설치 및 세팅
설치
npm install jest --save-dev- 개발환경에서만 테스트를 사용을 하니 개발환경에 설치
세팅
npm test를 치면 테스트가 가능~.test.js에 해당하는 파일을 전부 검사
참고 : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g4MdUjxA-S4
Matcher
toBe
test("1은 1이야", () => {
expect(1).toBe(1);
});expect: test할 값toBe: 예상하는 값
test("1은 2가 아니야", () => {
expect(1).not.toBe(2);
});- 부정값을 예상하는 경우
test("0.1+0.2 = 0.3??", () => {
expect(fn.add(0.1, 0.2)).toBeCloseTo(0.3);
});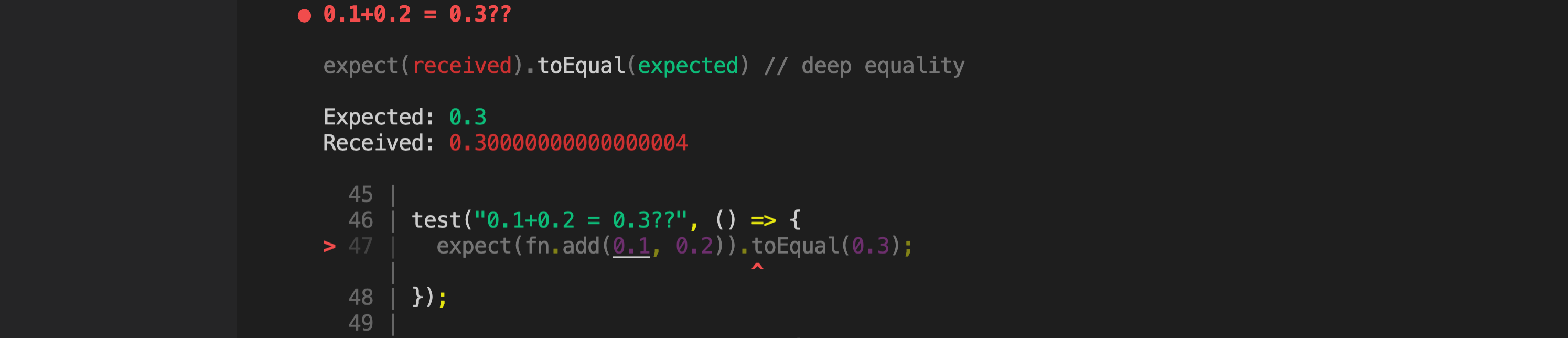
- javascript 소수 계산시 무한소수가 되기 때문에
toBeCloseTo사용
그외
toBeNulltoBeDefinedtoBeTrutytoBeFalsytoBeGreaterThantoBeGeaterThanOrEqualtoBeLessThantoBeLessThanOrEqual
toEqual
//fn.js
const fn ={
makeUser: (name, age, gender) => ({ name, age, gender: undefined }),
}- user를 만드는 함수를 정의
//fn.test.js
test("toBe : name and age to object", () => {
expect(fn.makeUser("Mike", 30)).toBe({
name: "Mike",
age: 30,
});
});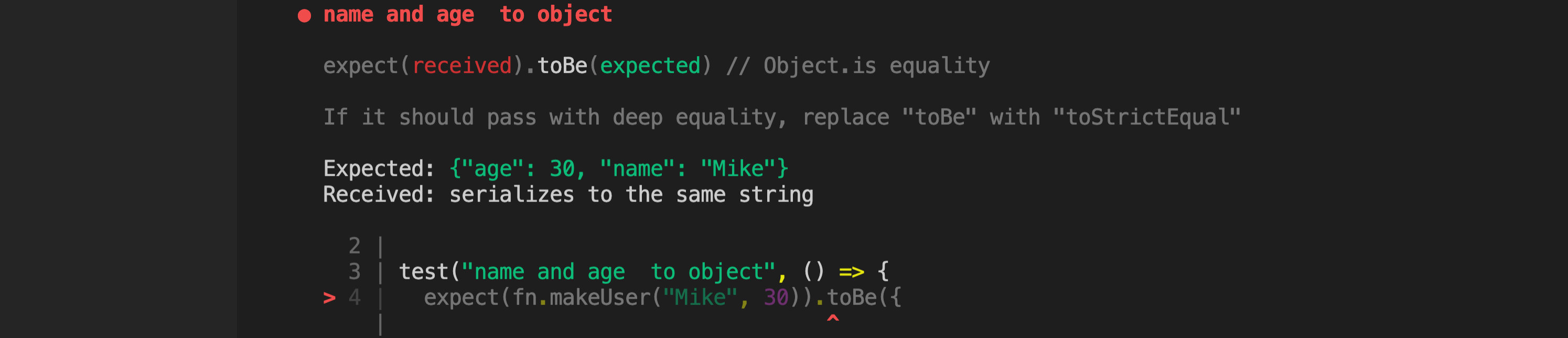
- 에러가 나오는 이유는 toBe는
같은 객체인지 확인 - 위에는 내용이 같을 뿐 다른 객체
test("ToEqual : name and age to object", () => {
expect(fn.makeUser("Mike", 30)).toEqual({
name: "Mike",
age: 30,
});
