MySQL에서 테이블 간 데이터를 연결하기 위해서
JOIN이 사용됩니다.JOIN의 방법에는 여러 가지 있으며, 각JOIN유형은 테이블 간의 관계에 따라 다르게 사용됩니다.
예시 테이블 생성 및 데이터 삽입
-- 1:N 관계
CREATE TABLE Professor (
ProfessorID INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
Name VARCHAR(100),
Department VARCHAR(100)
);
INSERT INTO Professor (Name, Department)
VALUES ('Dr. Kim', 'Mathematics'),
('Dr. Lee', 'History'),
('Dr. Choi', 'Science');
CREATE TABLE Student (
StudentID INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
Name VARCHAR(100),
Major VARCHAR(100),
ProfessorID INT,
FOREIGN KEY (ProfessorID) REFERENCES Professor(ProfessorID)
);
-- 1:1 관계
CREATE TABLE ID_Card (
CardID INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
StudentID INT UNIQUE, -- UNIQUE로 1:1 관계 설정
IssueDate DATE,
FOREIGN KEY (StudentID) REFERENCES Student(StudentID) ON DELETE CASCADE
);
CREATE TABLE Course (
CourseID INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
CourseName VARCHAR(100)
);
-- N:M 관계를 위한 중간 테이블
CREATE TABLE Student_Course (
StudentID INT,
CourseID INT,
PRIMARY KEY (StudentID, CourseID),
FOREIGN KEY (StudentID) REFERENCES Student(StudentID),
FOREIGN KEY (CourseID) REFERENCES Course(CourseID)
);
INSERT INTO Student (Name, Major)
INSERT INTO Student (Name, Major, ProfessorID)
VALUES ('Alice Johnson', 'Mathematics', 1),
('Bob Lee', 'Science', 3),
('Charlie Kim', 'History', 2),
('David Park', 'Mathematics', 1);
INSERT INTO ID_Card (StudentID, IssueDate)
VALUES (1, '2023-09-01'),
(2, '2023-08-15'),
(3, '2023-10-05'),
(4, '2023-11-12');
INSERT INTO Course (CourseName)
VALUES ('Mathematics'),
('Science'),
('History');
INSERT INTO Student_Course (StudentID, CourseID)
VALUES (1, 1), -- Alice Mathematics
(1, 3), -- Alice History
(3, 3), -- Charlie History
(4, 3); -- David HistoryJOIN
1. INNER JOIN
두 테이블 간에서 공통된 값이 있는 행만 반환합니다.
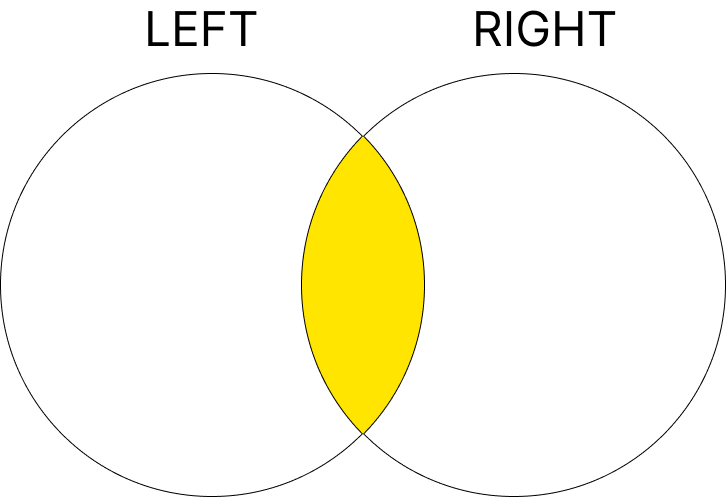
구문
SELECT columns
FROM table1
INNER JOIN table2
ON table1.column = table2.column;예시 코드
강의를 수강하는 학생의 정보만 반환합니다.
