프로토타입
객체지향 프로그래밍
const circle = {
radius: 5, // 반지름
// 원의 지름: 2r
getDiameter() {
return 2 * this.radius;
},
// 원의 둘레: 2πr
getPerimeter() {
return 2 * Math.PI * this.radius;
},
// 원의 넓이: πrr
getArea() {
return Math.PI * this.radius ** 2;
}
};
console.log(circle);
// {radius: 5, getDiameter: ƒ, getPerimeter: ƒ, getArea: ƒ}
console.log(circle.getDiameter()); // 10
console.log(circle.getPerimeter()); // 31.41592653589793
console.log(circle.getArea()); // 78.53981633974483
- 객체란 속성을 통해 여러개의 값을 하나의 단위로 구성한 복합적인 자료구조를 말한다.
- 객체지향 프로그래밍은 객체의 상태를 나타내는 데이터와 상태 데이터를 조작할 수 있는 동작을 하나의 논리적인 단위로 묶어 생각한다.
- 따라서 객체는 상태 데이터와 동작을 하나의 논리적인 단위로 묶은 복합적인 자료구조이다.
상속과 프로토타입
// 생성자 함수
function Circle(radius) {
this.radius = radius;
this.getArea = function () {
return Math.PI * this.radius ** 2;
};
}
// 반지름이 1인 인스턴스 생성
const circle1 = new Circle(1);
// 반지름이 2인 인스턴스 생성
const circle2 = new Circle(2);
console.log(circle1.getArea === circle2.getArea); // false
console.log(circle1.getArea()); // 3.141592653589793
console.log(circle2.getArea()); // 12.566370614359172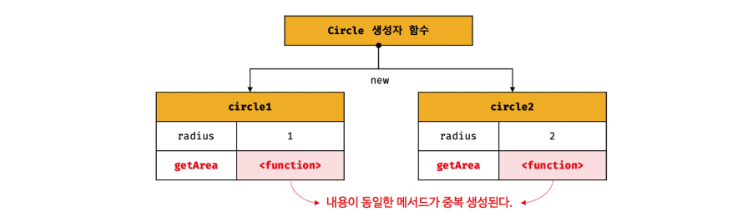
- Circle 생성자 함수는 인스턴스를 생성할 때마다 동일한 동작을 하는 getArea 메서드를 중복 생성하고 모든 인스턴스가 중복 소유한다.
- getArea 메서드는 하나만 생성하여 모든 인스턴스가 공유해서 사용하는 것이 바람직하다.
// 생성자 함수
function Circle(radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
Circle.prototype.getArea = function () {
return Math.PI * this.radius ** 2;
};
// 인스턴스 생성
const circle1 = new Circle(1);
const circle2 = new Circle(2);
console.log(circle1.getArea === circle2.getArea); // true
console.log(circle1.getArea()); // 3.141592653589793
console.log(circle2.getArea()); // 12.566370614359172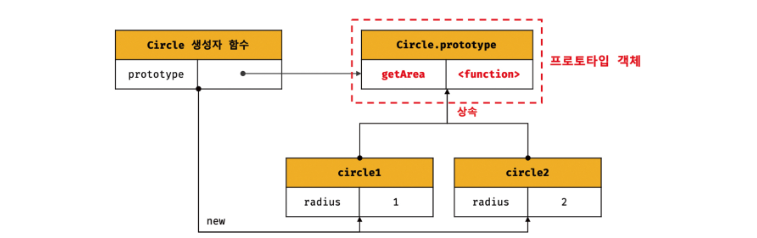
- 자바스크립트는 프로토타입을 기반으로 상속을 구현한다
- Circle 생성자 함수가 생성한 모든 인스턴스가 getArea 메서드를 유해서 사용할 수 있도록 프로토타입에 추가한다.
- Circle 생성자 함수가 생성하는 모든 인스턴스는 하나의 getArea 메서드를 공유한다.
프로토타입 객체
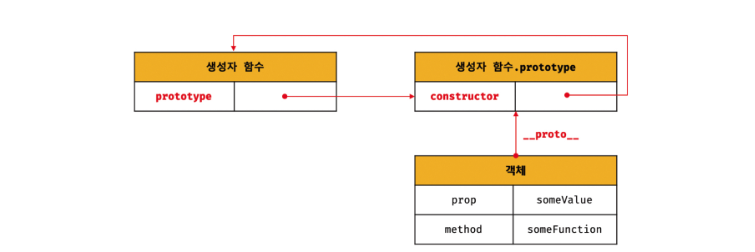
- 프로토타입의 객체란 객체 간 상속을 구현하기 위해 사용된다
- [[Prototype]] 내부 슬롯에는 직접 접근 할 수 없지만 간접적으로 접근 할 수 있다
proto 접근자 프로퍼티
모든 객체는 proto 접근자 프로퍼티를 통해 자신의 프로토타입 즉, [[Prototype]] 내부 슬롯에 간접적으로 접근할 수 있다.