});- 내용이 같은지 확인을 할 때는
toEqual사용
//fn.test.js
test("toStrictEqual : name and age to object", () => {
expect(fn.makeUser("Mike", 30)).toStrictEqual({
name: "Mike",
age: 30,
});
});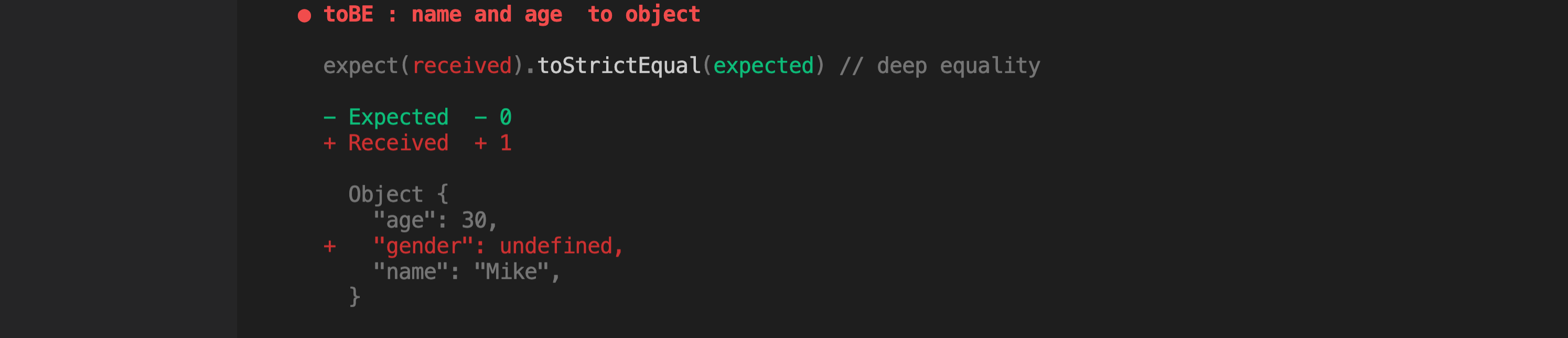
strictEqual로 할 시에는gender가undefined상태이기 때문에 테스트에 실패
toMatch
test("check the letter with RegEx ", () => {
expect("hello world").toMatch(/h/);
});정규표현식을 사용해서 문자열 체크가 가능
toContain
test("check the list ", () => {
const user = "Mike";
const userList = ["Tom", "Jane", "Kai"];
expect(userList).toContain("Kai");
});- 베열안에 요소 확인 가능
toThrow
//fn.js
const fn = {
throwErr: () => {
throw new Error("xx");
}
};
//fn.test.js
test("check the err ", () => {
expect(() => fn.throwErr()).toThrow("xx");
});- 설정한 에러메시지대로 출력이 됐는지 확인 가능
비동기 함수 결과
callback
//fn.js
const fn = {
getName: (callback) => {
const name = "Mike";
setTimeout(() => {
callback(name);
}, 3000);
}
}
//fn.test.js
test("async func ", (done) => {
function callback(name) {
expect(name).toBe("Mike");
done();
}
fn.getName(callback);
});- callback을 사용하는 경우
- 이제는 거의 사용 x
promise
//fn.js
const fn = {
getAge: () => {