Bob Lee는 강의를 수강하지 않으므로 결과에 포함되지 않으며, Science 강의도 수강생이 없기 때문에 결과에 포함되지 않습니다.
SELECT Student.Name, Student.Major, Course.CourseName
FROM Student
INNER JOIN Student_Course ON Student.StudentID = Student_Course.StudentID
INNER JOIN Course ON Student_Course.CourseID = Course.CourseID;| Name | Major | CourseName | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alice Johnson | Mathematics | Mathematics | |
| Alice Johnson | Mathematics | History | |
| Charlie Kim | History | History | |
| David Park | Mathematics | History |
2. LEFT JOIN
왼쪽 테이블의 모든 행을 반환하고, 오른쪽 테이블에 일치하는 값이 없으면 NULL을 반환합니다.
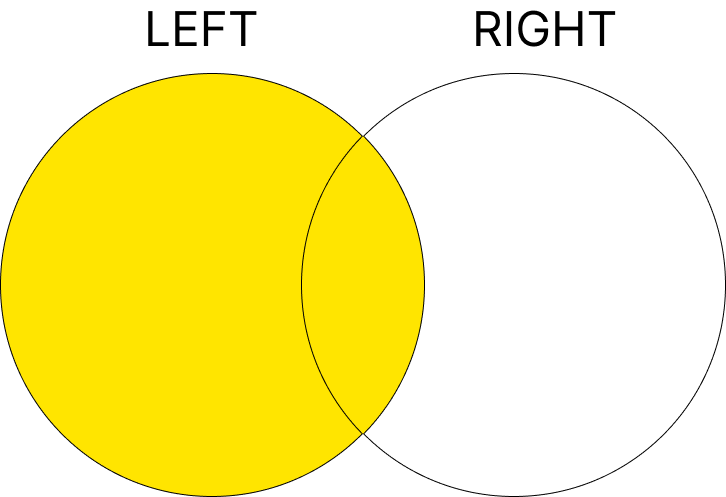
구문
SELECT columns
FROM table1
LEFT JOIN table2
ON table1.column = table2.column;예시 코드
학생이 수강하는 강의뿐만 아니라, 수강하지 않는 학생도 조회됩니다.
Bob Lee는 강의를 수강하지 않으므로, CourseName이 NULL로 표시됩니다.
SELECT Student.Name, Student.Major, Course.CourseName
FROM Student
LEFT JOIN Student_Course ON Student.StudentID = Student_Course.StudentID
LEFT JOIN Course ON Student_Course.CourseID = Course.CourseID;| Name | Major | CourseName | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alice Johnson | Mathematics | Mathematics | |
| Alice Johnson | Mathematics | History | |
| Bob Lee | Science | NULL | |
| Charlie Kim | History | History | |
| David Park | Mathematics | History |
3. RIGHT JOIN
오른쪽 테이블의 모든 행을 반환하고, 왼쪽 테이블에 일치하는 값이 없으면 NULL을 반환합니다.
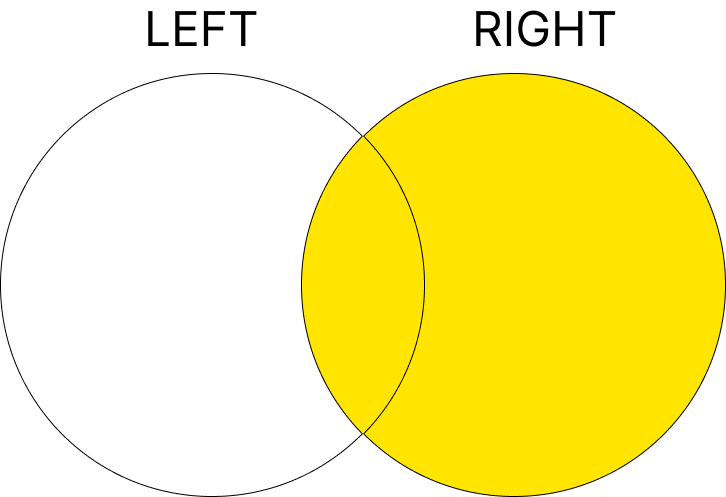
구문
SELECT columns
FROM table1
LEFT JOIN table2
ON table1.column = table2.column;예시 코드
수강생이 없는 강의가 있을 때, 그 강의의 학생 정보가 NULL로 반환됩니다.
