-
❓ Q.
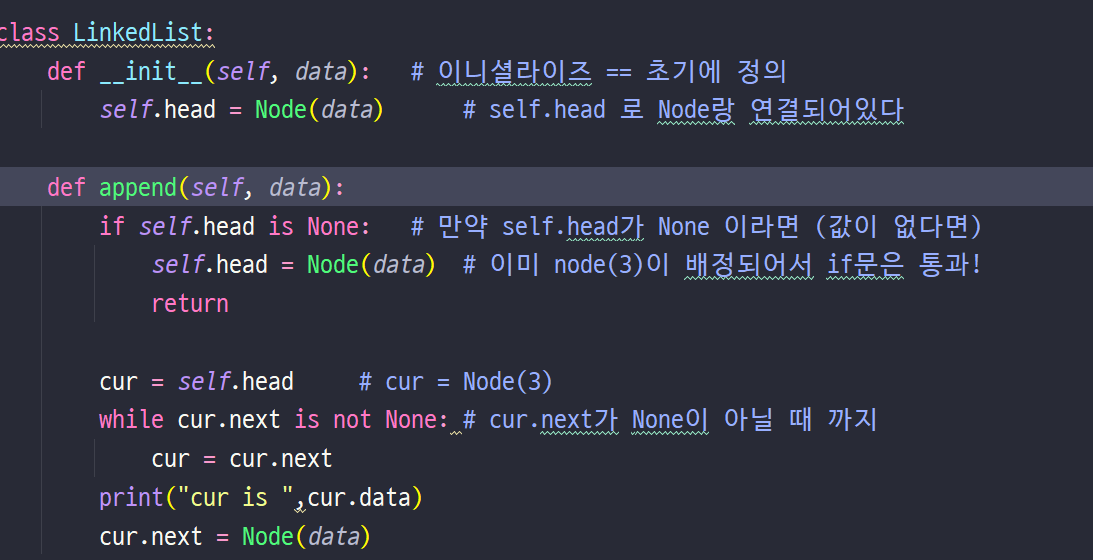
링크드 리스트에서 index번째 원소를 반환하시오.class Node: def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.next = None class LinkedList: def __init__(self, value): self.head = Node(value) def append(self, value): cur = self.head while cur.next is not None: cur = cur.next cur.next = Node(value) def print_all(self): cur = self.head while cur is not None: print(cur.data) cur = cur.next def get_node(self, index): return "index 번째 노드를 반환해보세요!" linked_list = LinkedList(5) linked_list.append(12) linked_list.get_node(0) # -> 5를 들고 있는 노드를 반환해야 합니다!-
💡 해결방법
노드를 따라가면서 값을 찾아야 합니다.
head에 저장되어있는 노드를 node 라는 변수에 담고,
count 라는 인덱스를 저장하기 위한 변수를 저장합니다.그리고 count 가 index 가 될 때까지
(이 때, while 문 내부에서 1씩 더해주니까 작을때까지로 조건을 넣습니다)
node의 next 값을 node 에 대입하고 count 를 증가합니다.
이 과정을 count 가 index가 아닐때까지 반복하면 됩니다!그리고 node 를 반환해줍니다.
def get_node(self, index): node = self.head count = 0 while count < index: node = node.next count += 1 return node
-
-
❓ Q.
링크드 리스트에서 index번째 원소를 반환하시오.class Node: def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.next = None class LinkedList: def __init__(self, value): self.head = Node(value) def append(self, value): cur = self.head while cur.next is not None: cur = cur.next cur.next = Node(value) def print_all(self): cur = self.head while cur is not None: print(cur.data) cur = cur.next def get_node(self, index): node = self.head count = 0 while count < index: node = node.next count += 1 return node def add_node(self, index, value): return "index 번째 Node 뒤에 value 를 추가하세요!" linked_list = LinkedList(5) linked_list.append(12) linked_list.add_node(0, 3) linked_list.print_all()-
💡 내 코드
class Node: def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.next = None class LinkedList: def __init__(self, value): self.head = Node(value) def append(self, value): cur = self.head while cur.next is not None: cur = cur.next cur.next = Node(value) def print_all(self): cur = self.head while cur is not None: print(cur.data) cur = cur.next def get_node(self, index): node = self.head count = 0 while count < index: node = node.next count += 1 return node def add_node(self, index, value): new_node = Node(value) #[6] if index == 0: new_node.next = self.head #new.node.next == 5 self.head = new_node # self.head == 6 return node = self.get_node(index -1) #index = 인수 # index번째 노드를 가져와서 node에 넣어준다 next_node = node.next # [5] 다음인 현재[12] # next 노드는 현재있는 node.next(다음것) node.next = new_node # [5] -> [6] new_node.next = next_node # [6] -> [12] linked_list = LinkedList(5) linked_list.append(12) linked_list.append(8) linked_list.add_node(1, 6) linked_list.print_all() -
🚩 해결방법
우리가 전에 이야기 했던 화물을 생각하면 됩니다!