const age = 30;
return new Promise((res, rej) => {
setTimeout(() => {
res(age);
}, 3000);
});
}
}
//fn.test.js
//방법1
test("async func ", () => {
return fn.getAge().then((age) => {
expect(age).toBe(30);
});
});
//방법2
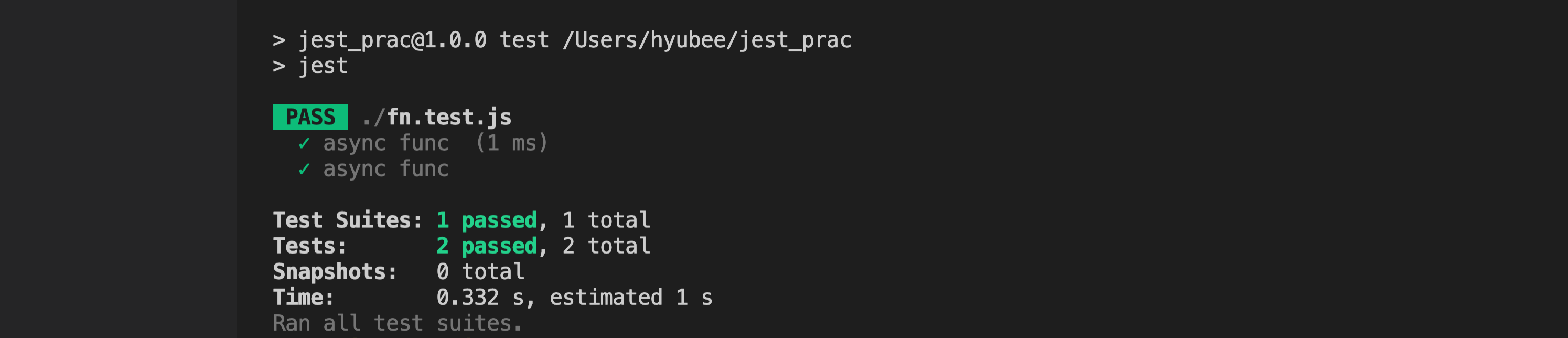
test("async func ", () => {
return expect(fn.getAge()).resolves.toBe(30);
});
-
테스트에서
return을 안걸면 비동기작업이 이루어지지 않아서 테스트를 통과해버리는 상황이 벌어짐 - 소요시간이 1ms
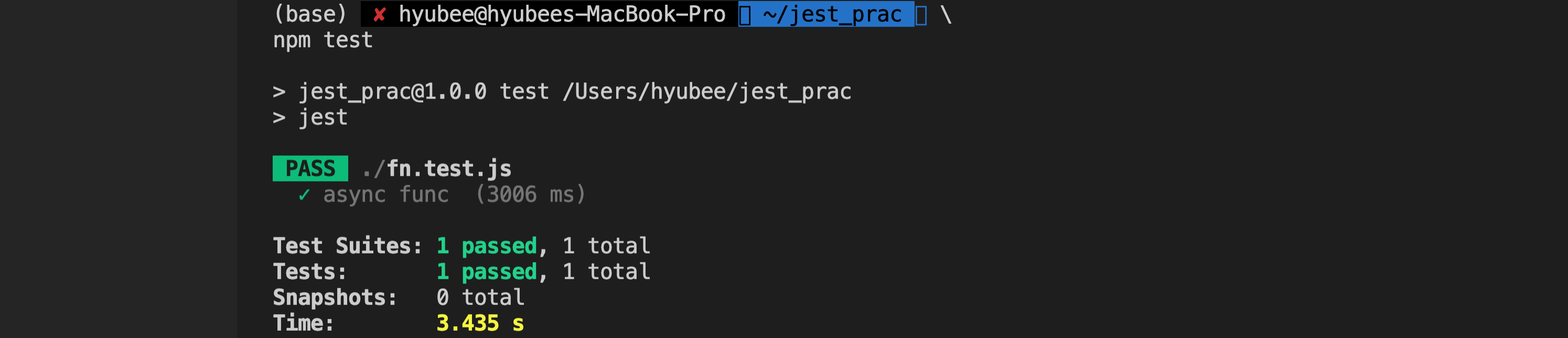
-
return을 걸면 비동기처리가 잘 작동(settimeout 3 sec)하며 테스트
async await
test("check the promise ", async () => {
const age = await fn.getAge();
expect(age).toBe(30);
});
test("check the promise ", async () => {
await expect(fn.getAge()).resolves.toBe(30);
});- async await를 테스트 하는 방법
테스트 전후 처리
각 테스트 전후
beforeEach, afterEach
//각 테스트 전후 변수 초기화
let num = 0;
beforeEach(() => {
num = 0;
});
test(" 0 + 1 = 1? ", () => {
num = fn.add(num, 1);
expect(num).toBe(1);
});
test(" 0 + 2 = 2? ", () => {
num = fn.add(num, 2);
expect(num).toBe(2);
});
test(" 0 + 3 = 3? ", () => {
num = fn.add(num, 3);
expect(num).toBe(3);
});
전체 테스트 전후
beforeAll, afterAll