Science 강의는 수강생이 없으므로, Name, Major 가 NULL로 표시됩니다.
SELECT Student.Name, Student.Major, Course.CourseName
FROM Student
RIGHT JOIN Student_Course ON Student.StudentID = Student_Course.StudentID
RIGHT JOIN Course ON Student_Course.CourseID = Course.CourseID;| Name | Major | CourseName | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alice Johnson | Mathematics | Mathematics | |
| NULL | NULL | Science | |
| Alice Johnson | Mathematics | History | |
| Charlie Kim | History | History | |
| David Park | Mathematics | History |
4. UNION
두 개 이상의 SELECT 쿼리의 결과를 결합합니다.
중복된 값은 제거되며, UNION ALL을 사용하면 중복된 값도 포함됩니다.
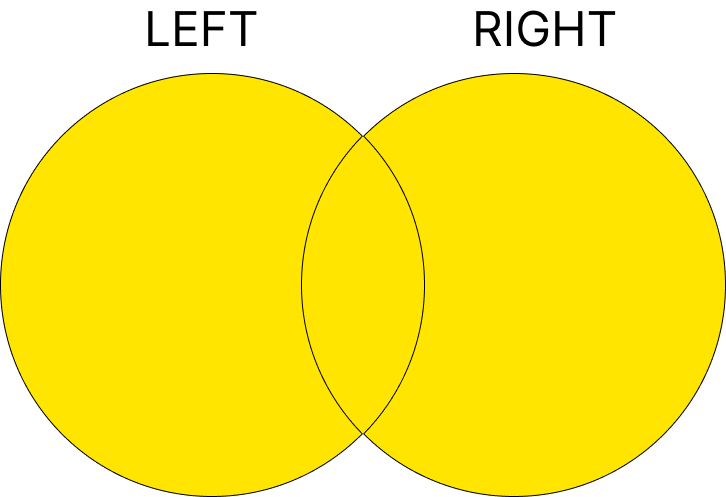
구문
SELECT columns FROM table1
UNION
SELECT columns FROM table2;
-- 중복된 값을 포함하려면
SELECT columns FROM table1
UNION ALL
SELECT columns FROM table2;예시 코드
학생 이름과 강의 이름을 하나의 결과로 결합합니다.
중복된 값은 제거되므로, Alice Johnson이 두 번 표시되지 않습니다.
SELECT Name FROM Student
UNION
SELECT CourseName FROM Course;| Name | |
|---|---|
| Alice Johnson | |
| Bob Lee | |
| Charlie Kim | |
| David Park | |
| Mathematics | |
| Science | |
| History |
5. FULL OUTER JOIN
MySQL에서는 FULL OUTER JOIN을 지원하지 않기 때문에, LEFT JOIN과 RIGHT JOIN을 결합하는 UNION을 사용하여 동일한 효과를 낼 수 있습니다. 이 방법을 사용하면, 두 테이블의 모든 행을 반환하고, 대응되지 않는 값은 NULL로 채웁니다.
