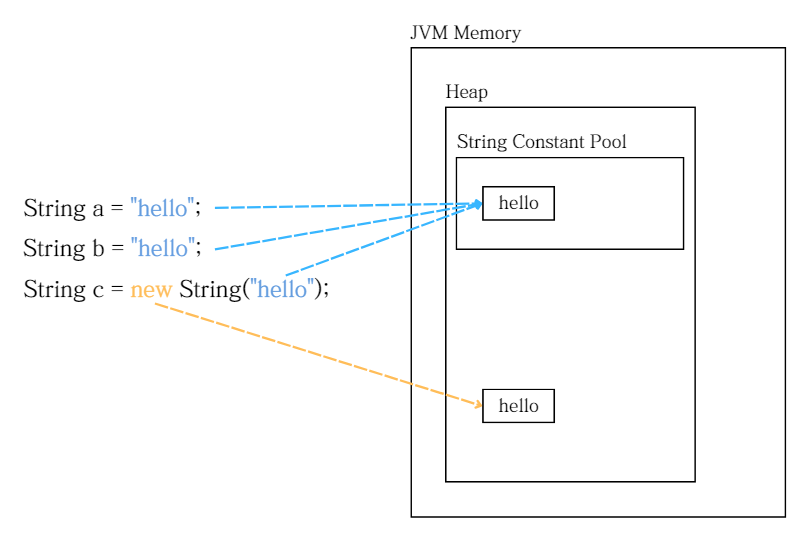
자바에서 문자열을 비교할 때 ==연산자는 참조값을 비교합니다. 근데 a와 b에 같은 문자열을 변수에 넣었을 뿐인데 왜 참조값이 같은거고 c도 "hello"로 만든 문자열인데 왜 다를까요..?🤔
package basic.probJungsuk;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a = "hello";
String b = "hello";
String c = new String("hello");
System.out.println(a==b); //true
System.out.println(a.equals(b)); //true
System.out.println(a==c); //false
System.out.println(a.equals(c)); //true
}
}
참고)
== : 주소 비교
equals() : 값비교 (Strring에서 오버라이딩)문자열 리터럴이란?
변하지 않는 문자열 값으로, 자바 소스 코드에 작성된 모든 문자열 리터럴은 클래스 파일에 저장합니다.
중복된 리터럴은 한 번만 저장!
🔍 어떤 과정을 거칠까?
1. [컴파일] .class 파일의 Constant Pool에 리터럴 저장
📝 .class 파일 만들기
javac {파일명}.java
javap -c -verbose {파일명}📝.class 파일 내부에는 Constant Pool이라는 영역이 있고
이곳에서 문자열 리터럴이 어떻게 처리되는지 확인할 수 있다
Constant pool:
#1 = Methodref #2.#3 // java/lang/Object."<init>":()V
#2 = Class #4 // java/lang/Object
#3 = NameAndType #5:#6 // "<init>":()V
#4 = Utf8 java/lang/Object
#5 = Utf8 <init>
#6 = Utf8 ()V
#7 = String #8 // hello
#8 = Utf8 hello
#9 = Class #10 // java/lang/String
#10 = Utf8 java/lang/String
#11 = Methodref #9.#12 // java/lang/String."<init>":(Ljava/lang/String;)V
#12 = NameAndType #5:#13 // "<init>":(Ljava/lang/String;)V
.
.
.
(생략)📌Constant Pool이란?
컴파일된 클래스에서 사용하는 문자열, 정수, 클래스 이름과 같은 상수 정보들이 저장되는 공간
생성된 .class 파일을 읽으면
"hello"를 찾을 수 있는데 자바 소스 코드에서는 "hello"를 3번 사용했지만 Constant pool에는 "hello"가 한번 저장된 것을 알 수 있다!
#7 = String #8 // "hello" <- 이후 ldc #7을 통해 재사용
#8 = Utf8 hello2. [JVM 로딩] Constant Pool → String Constant Pool로 복사
🔍처음 "hello"를 만났을 때
- JVM이
String Constant Pool에"hello"가 있는지 먼저 확인 - 없으면 새로운 String 객체를 생성하여
String Constant Pool에 등록 - 해당 객체의 참조값을 변수에 저장
(1) 0: ldc #7 // String hello
2: astore_1
#7은 Constant Pool에서 "hello"를 참조🔍두 번째 "hello"를 만났을 때
- JVM이 다시
String Constant Pool을 확인 - 이미
"hello"객체가 존재하므로 동일한 참조값을 재사용 - 같은 참조값을 변수에 저장
(2) 3: ldc #7 // String hello
5: astore_2✅즉, a와 b는
"hello"라는 동일한 String객체의 참조값을 공유한다
2-1. [JVM 로딩] new String("hello")
"hello"→ 이미String Constant Pool에 존재하거나 새로 추가됨new연산자를 통해Heap에 새로운 String 인스턴스를 위한 공간이 할당됨- 기존
"hello"의 참조값을 생성자에 넘겨 새로운 객체가 초기화됨 - 최종적으로 새로운 참조값이 변수에 저장됨
6: new #9 // class java/lang/String
9: dup
10: ldc #7 // String hello
12: invokespecial #11 // Method java/lang/String."<init>":(Ljava/lang/String;)V
15: astore_3✅
new String("hello")는 기존 문자열을 복사해서 새 객체를 생성하는 것이기 때문에 같은 내용을 담고 있어도 다른 참조값을 가진다
🍀최종적으로 다음 그림과 같다