// 테스트 전 db connect , 테스트 후 db disconnect
beforeAll(async ()=>{
user = await fn.connectUserDb()
})
afterAll(async ()=>{
user = await fn.disConnectUserDb()
})
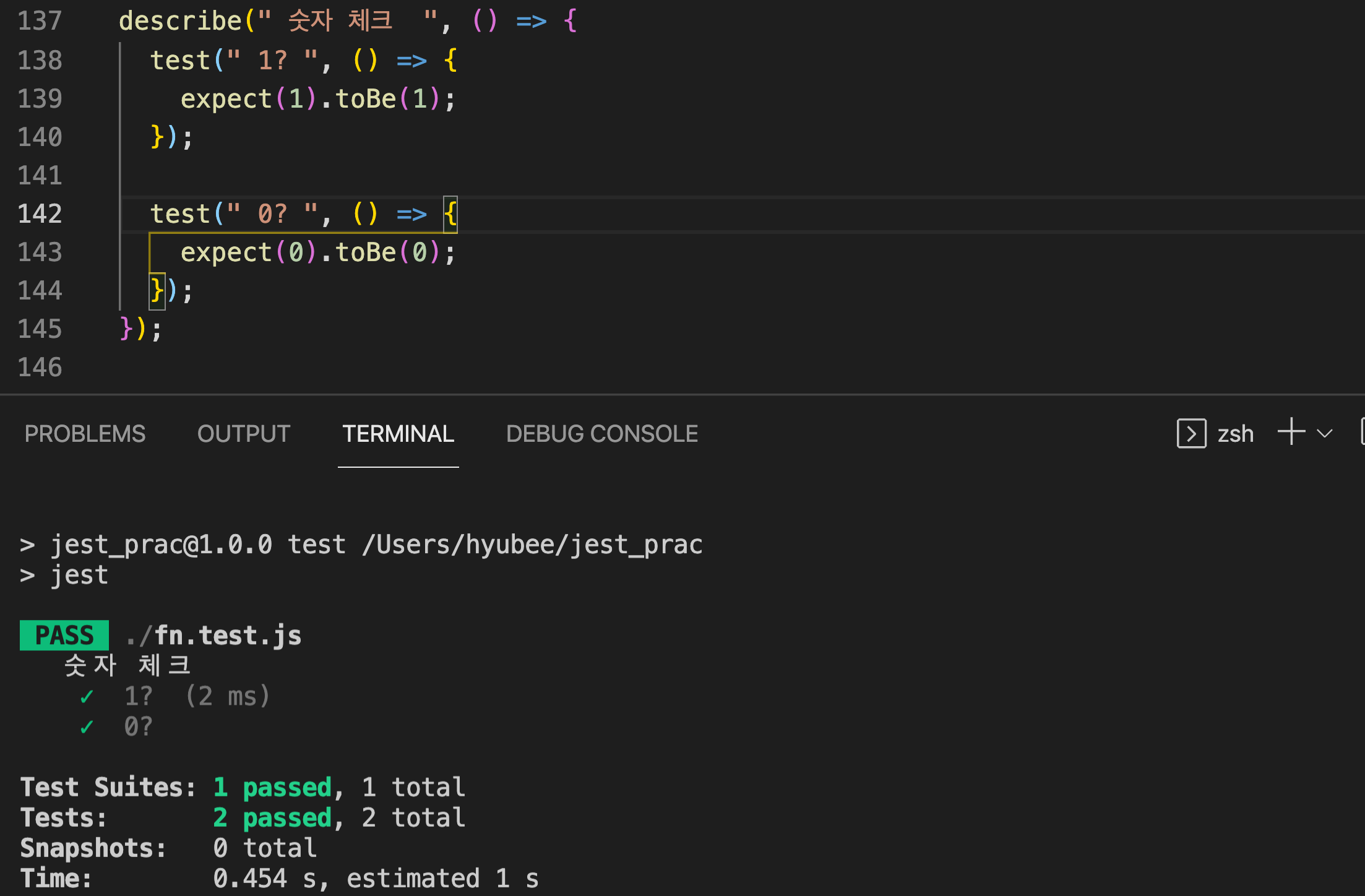
describe 관련 테스트 하나로 묶기
describe(" 숫자 체크 ", () => {
test(" 1? ", () => {
expect(1).toBe(1);
});
test(" 0? ", () => {
expect(0).toBe(0);
});
});
여러 테스트 중 하나만 테스트
describe(" 숫자 체크 ", () => {
test.only(" 1? ", () => {
expect(1).toBe(1);
});
test(" 0? ", () => {
expect(0).toBe(0);
});
});test.only사용
여러 테스트 중 특정 테스트 제외
describe(" 숫자 체크 ", () => {
test(" 1? ", () => {
expect(1).toBe(1);
});
test.skip(" 0? ", () => {
expect(0).toBe(0);
});
});test.skip사용
Mocking
- 외부 함수에 의존하지 않고 테스트 하고자할 때
- user db 에서 가져와야 하는 경우 등 - 외부 요인(네트워크)에 의해 영향 많이 받음
const mockFn = jest.fn();
mockFn();
mockFn(1);
test(" 0 + 3 = 3? ", () => {
console.log(mockFn.mock.calls);
let num = 0;
num = fn.add(num, 3);
expect(num).toBe(3);
});
test("함수는 2번 호출됩니다. ", () => {
expect(mockFn.mock.calls.length).toBe(2);
});
test("2번째로 호출된 함수에 전달된 첫번째 인수슨 1입니다. ", () => {
expect(mockFn.mock.calls[1][0]).toBe(1);
});

- 함수에서