proto는 접근자 프로퍼티는 상속을 통해 사용된다.
proto 접근자 프로퍼티는 객체가 직접 소유하는 프로퍼티가 아니라 Object.prototype의 프로퍼티이다. 모든 객체는 상속을 통해 Object.prototype.proto 접근자 프로퍼티를 사용할 수 있다.
proto 접근자 프로퍼티를 통해 프로토타입에 접근하는 이유
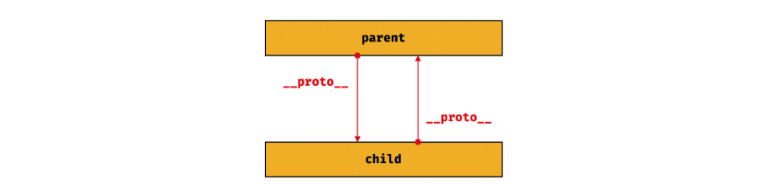
프로토타입 체인은 단방향 링크드 리스트로 구현되어야 한다.
순환참조하는 프로토타입 체이닝 만들어지면 프로토타입 체인 종점이 존재하지 않기 때문에 무한루프에 빠진다.
함수 객체의 prototype 프로퍼티
// 함수 객체는 prototype 프로퍼티를 소유한다.
(function () {}).hasOwnProperty('prototype'); // -> true
// 일반 객체는 prototype 프로퍼티를 소유하지 않는다.
({}).hasOwnProperty('prototype'); // -> false-
함수 객체만이 소유하는 prototype 프로퍼티는 생성자 함수가 생성할 인스턴스의 프로토타입을 가리킨다.
-
non-constructord인 화살표 함수와 메서드 축약 표현으로 정의한 메서드는 prototype 프로퍼티를 소유하지 않고 생성하지 않는다
// 생성자 함수
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
const me = new Person('Lee');
// 결국 Person.prototype과 me.__proto__는 결국 동일한 프로토타입을 가리킨다.
console.log(Person.prototype === me.__proto__); // true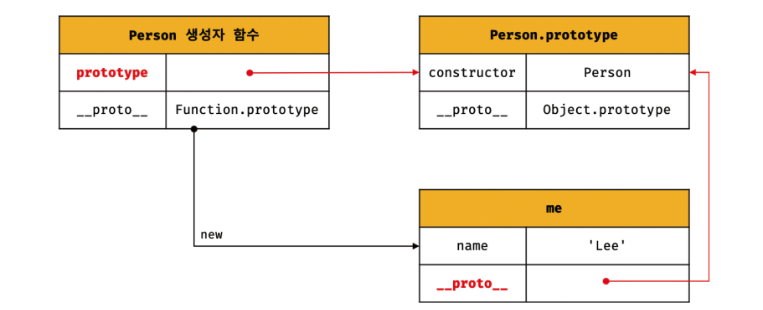
모든 객체가 가지고 있는 proto 접근자 프로퍼티와 함수 객체가 가지고 있는 prototype 프로퍼티는 결국 동일한 프로토타입을 가진다.
프로토타입의 constructor 프로퍼티와 생성자 함수
// 생성자 함수
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
const me = new Person('Lee');
// me 객체의 생성자 함수는 Person이다.
console.log(me.constructor === Person); // true- 모든 프로토타입은 constructor 프로퍼티를 갖는다. 자신을 참조하고 있는 생성자 함수를 가리킨다
프로토타입의 생성 시점
프로토탕비은 생성자 함수가 생성되는 시점에 더불어 생성된다
사용자 정의 생성자 함수외 프로토타입 생성시점
// 함수 정의(constructor)가 평가되어 함수 객체를 생성하는 시점에 프로토타입도 더불어 생성된다.
console.log(Person.prototype); // {constructor: ƒ}
// 생성자 함수
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}생성자 함수로서 호출할 수 있는 즉, construtor 함수는 정의가 평가되어 함수 객체를 생성하는 시점에 프로토타입도 더불어 생성된다
// 화살표 함수는 non-constructor다.
const Person = name => {
this.name = name;
};
// non-constructor는 프로토타입이 생성되지 않는다.
console.log(Person.prototype); // undefined생성자 함수로서 호출할 수 없는 non-constructor는 프로토타입이 생성되지 않는다.
