델들은 api나 데이터베이스 로직을 포합합니다.
DataModel fetches the data from required sources and present it to ViewModel.
데이터모델은 요구되는 소스들과 프레젠트로부터 데이터를 뷰모델에 불러옵니다.
This layer also handles business logic so that latest and required data is exposed to the ViewModel.
이 레이어는 또한 뷰모델에 최신으로 요구되는 데이터를 노출 시키기 위해서 비지니스 로직을 다룹니다.
ViewModel
This ViewModel is different from what we discussed above. This is term defined for MVVM Architecture.
이 뷰모델은 우리가 위에서 설명한 것과 다릅니다. 이건 mvvm 아키텍처 관점에서 정의되었습니다.
ViewModel interacts with Data Model by an observable and It exposes only needed data for View Layer by an observable.
뷰모델은 관찰함으로써 데이터모델에 통신하고 뷰 레이어에 대해 관찰함으로써 필요한 데이터만 노출시킵니다.
Basically ViewModel does the same job for View, what Model does for ViewModel.
기본적으로 뷰모델은 뷰에 대한 작업을 동일하게 처리합니다.
ViewModel prepares data for UI layer and keep it if needed,
Any action on UI will be handled by ViewModel and any data changes will be observed by UI in View Layer.
뷰모델은 ui레이어에 대한 데이터를 준비하고 필요하다면 유지하며 ui의 액션은 뷰모델에 의해 처리되고 변경된 데이터는 뷰레이어에 있는 ui에 의해 변경됩니다.
This helps to keep the UI and data Logic separated. ViewModel exposes only relevant and needed data to the View.
뷰모델은 ui와 데이터 로직 세분화를 유지하는걸 도와줍니다. 뷰모델은 오직 관련있고 필요한 데이터만 뷰로 노출 시킵니다.
If we need 2 properties of an object, we will fetch those 2 properties, combine them into single object and then expose for View.
만약에 2개의 객체 프로퍼티가 필요하다면 우린 2개의 하나의 객체로 결합한 두개의 프로퍼티를 불러오고 뷰에 노출 시킵니다.
View
View is the UI interface , It can be an activity, fragment or a custom view.
뷰모델은 ui 인터페이스입니다. 액티비티, 프래그먼트 혹은 커스텀 뷰가 될 수 있습니다.
ViewModel prepares data for View, Binding of ViewModel to View is done in layout XML This is called Data binding of Layout Files.
뷰모델은 뷰를 위해 레이아웃 파일에 데이터 바인딩으로 호출된 xml 레이아웃에 사용된 뷰모델 바인딩을 한 데이터를 준비합니다.
To make the XML bindable, layout tag needs to be included in the XML.
xml 바인더블을 만들기 위해서 xml에 layout 태그가 포함되는게 필요합니다.
By Default a Binding class would be generated which will have references of all views and properties.
기본적으로 바인딩클래스는 모든 뷰와 개체의 레퍼런스를 가지는게 일반적입니다.
if name of layout is activity_main, binding file would be ActivityMainBinding.
만일 레이아웃이 activity_main라면 바인딩 파일은 ActivityMainBinding이 될겁니다.
In layout XML file we can also include data object, with the help of which data can be populated to the views.
xml 레이아웃 파일에서 우린 뷰에 뷰에 데이터를 덧붙일 수 있게 도와주는 데이터 객체를 포함할 수 있습니다.
// ViewModel reference in XML
<data>
<variable
name="article"
type="com.gauravgoyal.mvvm_with_testing.service.model.Article" />
</data>
//using Viewmodel to display data
<TextView
android:id="@+id/title"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:contentDescription="@string/app_name"
android:text="@{article.title}"
android:textSize="@dimen/news_text"
android:textStyle="bold" />In the above example we have declared Article object and we are using this object to set the title in textview.
위 예제에서 우린 기사 객체를 선언했고 텍스트뷰에서 타이틀을 세팅하기위해 이 객체를 사용하고 있습니다.
Expressions within the layout are written in the attribute properties using the “@{}" syntax.
레이아웃 내부에 표현식은 @{} 문법을 사용합니다.
However some times we need to write custom implementation for a property,
Let’s say we are getting a Date as String from data object and want to format this date to another format,
For such cases we can write our own custom methods annotating with BindingAdapter and passing the property name.
그러나 몇몇 상황에 우리는 프로퍼티 커스텀 실행을 작성해야하는데 우리는 객체 데이터로부터 문자열인 날짜를 가져오고 그 날짜를 다른 포맷으로 바꾸길 원하고, 이런 경우들에서 우린 바인딩어댑터에 어노테이션과 프로퍼티 이름을 넘겨 커스텀 메소드들을 작성할 수 있습니다.
//xml
<TextView
android:id="@+id/publishedAt"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:dateText="@{article.publishedAt}"
android:textSize="@dimen/news_text" />
//handling dateText property
@BindingAdapter("dateText")
public static void convertToDate(TextView view, String date) {
view.setText(DateUtils.Companion.convertToDateString(date));
}In the example i am using dateText property.
Android does not know this property so we have to write a method which represents this property,
now anywhere in the application you can use this tag and on run time it will call the BindingAdapter annotated method.
이 예제에서 dateText 프로퍼티를 사용하고 있습니다. 안드로이드는 이 프로퍼티를 알지 못합니다 그래서 우리는 그 프로퍼티를 대표하는 메소드를 작성해주어야 합니다. 지금 어플리케이션 어디든 우린 이 태그(프로퍼티)를 사용할 수 있고 어노테이션 메소드가 사용된 바인딩 어댑터를 호출하여 실행할 수 있습니다.
You can pass multiple properties for BindingAdapter method, making them optional or mandatory. You can read more about binding from here.
당신은 바인딩 어댑터 메소드에 대한 다양한 프로퍼티들을 전달할 수 있습니다, 프로퍼티를 옵션 혹은 강제적으로 생성함으로써.