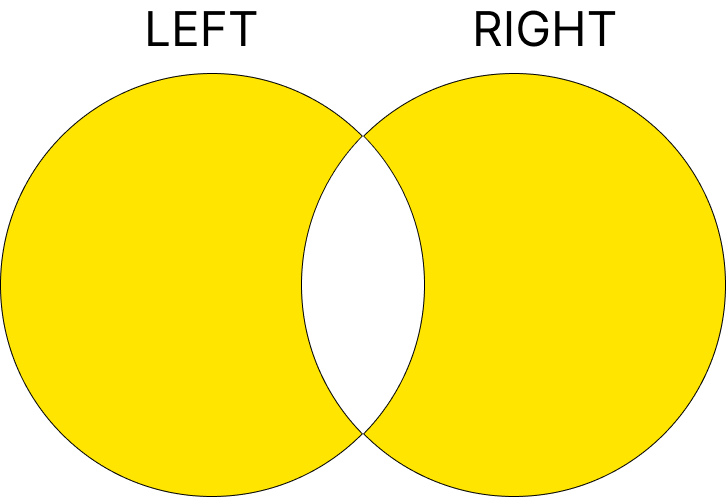
구문
SELECT columns
FROM table1
LEFT JOIN table2 ON table1.column = table2.column
UNION
SELECT columns
FROM table1
RIGHT JOIN table2 ON table1.column = table2.column;예시 코드
LEFT JOIN과 RIGHT JOIN을 결합하여, 학생이나 강의 어느 한 쪽에 대응되는 데이터가 없을 경우에도 모든 행을 반환합니다.
Bob Lee는 수강하는 강의가 없어 CourseName이 NULL로, Science 강의는 수강생이 없어서 Name, Major이 NULL로 표시됩니다.
SELECT Student.Name, Student.Major, Course.CourseName
FROM Student
LEFT JOIN Student_Course ON Student.StudentID = Student_Course.StudentID
LEFT JOIN Course ON Student_Course.CourseID = Course.CourseID
UNION
SELECT Student.Name, Student.Major, Course.CourseName
FROM Student
RIGHT JOIN Student_Course ON Student.StudentID = Student_Course.StudentID
RIGHT JOIN Course ON Student_Course.CourseID = Course.CourseID;| Name | Major | CourseName | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alice Johnson | Mathematics | Mathematics | |
| Alice Johnson | Mathematics | History | |
| Bob Lee | Science | NULL | |
| Charlie Kim | History | History | |
| David Park | Mathematics | History | |
| NULL | NULL | Science |
6. EXCLUSIVE LEFT JOIN
EXCLUSIVE LEFT JOIN은 LEFT JOIN의 결과에서 오직 왼쪽 테이블에만 존재하는 행을 반환합니다. 즉, 오른쪽 테이블에 일치하는 값이 없어서 NULL로 채워진 데이터만 선택하는 방식입니다.
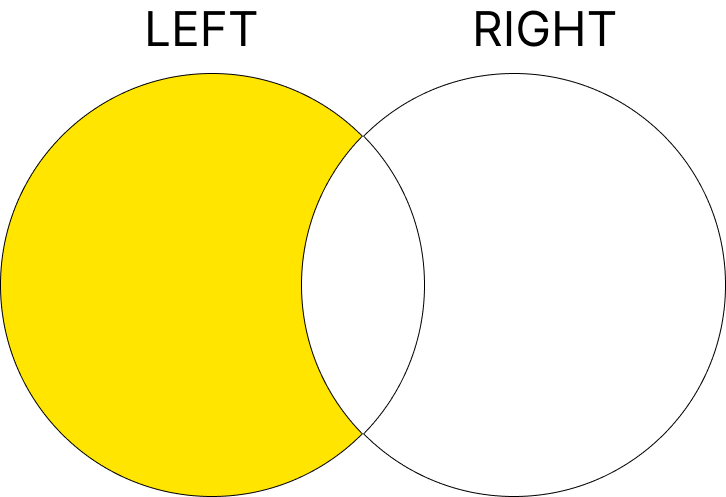
구문
SELECT columns
FROM table1
LEFT JOIN table2
ON table1.column = table2.column
WHERE table2.column IS NULL;예시 코드
Student_Course를 왼쪽에 두고 Student와 LEFT JOIN를 수행하여 강의를 수강하지 않는 학생들만 반환합니다. WHERE Student.StudentID IS NULL 조건은 강의를 수강하지 않는 학생만을 필터링합니다.