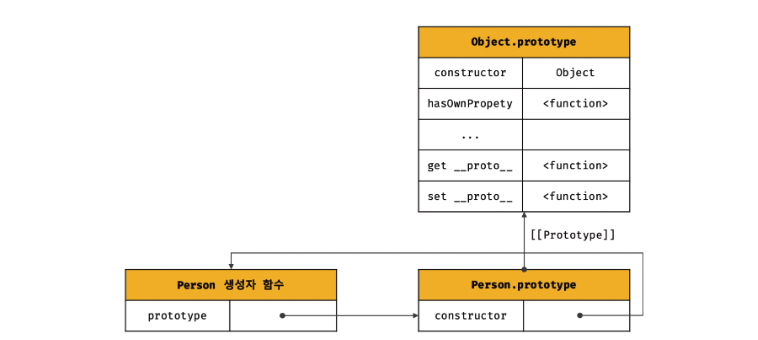
생성된 프로토타입은 오직 constructor 프로퍼티만을 갖는 객체다. 모든 객체는 프로토타입을 가지므로 프로토타입 자신도 프로토타입을 갖는다. 생성된 프로토타입의 프로토타입은 Object.prototype이다.
객체 생성 방식과 프로토타입의 결정
객체 리터럴에 의해 생성된 객체의 프로토타입
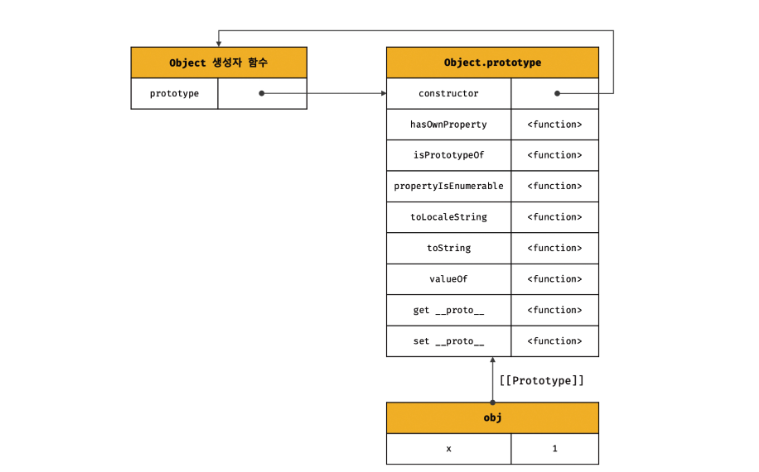
const obj = { x: 1 };
console.log(obj.constructor === Object); // true
console.log(obj.hasOwnProperty('x')); // true객체 리터럴에 의해 생성된 obj 객체는 Object.prototype을 상속받는다.
Object 생성자 함수에 의해 생성된 객체의 프로토타입
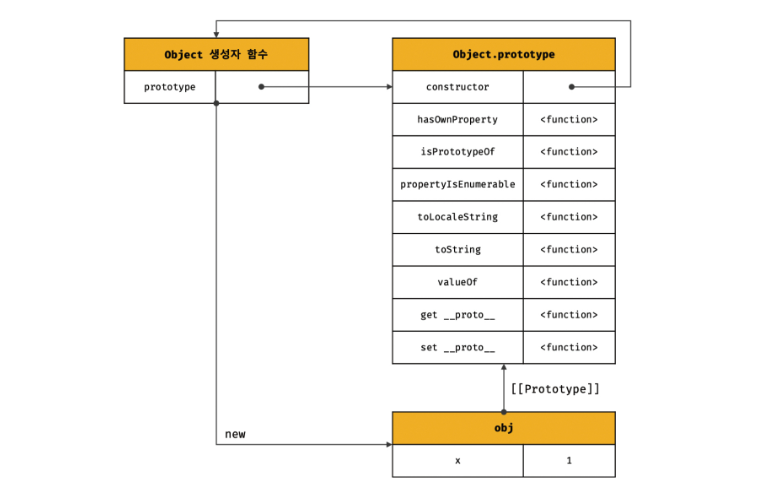
const obj = new Object();
obj.x = 1;
console.log(obj.constructor === Object); // true
console.log(obj.hasOwnProperty('x')); // trueObject 생성자 함수에 의해 생성된 obj 객체는 Object.prototype을 상속받는다.
객체리터럴과 Object 생성자함수에 의한 객체 생성 방식의 차이?
: 리터럴 방식은 객체 리터럴 내부에 프로퍼티를 추가하지만 Object 생성자 함수 방식은 빈 객체룰 생성한 이후 프로퍼티를 추가해야한다.