mockFn.mock.calls을 찍어보면 위처림[ [ ] , [1]]이 나온다. - 첫번째 mockFn()에서 받은 인자가 없어서 빈리스트
- 첫번째 mockFn()에서 받은 인자가 1이라 리스트 안에 1
mockFn.mock.calls.length: 2번 호출 해서 2mockFn.mock.calls[1][0]: 호출한 mock 중에 2번째 함수의 인자는 1
// 별도의 함수 만들지 않아도 테스트 가능 - 1을 더하는 콜백함수 없이 테스트
const mockFn = jest.fn();
function forEachAdd1(arr) {
arr.forEach((num) => {
mockFn(num + 1);
});
}
forEachAdd1([10, 20, 30]);
test("함수는 3번 호출됩니다.", () => {
expect(mockFn.mock.calls.length).toBe(3);
});
test("전달된 값은 11, 21, 31입니다. ", () => {
expect(mockFn.mock.calls[0][0]).toBe(11);
expect(mockFn.mock.calls[1][0]).toBe(21);
expect(mockFn.mock.calls[2][0]).toBe(31);
});
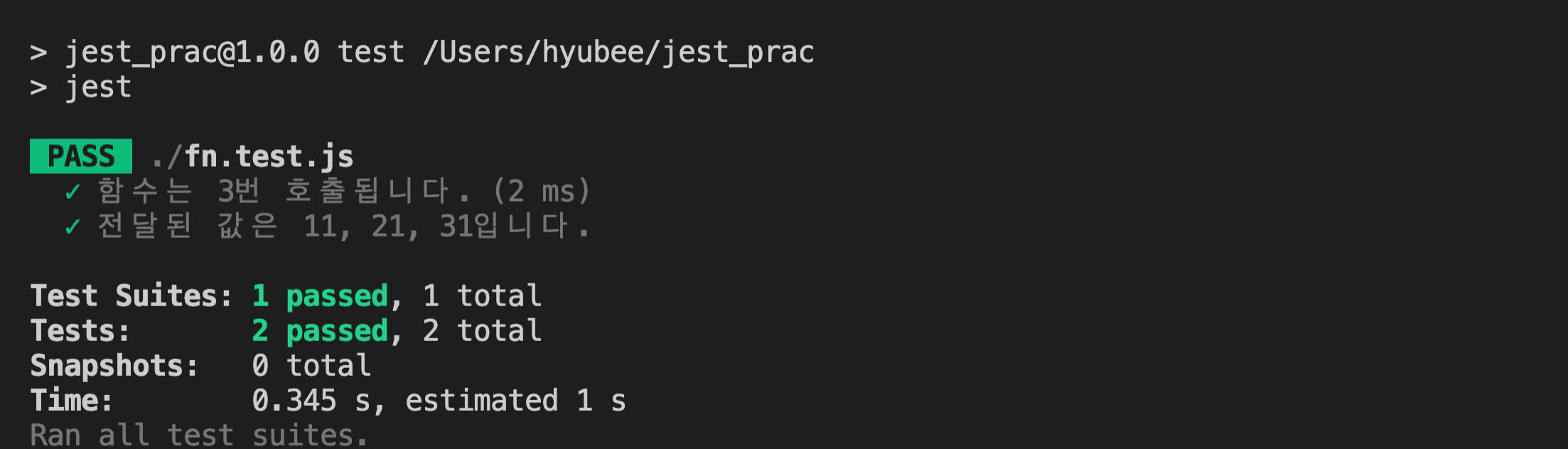
- 별도의 파일에 함수를 만들지 않고
테스트 내부에서 함수를 정의해도 테스트 가능 - loop를 3번 돌때마다 mock이 일어나서 length = 3
- 각각에 인자는 배열의 인자 +1
const mockFn = jest.fn((num) => num + 1);
mockFn(10);
mockFn(20);
mockFn(30);
test("10에서 1증가한 값이 반환 ", () => {
expect(mockFn.mock.results[0].value).toBe(11);
});
test("20에서 1증가한 값이 반환 ", () => {
expect(mockFn.mock.results[1].value).toBe(21);
});
test("20에서 1증가한 값이 반환 ", () => {
expect(mockFn.mock.results[2].value).toBe(31);