Bob Lee는 강의를 수강하지 않으므로 결과에 포함되고, Alice Johnson과 Charlie Kim은 강의를 수강하므로 제외됩니다.
SELECT Student.Name, Student.Major
FROM Student
LEFT JOIN Student_Course ON Student.StudentID = Student_Course.StudentID
WHERE Student_Course.StudentID IS NULL;| Name | Major | |
|---|---|---|
| Bob Lee | Science |
7. EXCLUSIVE RIGHT JOIN
EXCLUSIVE RIGHT JOIN은 RIGHT JOIN의 결과에서 오직 오른쪽 테이블에만 존재하는 행을 반환합니다. 즉, 왼쪽 테이블에 일치하는 값이 없어서 NULL로 채워진 데이터만 선택하는 방식입니다.
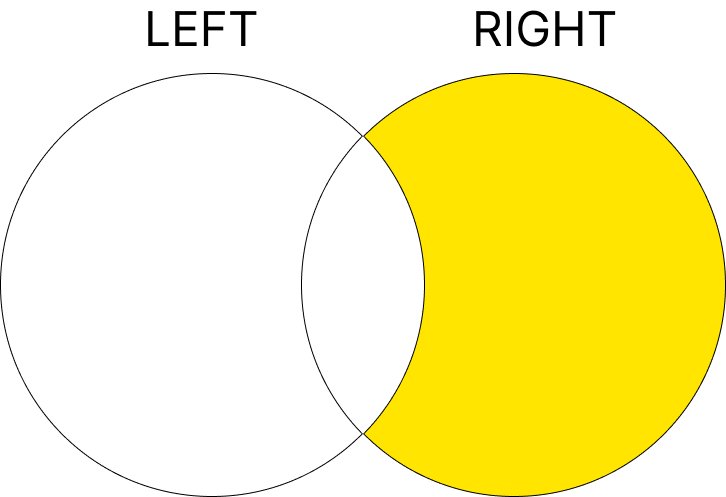
구문
SELECT columns
FROM table1
LEFT JOIN table2
ON table1.column = table2.column
WHERE table2.column IS NULL;예시 코드
Student_Course와 Course를 오른쪽에 두고 Student와 RIGHT JOIN을 수행하여, 수강하는 학생이 없는 강의만을 반환합니다. WHERE Student.StudentID IS NULL 조건은 학생이 없는 강의만 필터링하는 역할을 합니다.
SELECT Course.CourseName
FROM Student
RIGHT JOIN Student_Course ON Student.StudentID = Student_Course.StudentID
RIGHT JOIN Course ON Student_Course.CourseID = Course.CourseID
WHERE Student.StudentID IS NULL;| CourseName | |
|---|---|
| Science |
8. SELF JOIN
SELF JOIN은 테이블 자기 자신과의 JOIN입니다. 주로 동일 테이블 내에서 데이터를 비교해야 하는 경우 사용됩니다.
구문
SELECT a.columns, b.columns
FROM table1 a
JOIN table1 b
ON a.column = b.column;예시 코드
동일한 전공을 가진 학생들을 짝지어 출력하는 경우, 같은 테이블인 Student 테이블에서 자기 자신과 JOIN을 수행합니다.
