Process vs Thread
정리하면, 다음과 같다.
- ✨프로세스== 자원+ 쓰레드
- 1 프로세스에 1 이상 쓰레드 필요
- 프로세스 : 쓰레드 = 공장 : 일꾼
새로운 쓰레드를 생성하는 것이 새로운 프로세스 생성보다 비용대비 효율적
멀티 프로레스 보단! 멀티 스레드
-
장점 : 효율적인 자원 사용, 응답성 향상
-
단점 : 동기화 주의 , 교착상태 발생위험(서로 대치), 기아 가능성 o
-
구현예시
// 동시에 진행됨!
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println("Hello World1");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println("Hello World2");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}).start();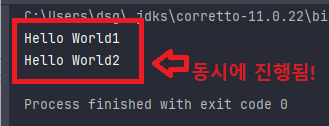
스레드의 종류
-
main메서드의 코드를 수행하는 스레드
-
스레드는 2가지 종류가 있다.
1) 사용자 스레드
2) 데몬 스레드(보조 스레드)
여기서 중요한 사실이 있다.
✨ 실행중인 사용자 스레드가 하나도 없을 때 프로그램은 종료된다. 즉, 사용자 스레드가 하나라도 있다면 프로그램은 종료가 안된다!
Thread 생성
기본 Thread 생성
1) Thread 상속(extends)
Thread 상속(extends)해, 새로 Thread(NewThread)를 만들어서 구현
public class ThreadTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new NewThread();
thread.start();
}
private static class NewThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Hello from " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
}2) Runnable 인터페이스에 의해 구현
// Runnable 인터페이스 구현 -> 익명 클래스
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 스레드 구현부
}
});- 자바8버전의 lamba식으로 변경 가능
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
// 스레드 구현부
});실제 실행 순서
thread.start();가 실행되면 생성한 Thread가 실행됨.
그러나 스레드가 언제 실행될지는 OS 스케줄러가 실행순서를 결정한다!
public class ThreadTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
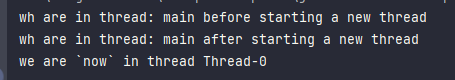
System.out.println("we are `now` in thread " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
System.out.println("wh are in thread: " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " before starting a new thread");
thread.start(); // 스레드 실행, 언제 실행될지는 OS 스케줄러가 실행순서를 결정
System.out.println("wh are in thread: " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " after starting a new thread");
Thread.sleep(10000);
}
}
thread name을 지정해줘서 디버깅하기 좋게 한다.
thread.setName("New Worker Thread");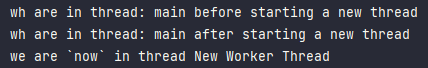
순서를 정하고 싶으면 !
1) join() 메서드 (추천)
// thread 다 마치고 main thread 실행 우선순위 설정
try {
thread.join(); // thread가 끝날 때까지 기다림
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}2) 우선순위(Priority) 설정
thread.setPriority()를 이용해서 가장 늦게 하는 설정으로 되어있음
thread.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); // default MAX_PRIORITY = 10구현
public class ThreadTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("we are `now` in thread " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
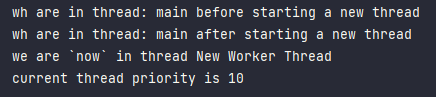
System.out.println("current thread priority is " + Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
});
thread.setName("New Worker Thread");
thread.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); // default MAX_PRIORITY = 10
System.out.println("wh are in thread: " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " before starting a new thread");
thread.start();
System.out.println("wh are in thread: " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " after starting a new thread");
Thread.sleep(10000);
}
}
스레드Pool 사용해 병렬처리
ExecutorService 인터페이스를 사용할 것
public class ThreadTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int inputN = 9000;
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// excutorService 테스트
// 한 스레드는 반목문 10000회 ABC... 문자열을 만드는
// 다른 스레드는 반복문 10000회 123... 문자열을 만드는
// 두 스레드가 동시에 실행되도록 만들어보자
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
Future<?> future1 = executorService.submit(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < inputN; i++) {
System.out.print("ABC");
}
});
Future<?> future2 = executorService.submit(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < inputN; i++) {
System.out.print("123");
}
});
try {
future1.get();
future2.get();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 스레드 풀 종료
executorService.shutdown();
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("===========================================================");
System.out.println();
// 비교 테스트
long startTime2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < inputN; i++) {
System.out.print("ABC");
}
for (int i = 0; i < inputN; i++) {
System.out.print("123");
}
long endTime2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println();
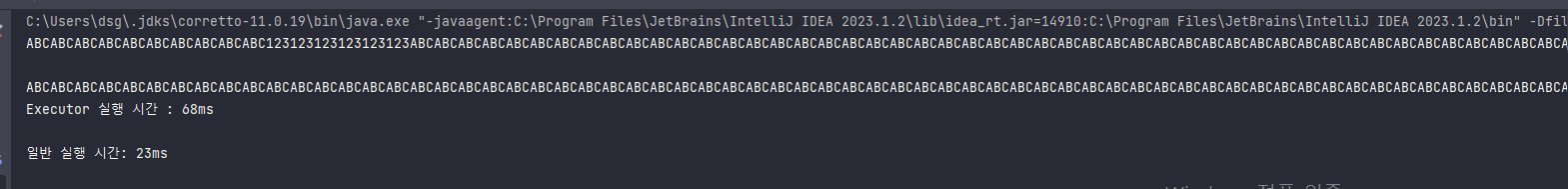
System.out.println("Executor 실행 시간 : " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("일반 실행 시간: " + (endTime2 - startTime2) + "ms");
}
}테스트 해보니 두 스레드로 동시에 병렬 처리하는 것이 시간이 더 오래 걸림...
그러면 왜 병렬 처리를 할까?
다른 스레드를 기다리지 앟아도 된다! ex. 채팅
결과)
exception Handler
UncaughtExceptionHandler
: 전체 스레드에 해당되는 예외 핸들러를 지정할 수 있음.
public class ThreadTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
throw new RuntimeException("intentional Exception"); // exception 반드시 실행
}
});
thread.setName("Misbehaving thread");
thread.setUncaughtExceptionHandler(new Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler() {
@Override
public void uncaughtException(Thread t, Throwable e) {
System.out.println("A critical error happened in thread " + t.getName()
+ " the error is " + e.getMessage());
}
});
thread.start();
}
}
