문제
코드
function solution(N, road, K) {
const arr = Array(N + 1).fill(Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER);
const lines = Array.from(Array(N + 1), () => []);
road.forEach((value) => {
let [a, b, c] = value;
lines[a].push({ to: b, cost: c });
lines[b].push({ to: a, cost: c });
});
let queue = [{ to: 1, cost: 0 }];
arr[1] = 0;
while (queue.length) {
let { to } = queue.pop();
lines[to].forEach((next) => {
if (arr[next.to] > arr[to] + next.cost) {
arr[next.to] = arr[to] + next.cost;
queue.push(next);
}
});
}
return arr.filter((item) => item <= K).length;
}
function solution(N, road, K) {
const ans = Array(N).fill(Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER);
const routes = {};
for(let route of road) {
const [v1, v2, time] = route;
if(routes[v1]) routes[v1].push([v2, time]);
else routes[v1] = [[v2, time]]
if(routes[v2]) routes[v2].push([v1, time]);
else routes[v2] = [[v1, time]];
}
const queue = [[1, 0]];
ans[0] = 0;
while(queue.length) {
const cur = queue.pop()[0];
routes[cur].forEach(route => {
const [next, time] = route;
if(ans[cur-1] + time < ans[next-1]) {
ans[next-1] = ans[cur-1] + time;
queue.push([next, ans[next-1]]);
}
})
}
return ans.filter(x => x <= K).length;
}
다익스트라 알고리즘
- 주로 최단거리를 구할 때 사용한다. (네비게이션 등)
- 이런 그림 나왔다 하면 다익스트라 생각하면 된다.
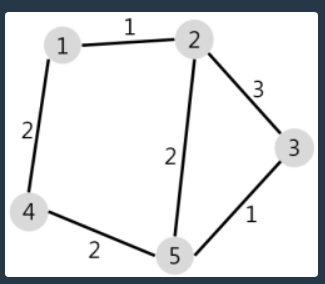
ans 배열 초기화
- ans를 미친 무한 수로 N의 개수만큼 저장
- 나중에 바꿔 줄 예정이다.
queue를 이용한 풀이
- 처음에 DFS를 이용해 풀려고 했는데 시간초과 개떡같이 나서 실패한 문제
- 먼저 이어져있는 길과 시간을 배열에 담는다. (난 객체가 편해서 객체로 함)
- queue에 시작점인 1과 초기시간인 0을 넣어준다.
- 1번은 시간이 0이니까 ans[0] 혹은 ans[1]을 바꿔준다.(밑에 내가 푼 풀이가 직관성은 떨어지는데 난 더 좋다. 암튼 내 자식이 더 좋음)
- 다음 이어질 곳의 시간과 total이 ans의 next 위치보다 작으면 바꿔주고, queue에 푸시해준다.
filter로 마무리
- K를 언제 사용하나 했는데 마지막에 filter로 걸러준다.
- 처음에 풀 땐 ans에 넣을 때마다 검증했는데 위 방법이 더 낫다. 왜냐면 내 방법은 시간초과로 검증도 못해봤다.