});
- jest.fn()에
익명함수를 정의하는 방법도 있음
비동기 함수 mock
const mockFn = jest.fn();
mockFn.mockResolvedValue({ name: "mike" });
test("비동기 콜백함수로 받아온 결과는 mike ", () => {
mockFn().then((res) => {
expect(res.name).toBe("mike");
});
});
- 콜백함수의 결과를 임의로 지정
- 지정한 값에 대해서 resolve된 결과를 미리 지정
- 그 값을 예측값과 비교
DB 값 삽입 없이 createUser테스트
jest.mock("./fn");
fn.createUser.mockReturnValue({ name: "mike" });
test("유저를 만든다", () => {
const user = fn.createUser("mike");
expect(user.name).toBe("mike");
});- 해당 함수에서 resolve가 잘되었다는 것을 전제로 결과 값을 지정
- 해당 함수가 실행이 되는 것이 아니기 때문에 db에 실제로 정보가 삽입되지 않음
기타 mocking method
const mockFn = jest.fn();
mockFn(10, 20);
mockFn();
mockFn(30, 40);
test("한번 이상 호출?", () => {
expect(mockFn).toBeCalled();
});
test("정확히 3번 호출?", () => {
expect(mockFn).toBeCalledTimes(3);
});
test("10이랑 20을 인수로 전달받은 함수가 있는가", () => {
expect(mockFn).toBeCalledWith(10, 20);
});
test("마지막 함수는 30이랑 40 받았음?", () => {
expect(mockFn).lastCalledWith(30, 40);
});
toBeCalled: 한 번이라도 호출toBeCalledTimes: 몇 번 mock이 호출되었나toBeCalledWith: 특정 인수를 전달받은 함수가 있는지lastCalledWith: 마지막 호출받을 때 특정 인수 받았는지
.jpeg)