SELECT a.Name AS Student1, b.Name AS Student2, a.Major
FROM Student a
JOIN Student b ON a.Major = b.Major
WHERE a.StudentID <> b.StudentID;| Student1 | Student2 | Major | |
|---|---|---|---|
| David Park | Alice Johnson | Mathematics | |
| Alice Johnson | David Park | Mathematics |
JOIN 요약
| JOIN 유형 | 설명 | 구문 |
|---|---|---|
| INNER JOIN | 두 테이블 간의공통된 값이 있는 행만 반환 | SELECT columns FROM table1 INNER JOIN table2 ON table1.column = table2.column; |
| LEFT JOIN | 왼쪽 테이블의 모든 행을 반환, 일치하지 않는 오른쪽 테이블은 NULL | SELECT columns FROM table1 LEFT JOIN table2 ON table1.column = table2.column; |
| RIGHT JOIN | 오른쪽 테이블의 모든 행을 반환, 일치하지 않는 왼쪽 테이블은 NULL | SELECT columns FROM table1 RIGHT JOIN table2 ON table1.column = table2.column; |
| EXCLUSIVE LEFT JOIN | 왼쪽 테이블에만 존재하는 행만 반환, 오른쪽 테이블에 NULL인 값 | SELECT columns FROM table1 LEFT JOIN table2 ON table1.column = table2.column WHERE table2.column IS NULL; |
| EXCLUSIVE RIGHT JOIN | 오른쪽 테이블에만 존재하는 행만 반환, 왼쪽 테이블에 NULL인 값 | SELECT columns FROM table1 RIGHT JOIN table2 ON table1.column = table2.column WHERE table1.column IS NULL; |
| UNION | 두 개 이상의 SELECT 쿼리의 결과를 결합 | SELECT columns FROM table1 UNION SELECT columns FROM table2; |
| FULL OUTER JOIN | 두 테이블 간의모든 행을 반환, MySQL에서는UNION으로 구현 가능 | SELECT columns FROM table1 LEFT JOIN table2 ON table1.column = table2.column UNION SELECT columns FROM table1 RIGHT JOIN table2 ON ... |
| SELF JOIN | 테이블을 자기 자신과 JOIN | SELECT a.columns, b.columns FROM table1 a JOIN table1 b ON a.column = b.column; |
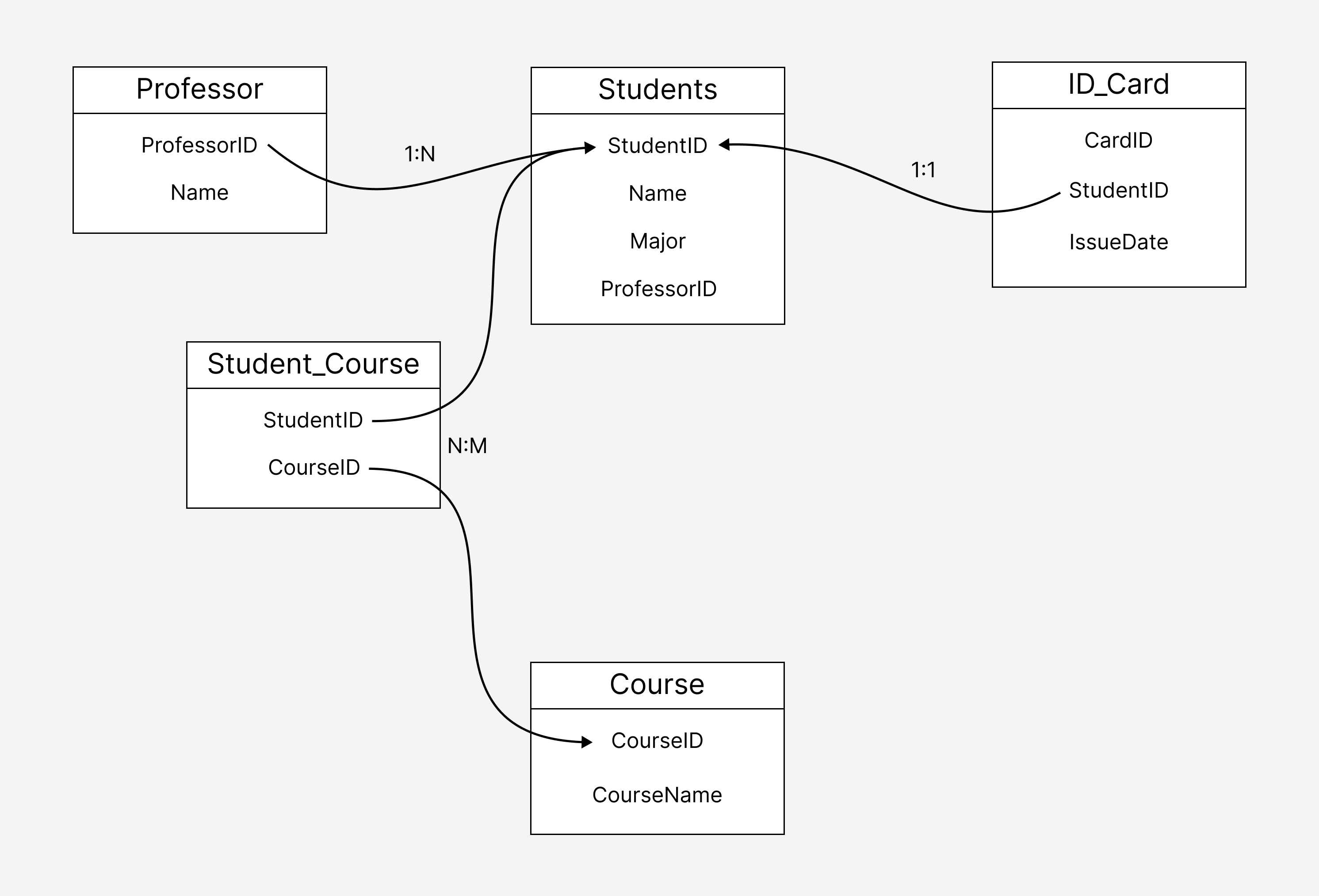