생성자 함수에 의해 생성된 객체의 프로토타입
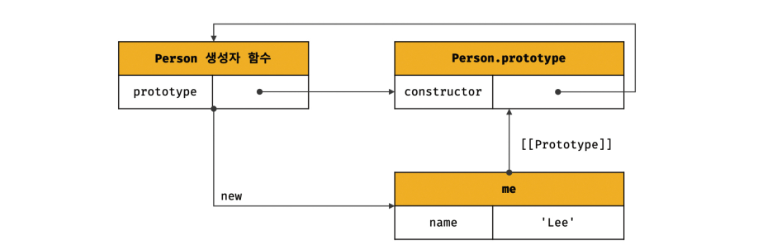
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
const me = new Person('Lee');- 사용자 정의 생성자 함수 person 과 더불어 생성된 프로토타입 Person.prototype의 프로퍼티는 constructor뿐이다.
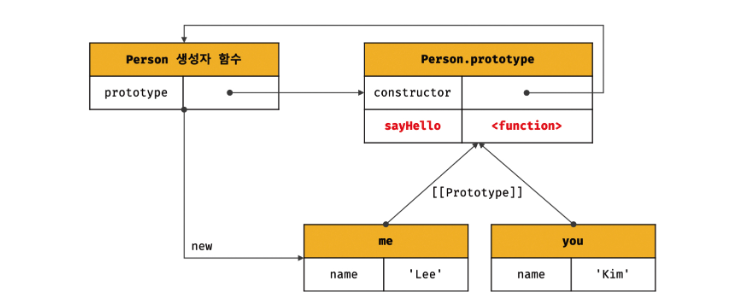
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
// 프로토타입 메서드
Person.prototype.sayHello = function () {
console.log(`Hi! My name is ${this.name}`);
};
const me = new Person('Lee');
const you = new Person('Kim');
me.sayHello(); // Hi! My name is Lee
you.sayHello(); // Hi! My name is Kim- person 생성자 함수를 통해 생성된 모든 객체는 프로토타입에 추가된 sayHello 메서드를 상속받아 자신의 메서드처럼 사용할 수 있다.
프로토타입 체인
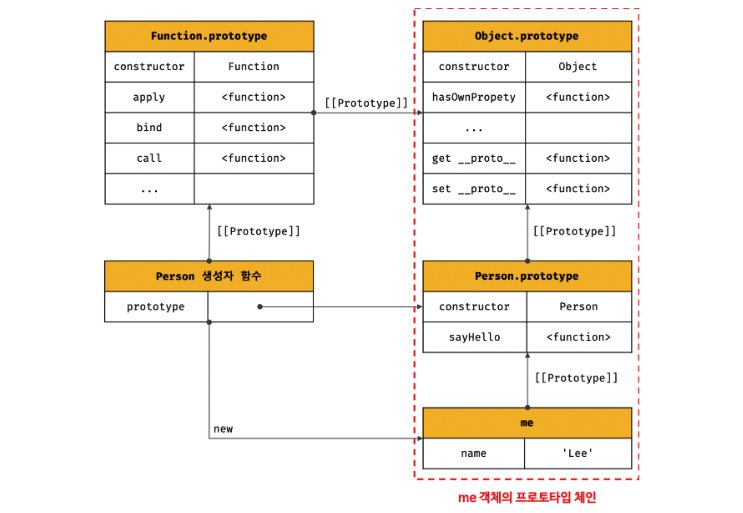
자바스크립트는 객체의 프로퍼티에 접근하려고 할 때 해당 객체에 접근하려는 프로퍼티가 없다면 [[Prototype]] 내부 슬롯의 참조를 따라 자신의 부모역할을 하는 프로토탕비의 프로퍼티를 순차적으로 검색한다. 이를 프로토타입 체인이라 한다.