-
자갈 칸의 연결고리를 흑연 칸으로 연결하고,
["자갈"] -> ["흑연"]["밀가루"] -> ["우편"] -
흑연 칸으로 연결고리를 밀가루 칸으로 연결합니다.
["자갈"] -> ["흑연"] -> ["밀가루"] -> ["우편"]이 때, 밀가루 칸의 위치를 저장해둬야 # 2 에서 흑연 칸을 밀가루 칸에 연결할 수 있습니다.
따라서 next_node 라는 변수에 현재 노드와 연결된 노드를 저장해두고,
1. 현재 노드의 다음 노드를 새로운 노드와 연결합니다.
2. 새로운 노드의 다음 노드를 이전에 저장해둔 노드에 연결합니다.Tip : 현재 노드를 구하기 위해서는 방금 만든 get_node 를 사용하면 됩니다!
def add_node(self, index, value): new_node = Node(value) node = self.get_node(index - 1) next_node = node.next node.next = new_node new_node.next = next_node그런데 이 때! 주의하셔야 할 점이 있습니다.
어느 코드에서나 index - 1 처럼 -1 하는 코드가 있으면,
0의 경우에는 어떻게 될까? 에 대한 걱정을 해주셔야 됩니다!만약 0이 입력된다면, get_node(-1) 이 호출되어서 원하지 않게 동작해버릴거에요!
따라서, 이런 경우는 예외처리를 따로 해주셔야 합니다.만약 0번째에 노드를 넣고 싶다면 어떻게 해줘야 할까요?
새로운 노드의 next 를 현재 가지고 있는 head 에 연결하고,
우선 현재 가지고 있는 head 를 새로운 노드로 교체해주시면 됩니다!def add_node(self, index, value): new_node = Node(value) if index == 0: new_node.next = self.head self.head = new_node return node = self.get_node(index - 1) next_node = node.next node.next = new_node new_node.next = next_node'
-
-
❓ Q.
링크드 리스트에서 index번째 원소를 제거하시오.class Node: def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.next = None class LinkedList: def __init__(self, value): self.head = Node(value) def append(self, value): cur = self.head while cur.next is not None: cur = cur.next cur.next = Node(value) def print_all(self): cur = self.head while cur is not None: print(cur.data) cur = cur.next def get_node(self, index): node = self.head count = 0 while count < index: node = node.next count += 1 return node def add_node(self, index, value): new_node = Node(value) if index == 0: new_node.next = self.head self.head = new_node return node = self.get_node(index - 1) next_node = node.next node.next = new_node new_node.next = next_node def delete_node(self, index): return "index 번째 Node를 제거해주세요!" linked_list = LinkedList(5) linked_list.append(12) linked_list.add_node(0, 3) linked_list.print_all() -
🚩 해결방법
우리가 전에 이야기 했던 화물을 생각하면 됩니다!
-
흑연 칸의 연결고리를 떼서
["자갈"] → ["흑연"]["밀가루"] → ["우편"] -
우편 칸으로 연결하면 됩니다!
["자갈"] -> ["흑연"] -> ["우편"]["밀가루"]흑연 칸의 포인터를 다음 다음 칸으로 연결하면 됩니다.
Tip : 현재 노드를 구하기 위해서는 방금 만든 get_node 를 사용하면 됩니다!
def delete_node(self, index): node = self.get_node(index - 1) node.next = node.next.next