테이블 관계
1. 1:1 (일대일) 관계
1:1 관계는 한 테이블의 하나의 레코드가 다른 테이블의 하나의 레코드와만 대응될 때 나타납니다.
예를 들어, Student 테이블과 ID_Card 테이블은 1:1 관계를 가집니다. 각 학생은 하나의 신분증만 발급받을 수 있습니다.
SELECT Student.Name, Student.Major, ID_Card.IssueDate
FROM Student
JOIN ID_Card ON Student.StudentID = ID_Card.StudentID;| Name | Major | IssueDate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alice Johnson | Mathematics | 2023-09-01 | |
| Bob Lee | Science | 2023-08-15 | |
| Charlie Kim | History | 2023-10-05 | |
| David Park | Mathematics | 2023-11-12 |
2. 1:N (일대다) 관계
1:N 관계는 한 테이블의 하나의 레코드가 다른 테이블의 여러 레코드와 관련될 때 발생합니다.
예를 들어, 한 교수가 여러 학생을 담당하는 경우입니다.
SELECT Professor.Name AS Professor Student.Name, Student.Major
FROM Student
INNER JOIN Professor ON Student.ProfessorID = Professor.ProfessorID;| Professor | StudentName | Major | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dr. Kim | Alice Johnson | Mathematics | |
| Dr. Kim | David Park | Mathematics | |
| Dr. Lee | Charlie Kim | History | |
| Dr. Choi | Bob Lee | Science |
3. N:M (다대다) 관계
N:M 관계는 두 테이블의 여러 레코드가 서로 여러 개의 레코드와 관련이 있을 때 발생합니다.
예를 들어, 한 명의 학생이 여러 강의를 수강할 수 있고, 하나의 강의도 여러 학생이 수강할 수 있습니다. 이를 구현하려면 중간 테이블을 사용해야 합니다.
SELECT Student.Name, Course.CourseName
FROM Student
JOIN Student_Course ON Student.StudentID = Student_Course.StudentID
JOIN Course ON Student_Course.CourseID = Course.CourseID;| Name | CourseName | |
|---|---|---|
| Alice Johnson | Mathematics | |
| Alice Johnson | History | |
| Charlie Kim | History | |
| David Park | History |
4. 예시 테이블 관계도