오버라이딩과 프로퍼티 섀도잉
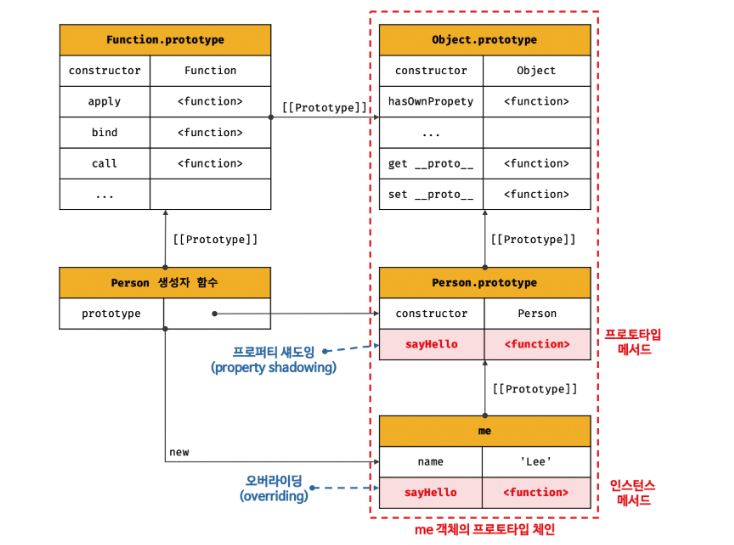
const Person = (function () {
// 생성자 함수
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
// 프로토타입 메서드
Person.prototype.sayHello = function () {
console.log(`Hi! My name is ${this.name}`);
};
// 생성자 함수를 반환
return Person;
}());
const me = new Person('Lee');
// 인스턴스 메서드
me.sayHello = function () {
console.log(`Hey! My name is ${this.name}`);
};
// 인스턴스 메서드가 호출된다. 프로토타입 메서드는 인스턴스 메서드에 의해 가려진다.
me.sayHello(); // Hey! My name is Lee- 프로퍼티 섀도잉: 상속 관계에 의해 프로퍼티가 가려지는 현상
- 오버라이딩 : 상위 클래스가 가지고 있는 메서드를 하위 클래스가 재정의 하여 사용하는 방식.
삭제의 경우
// 프로토타입 메서드 변경
Person.prototype.sayHello = function () {
console.log(`Hey! My name is ${this.name}`);
};
me.sayHello(); // Hey! My name is Lee
// 프로토타입 메서드 삭제
delete Person.prototype.sayHello;
me.sayHello(); // TypeError: me.sayHello is not a function프로토타입 프로퍼티를 변경 또는 삭제하려면 하위 객체를 통해 프로토타입 체인으로 접근하는 것이 아니라 프로토타입에 직접 접근해야 한다.
instanceof 연산자
// 생성자 함수
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
const me = new Person('Lee');
// 프로토타입으로 교체할 객체
const parent = {};
// 프로토타입의 교체
Object.setPrototypeOf(me, parent);
// Person 생성자 함수와 parent 객체는 연결되어 있지 않다.
console.log(Person.prototype === parent); // false
console.log(parent.constructor === Person); // false
// parent 객체를 Person 생성자 함수의 prototype 프로퍼티에 바인딩한다.
Person.prototype = parent;
// Person.prototype이 me 객체의 프로토타입 체인 상에 존재하므로 true로 평가된다.
console.log(me instanceof Person); // true
// Object.prototype이 me 객체의 프로토타입 체인 상에 존재하므로 true로 평가된다.
console.log(me instanceof Object); // true- 우변의 생성자 함수의 prototype에 바인딩된 객체가 좌변의 객체의 프로토타입 체인 상에 존재하면 true로 평가되고 아니면 false로 평가된다
프로퍼티 존재 확인
in 연산자
const person = {
name: 'Lee',
address: 'Seoul'
};
// person 객체에 name 프로퍼티가 존재한다.
console.log('name' in person); // true
// person 객체에 address 프로퍼티가 존재한다.
console.log('address' in person); // true
// person 객체에 age 프로퍼티가 존재하지 않는다.
console.log('age' in person); // false
console.log('toString' in person); // true-
프로퍼티 체인 상에 존재ㅔ하는 모든 프로토타입에서 toString 프로퍼티를 검색했기 때문에 true.
-
toString은 Object.prototype의 메서드이다.
Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty 메서드
console.log(person.hasOwnProperty('name')); // true
console.log(person.hasOwnProperty('age')); // false
console.log(person.hasOwnProperty('toString')); // false- Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty 메서드는 인수로 전달받은 프로퍼티 키가 객체 고유의 프로퍼티 키인 경우에만 true를 반환하고 상속받은 키인 경우 false를 반환한다.
프로퍼티 열거
for...in 문
const person = {
name: 'Lee',
address: 'Seoul'
};
// for...in 문의 변수 key에 person 객체의 프로퍼티 키가 할당된다.
for (const key in person) {
console.log(key + ': ' + person[key]);
}
// name: Lee
// address: Seoul- 상속받은 프로퍼티까지 열거하지만 toString과 같은 메서드는 열거되지 않느다. Object.prototype.toSting 프로퍼티의 프로퍼티 어트리뷰트 [[Enumerable]]의 값이 false이기 때문이다.